The Heart
Lab Summary
This lab explores the relationships of the heart to surrounding structure and their clinical importance. Cardiac surfaces, the interior structure of the heart and coronary circulation is taught. The interior of the heart is taught through in situ and isolated dissections.
Lab Objectives
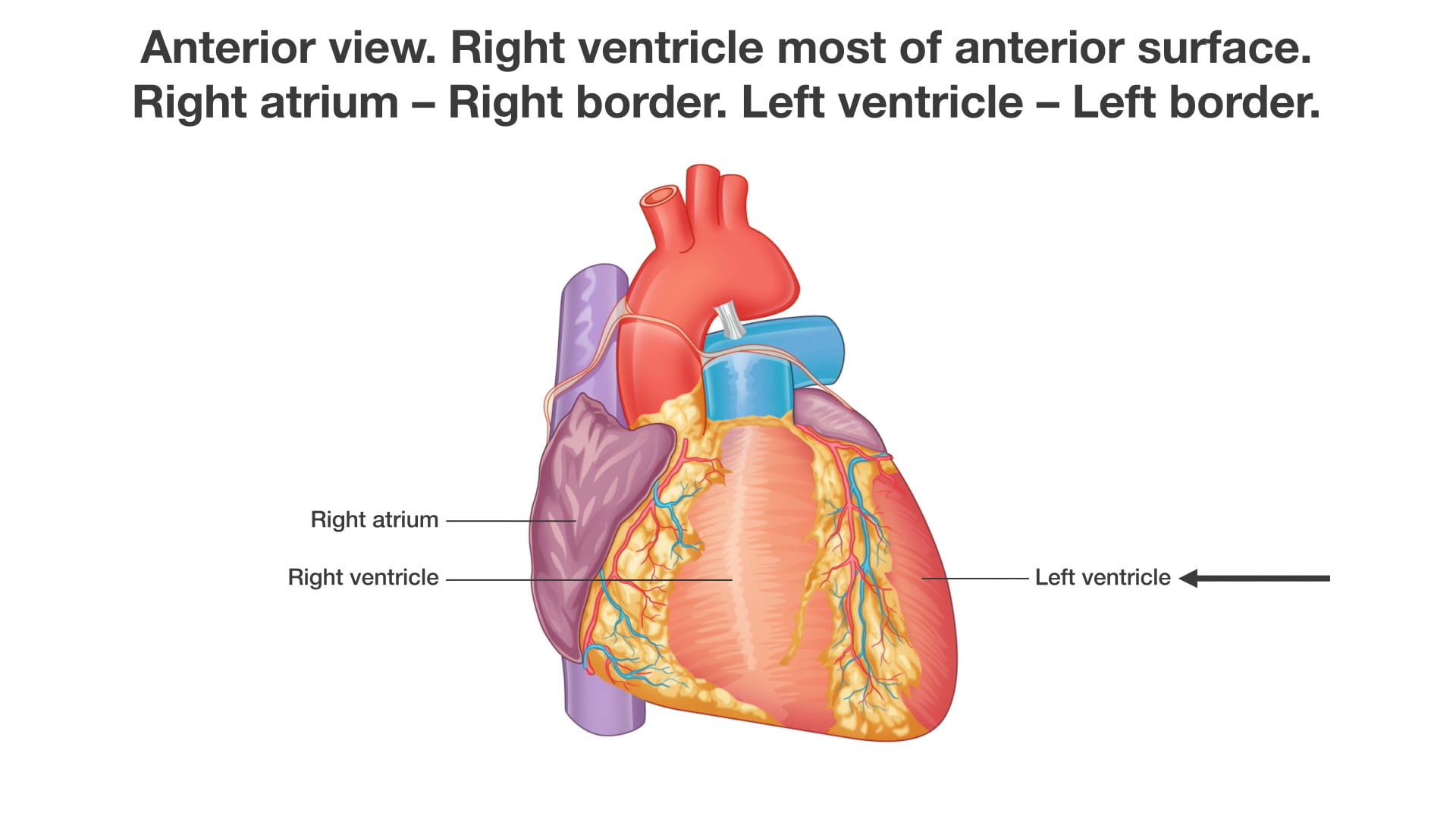
- Describe the chambers of the heart that contribute to the cardiac surfaces and borders.
- Describe the pericardium.
- Explain the significance of the transverse pericardial sinus.
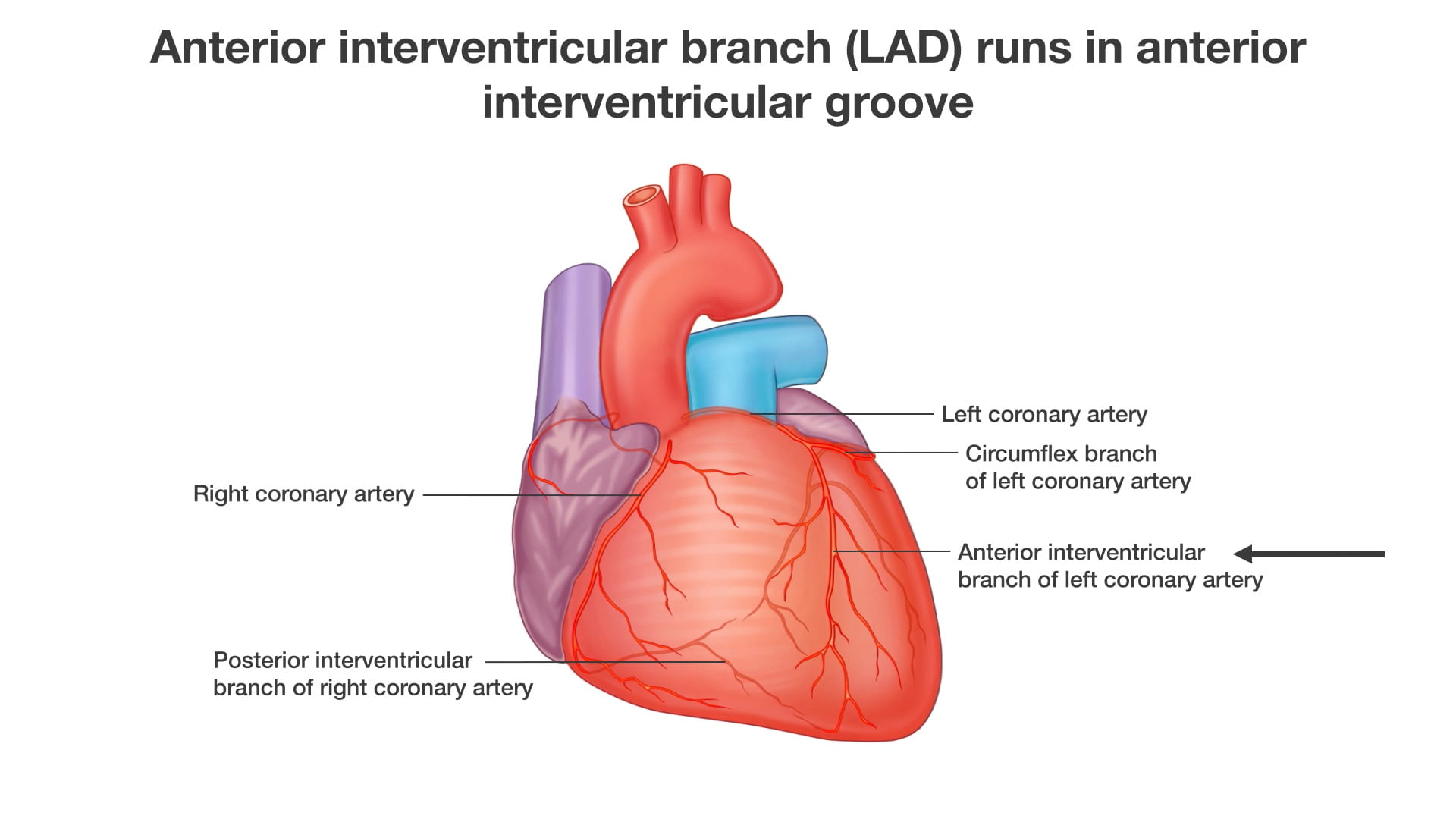
- Describe the location of the major branches of the coronary arteries in relation to the atrioventricular and interventricular grooves.
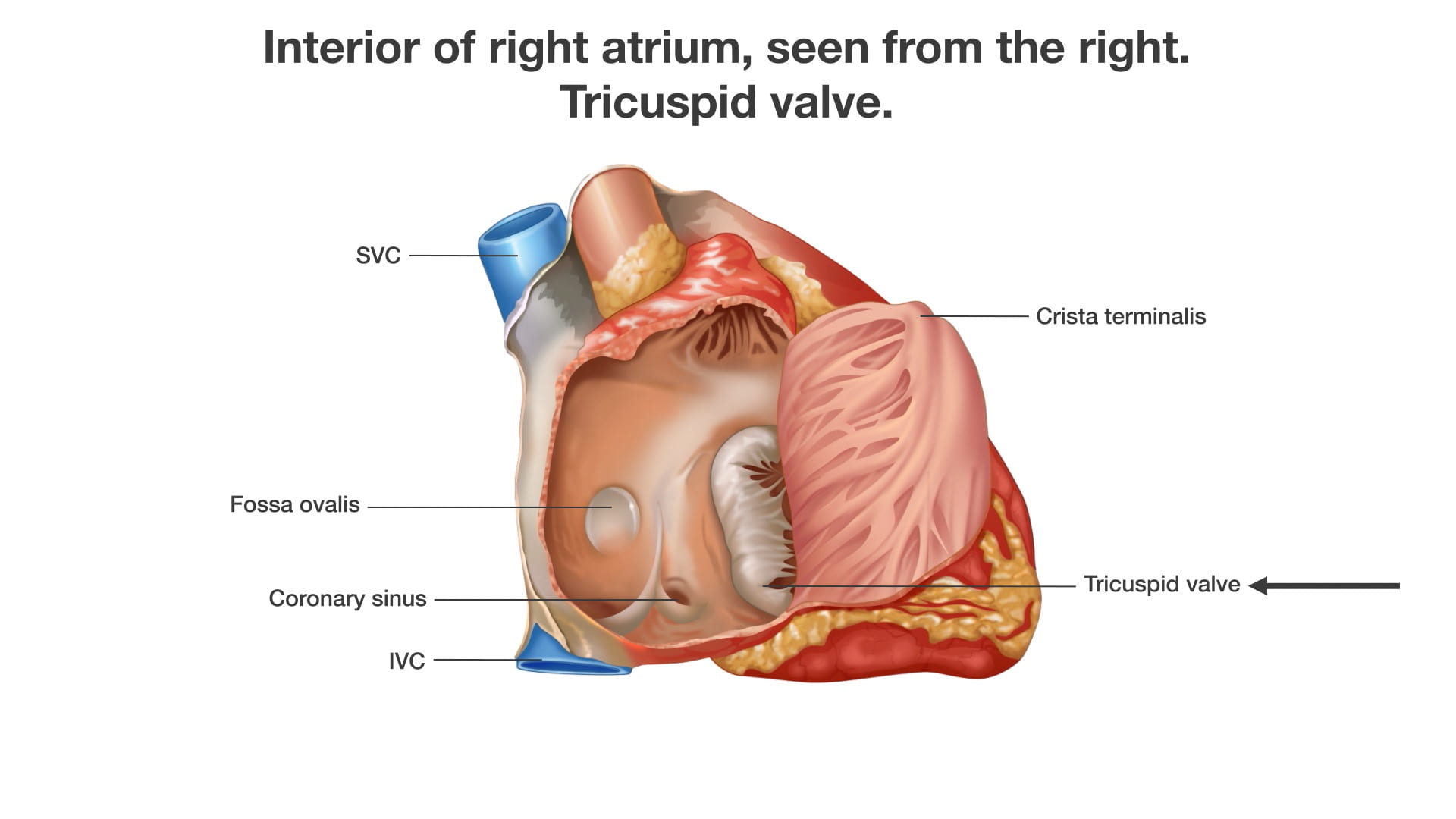
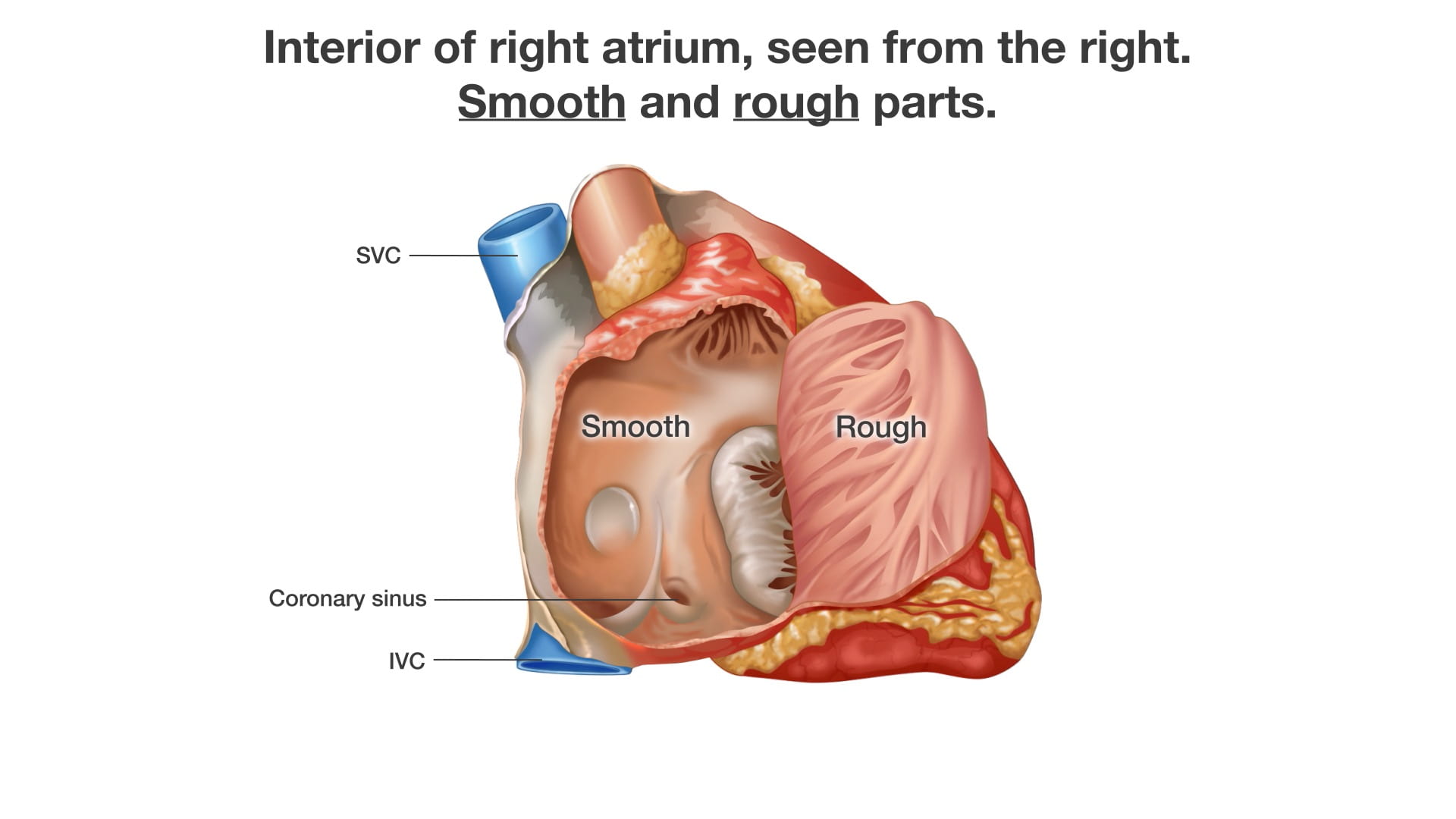
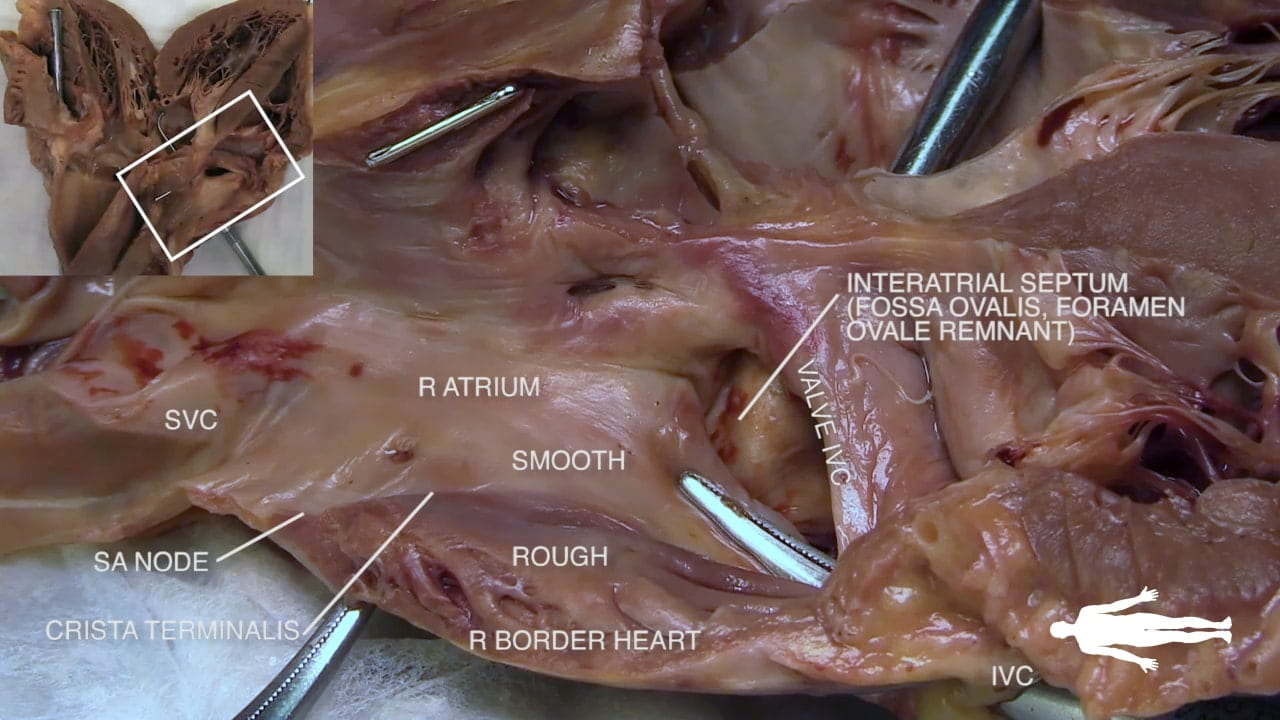
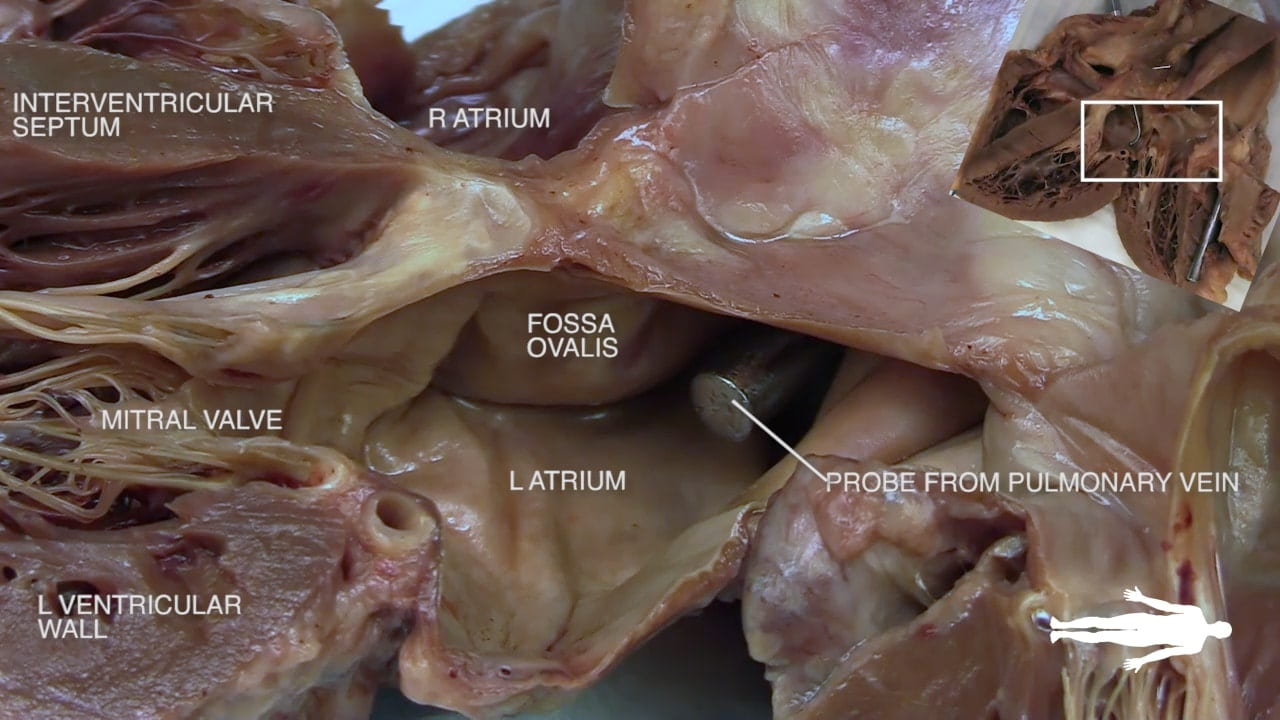
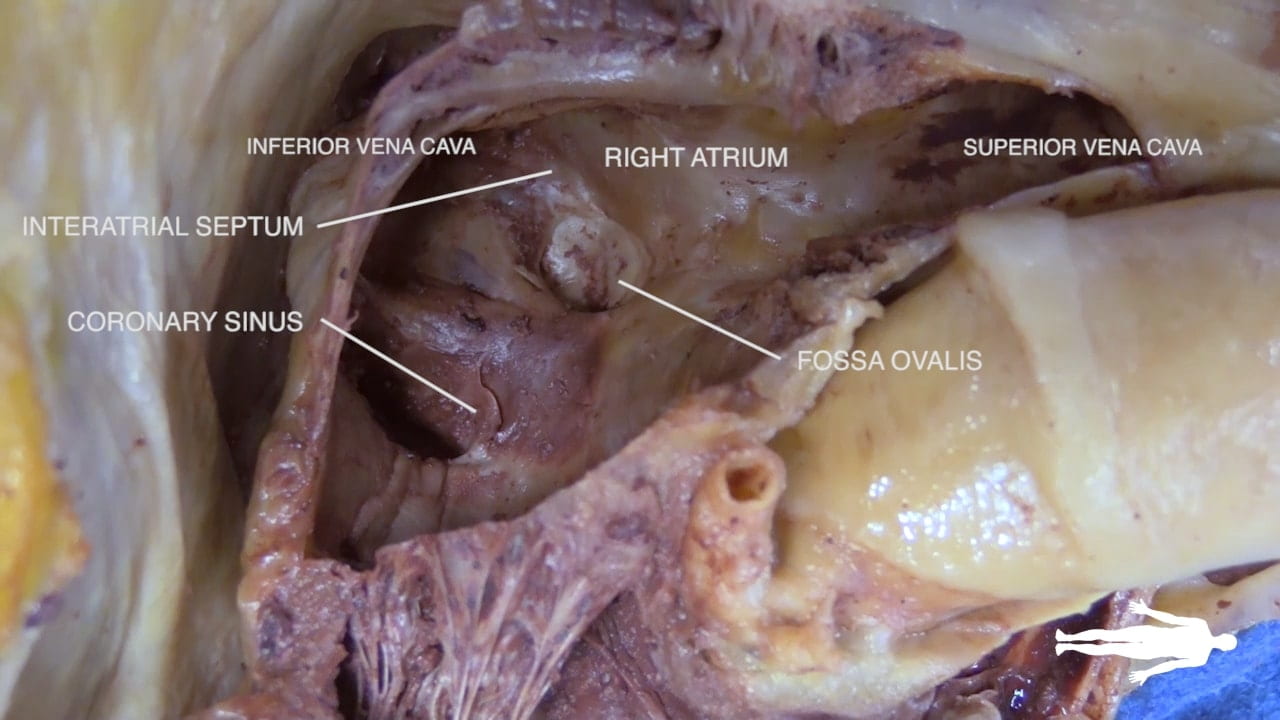
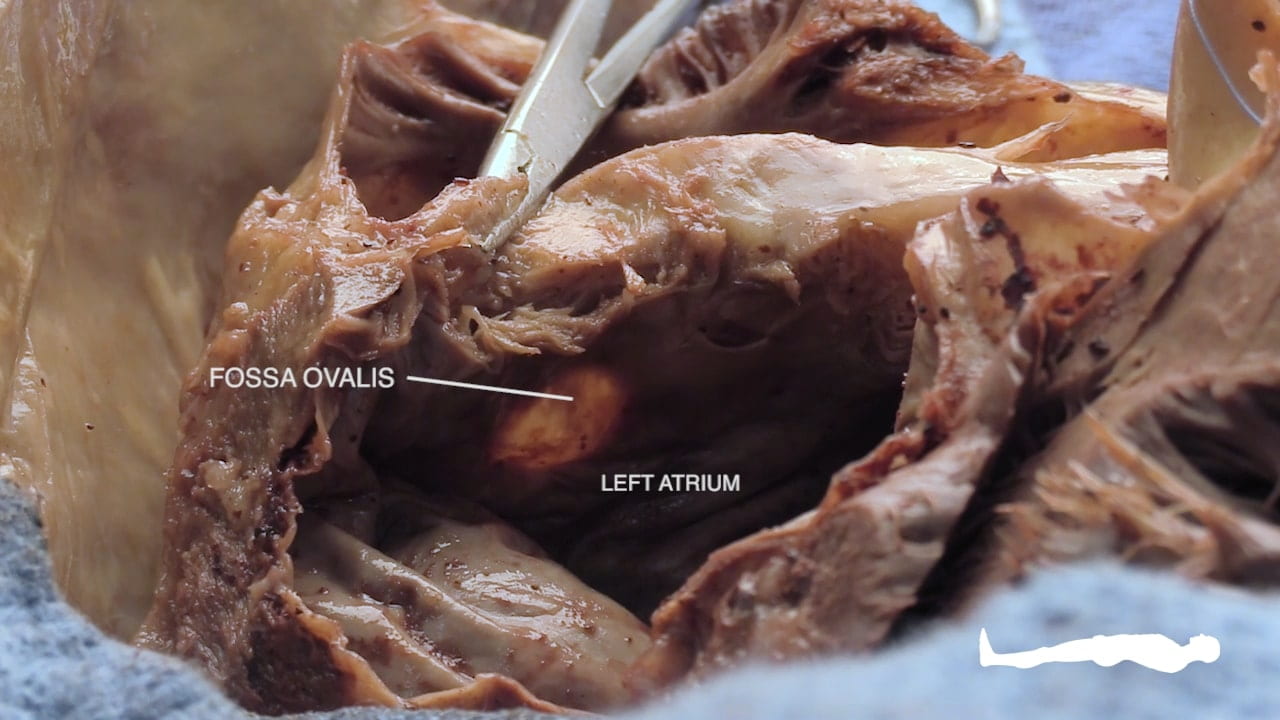
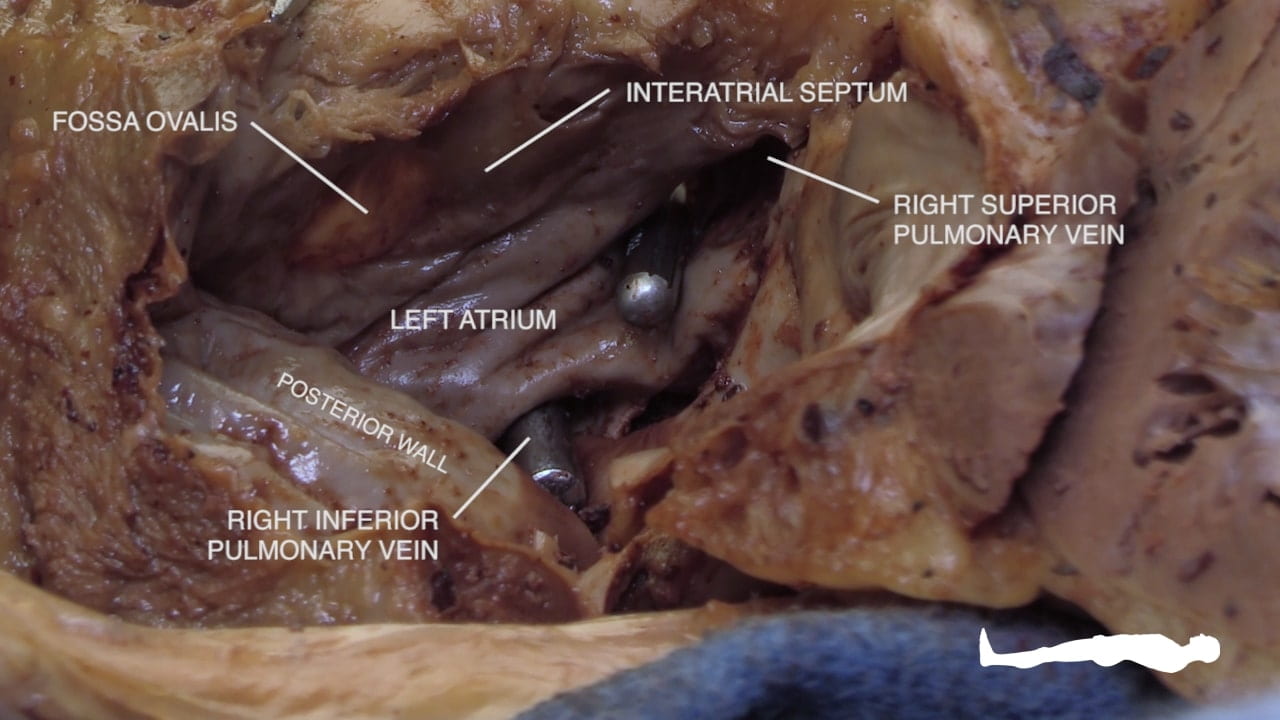
- Describe the position and significance of the ligamentum arteriosum and fossa ovalis.
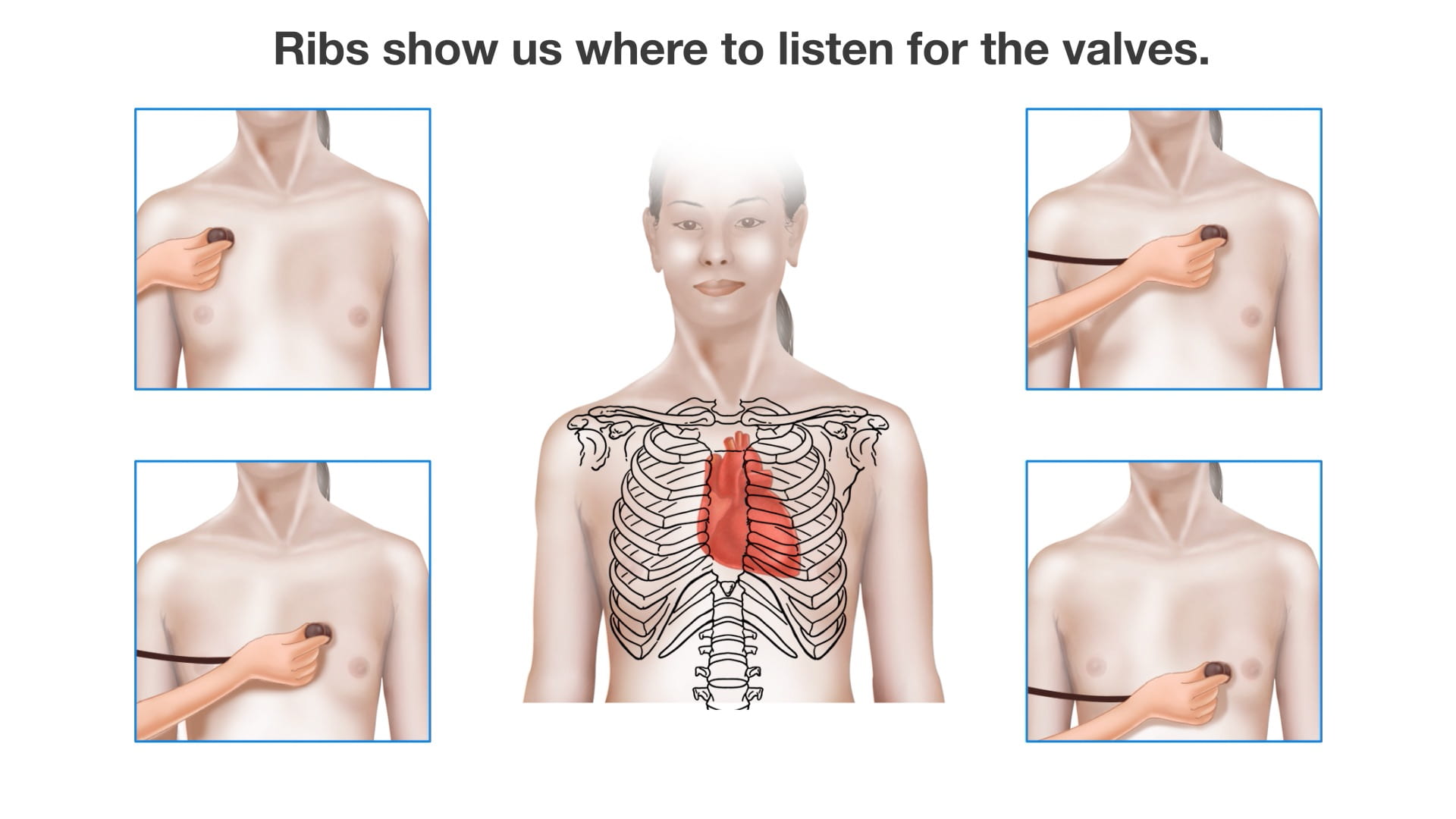
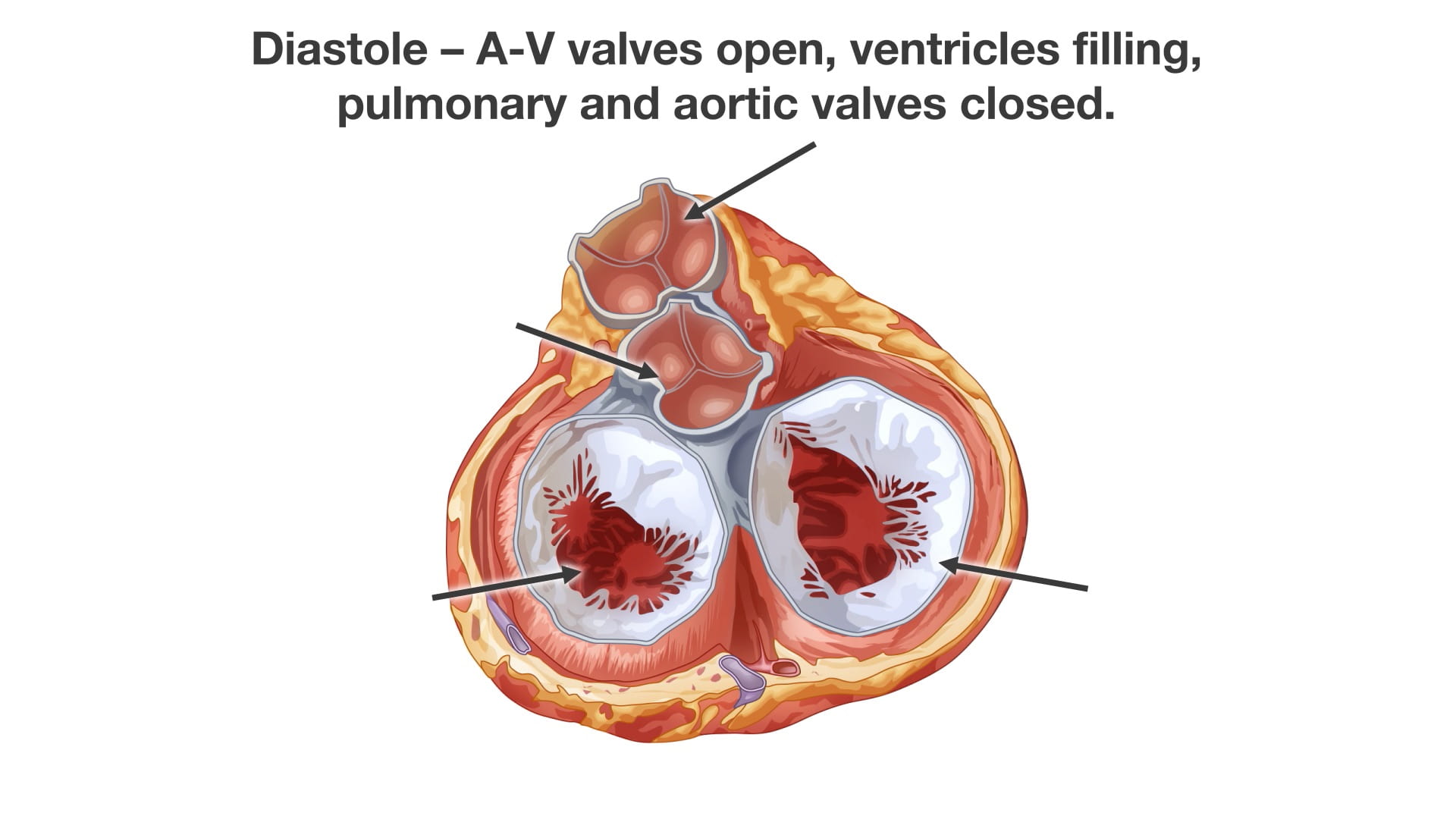
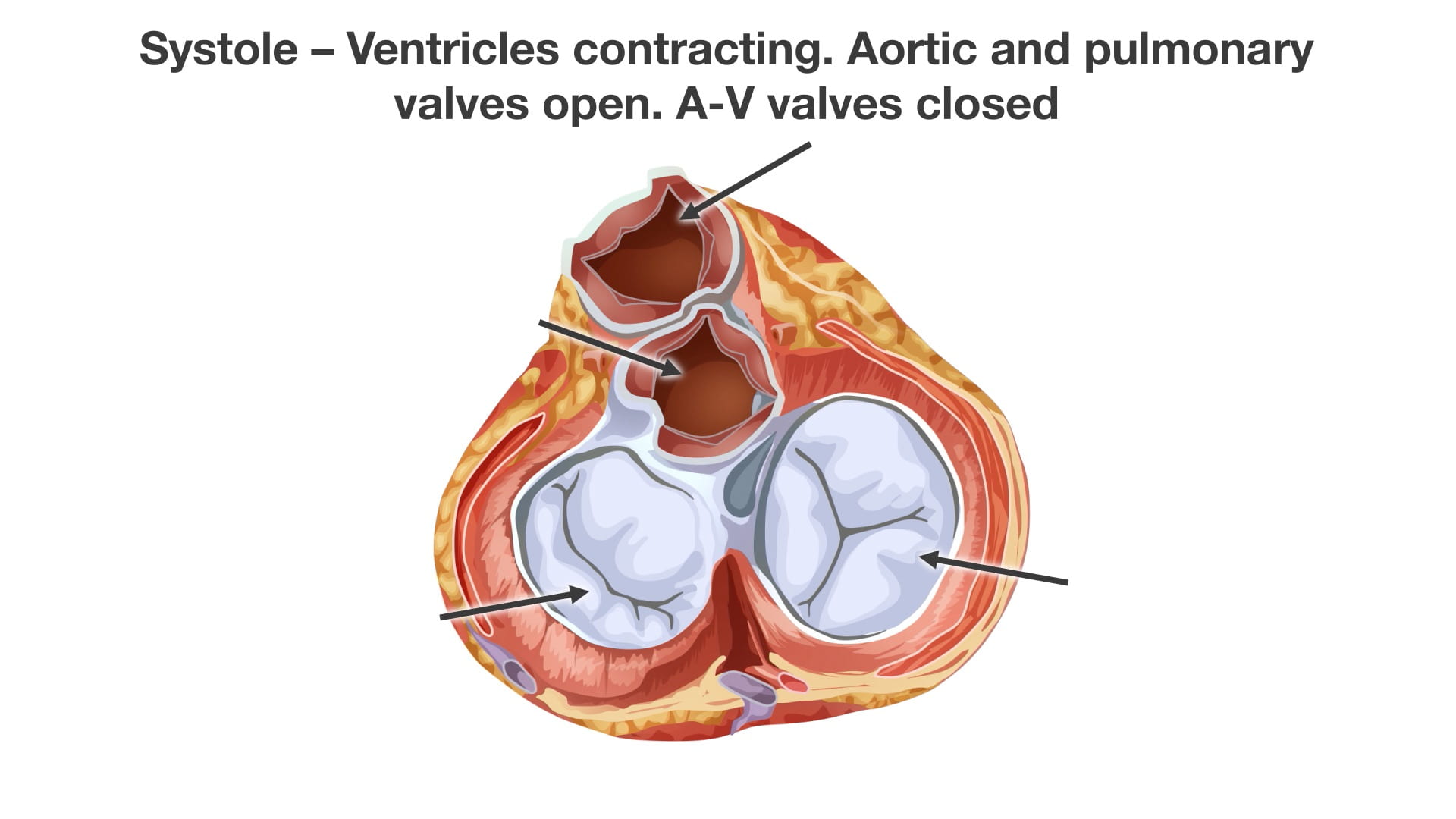
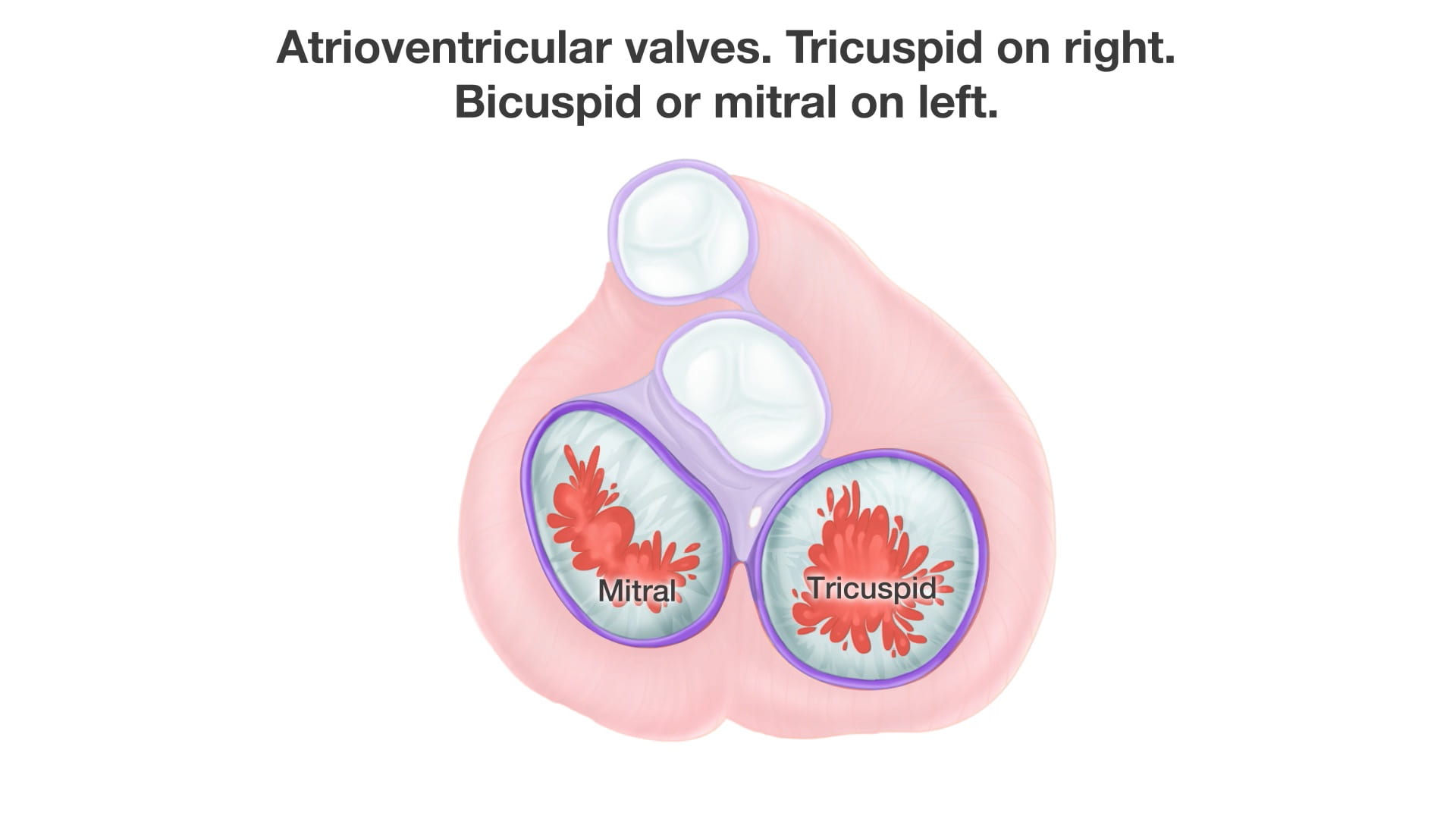
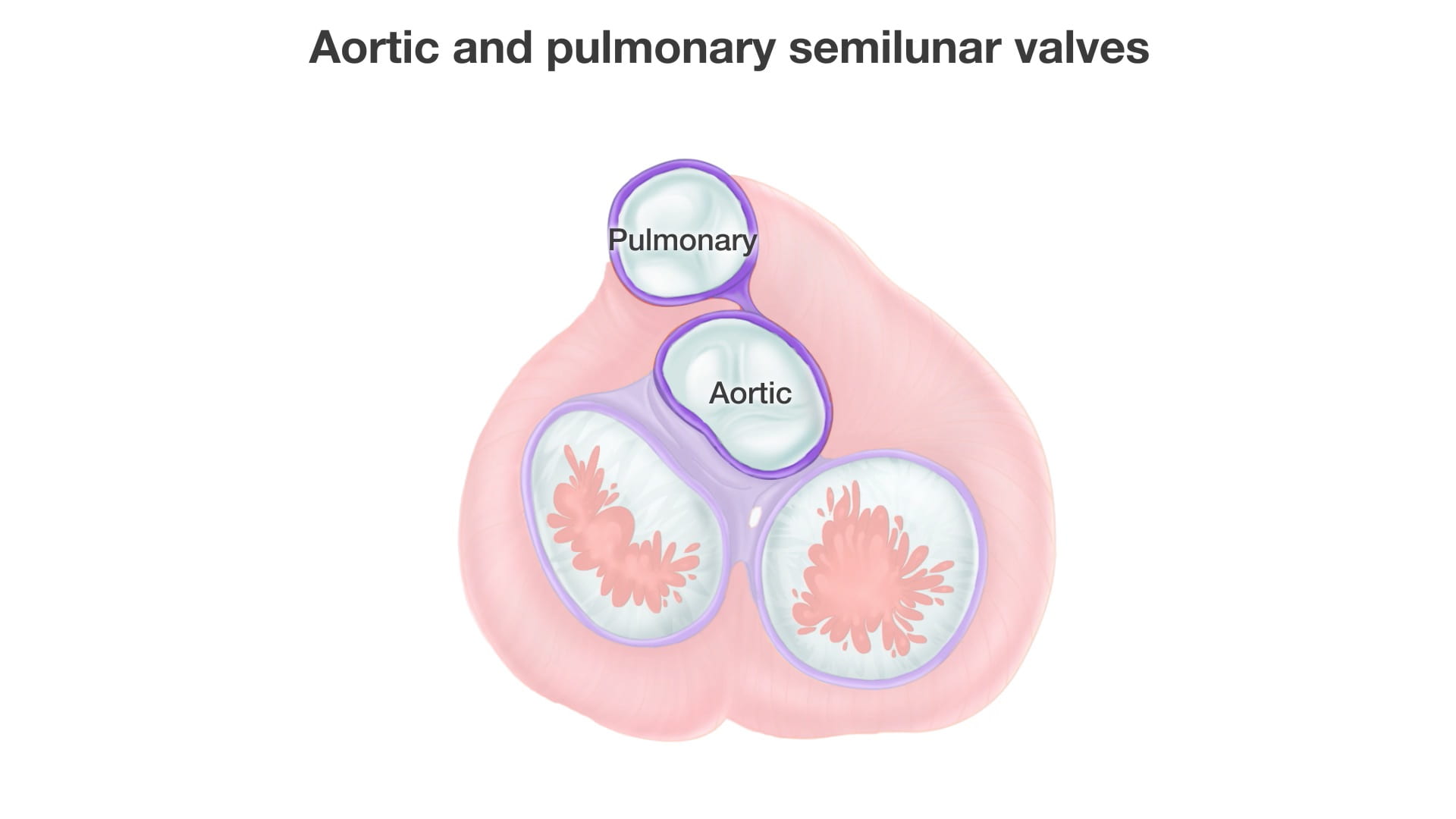
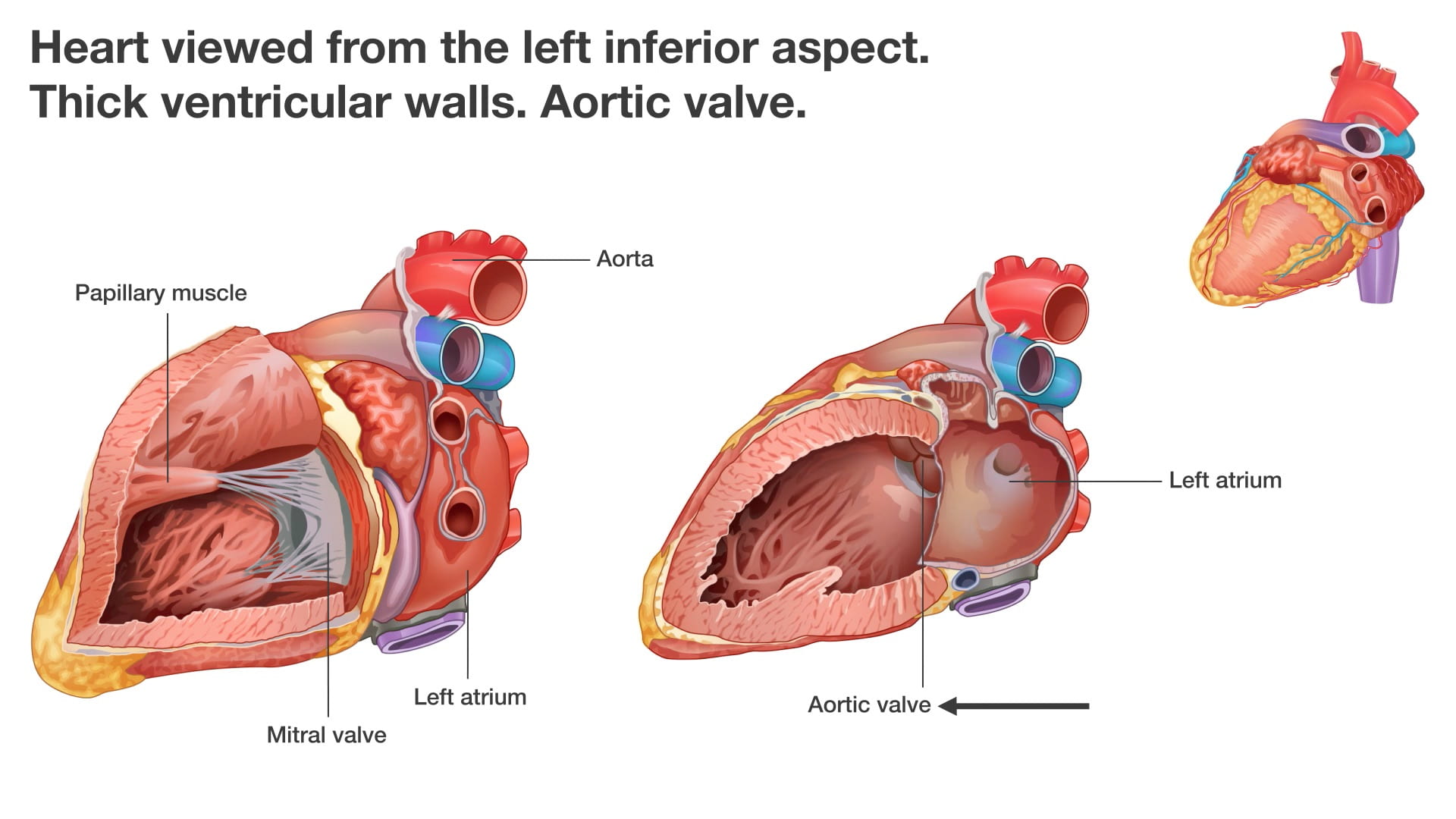
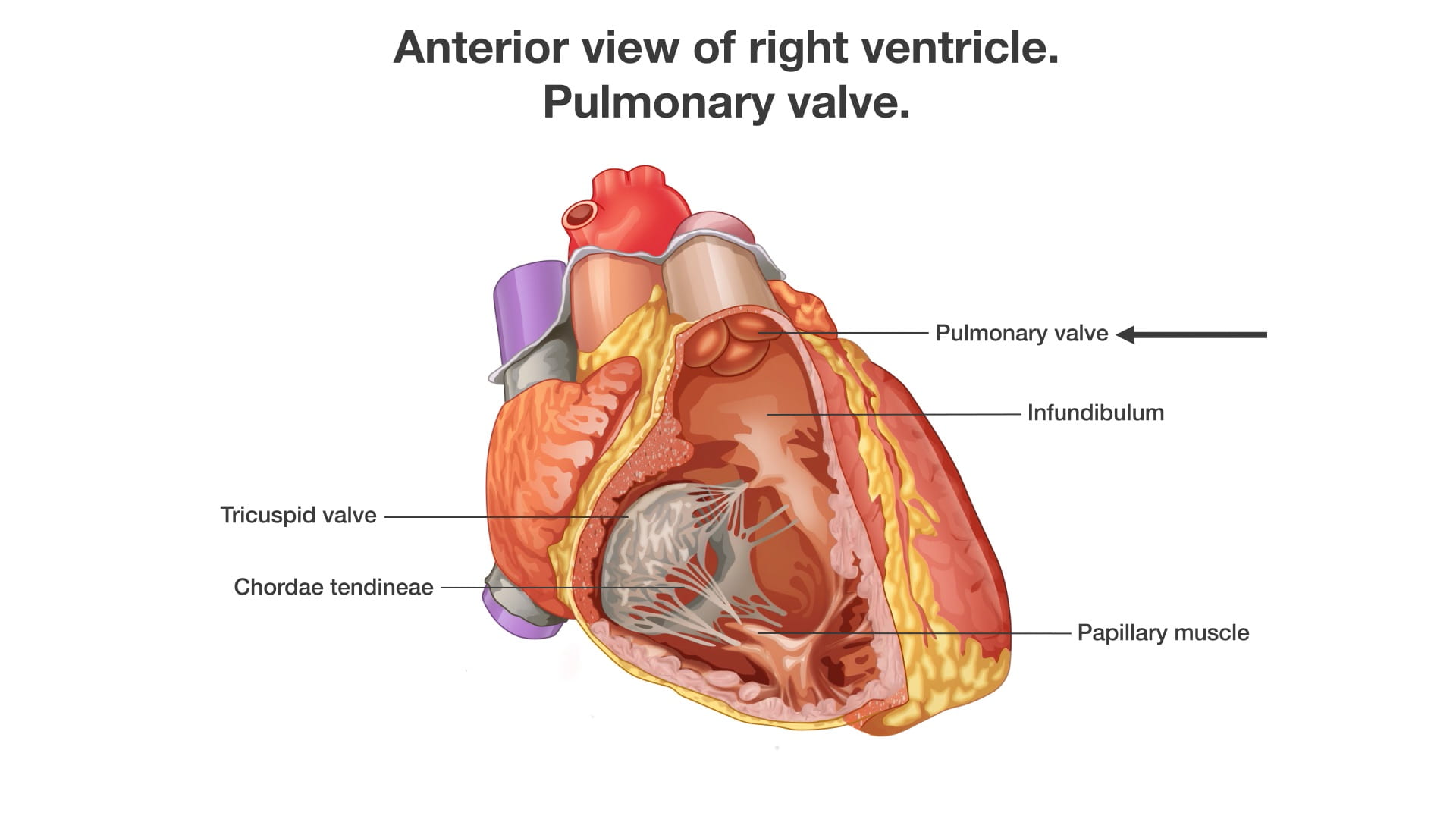
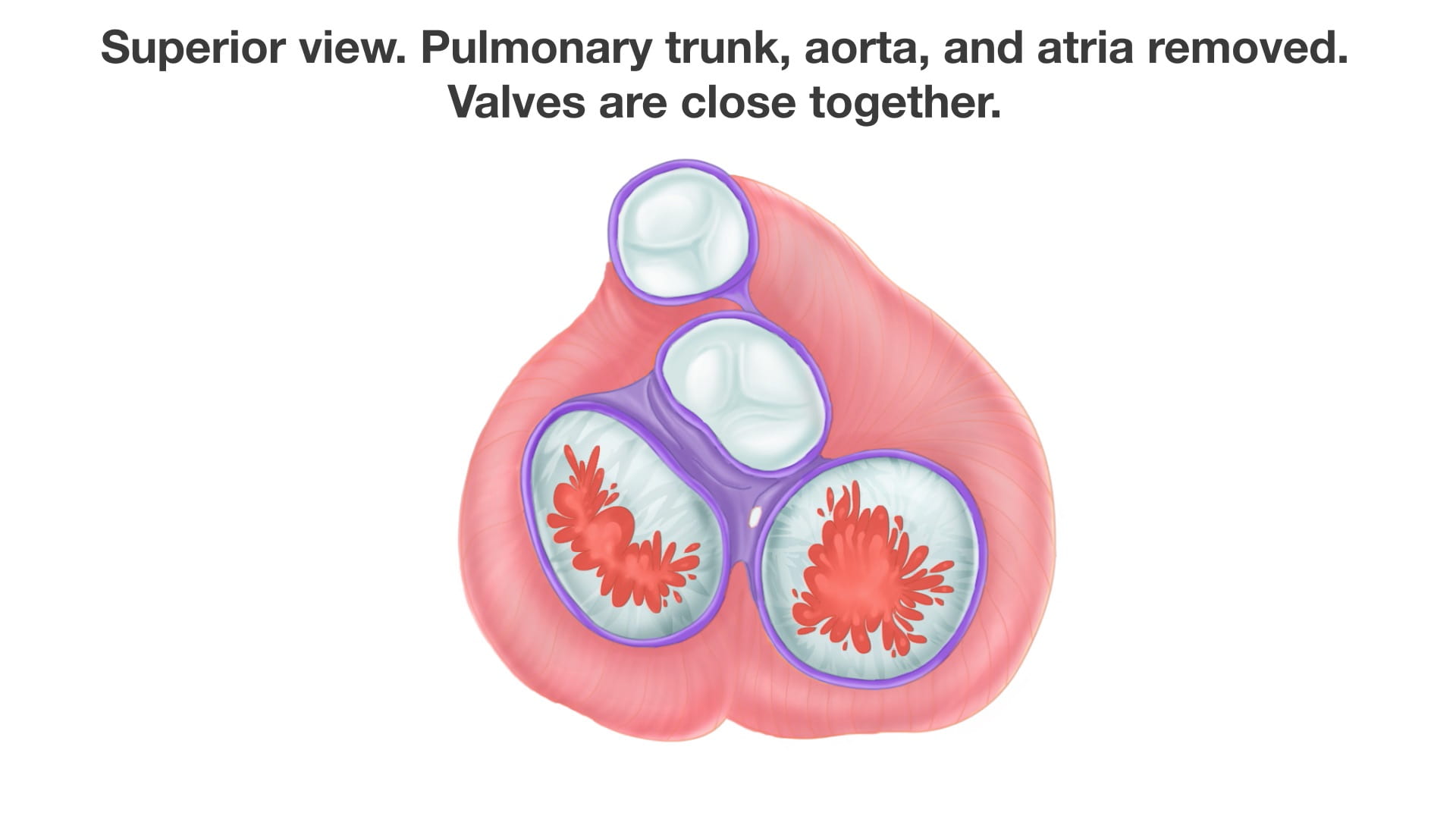
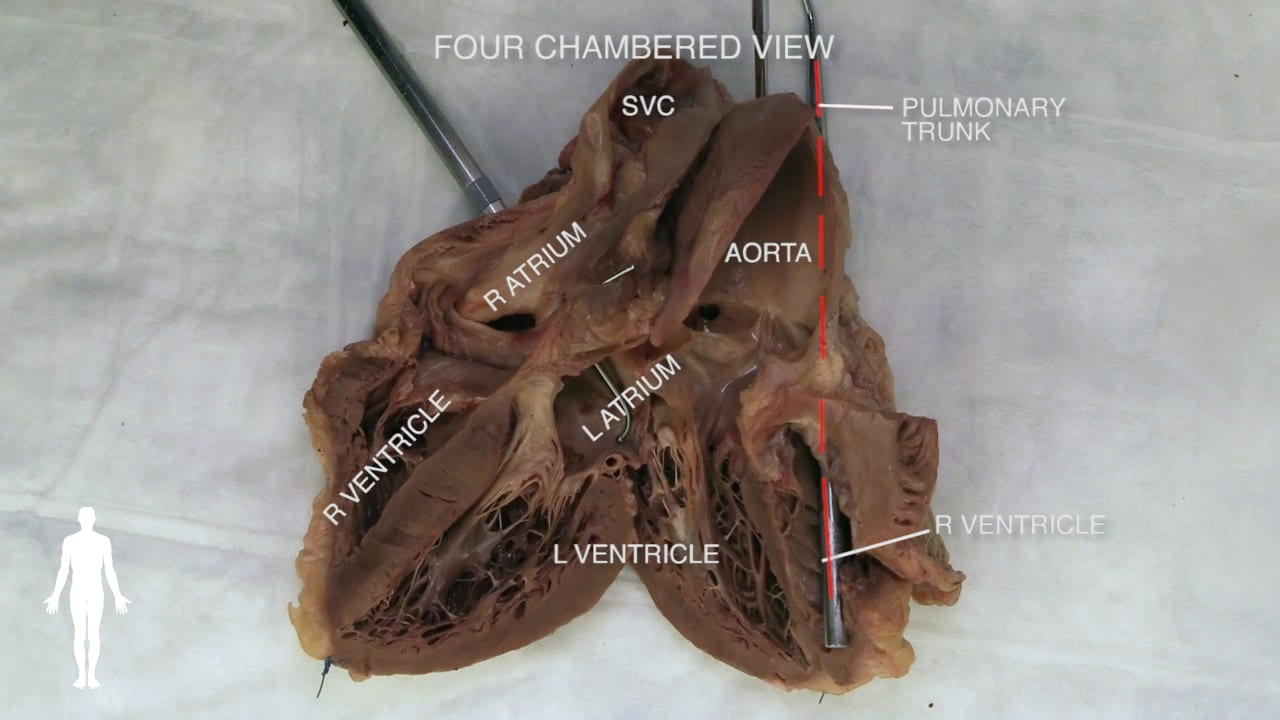
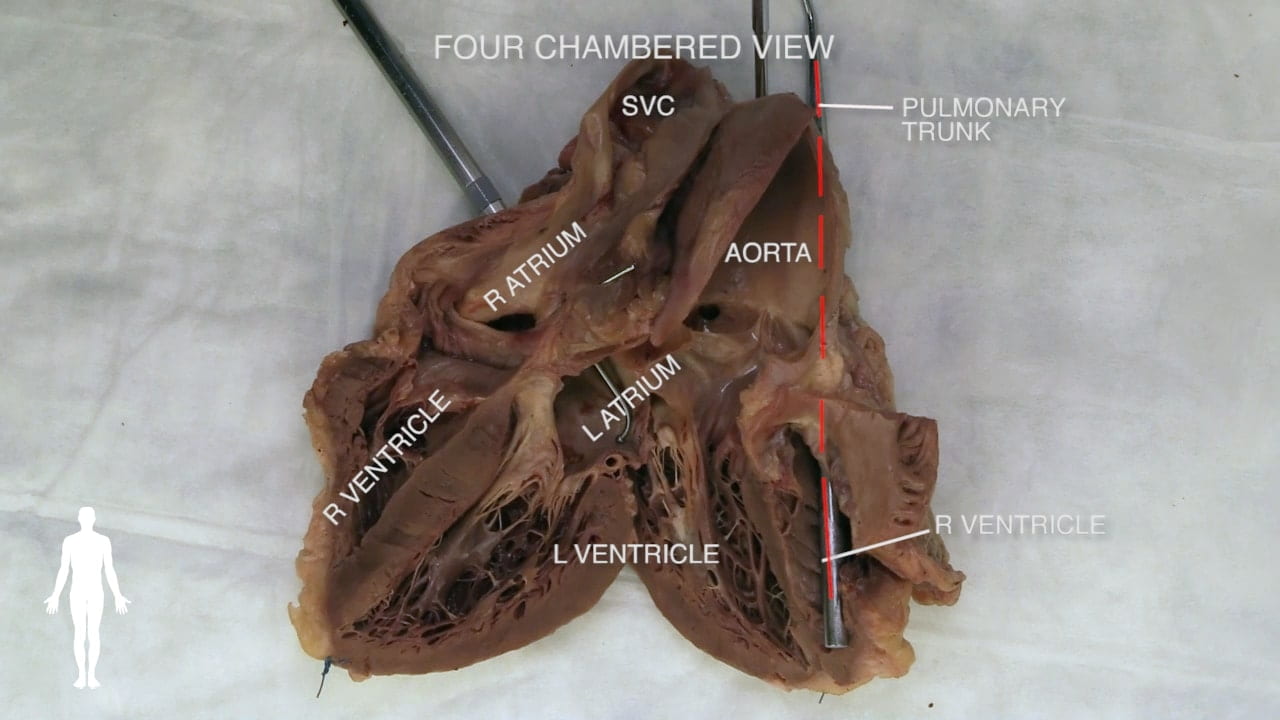
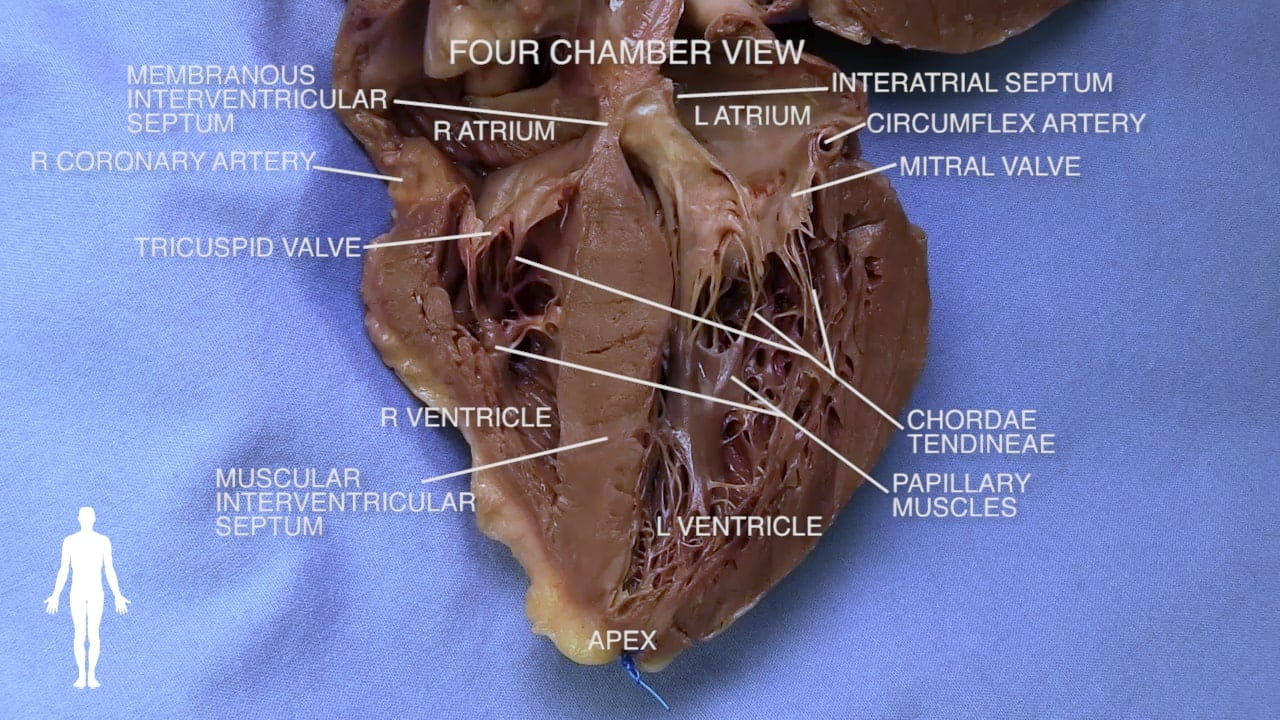
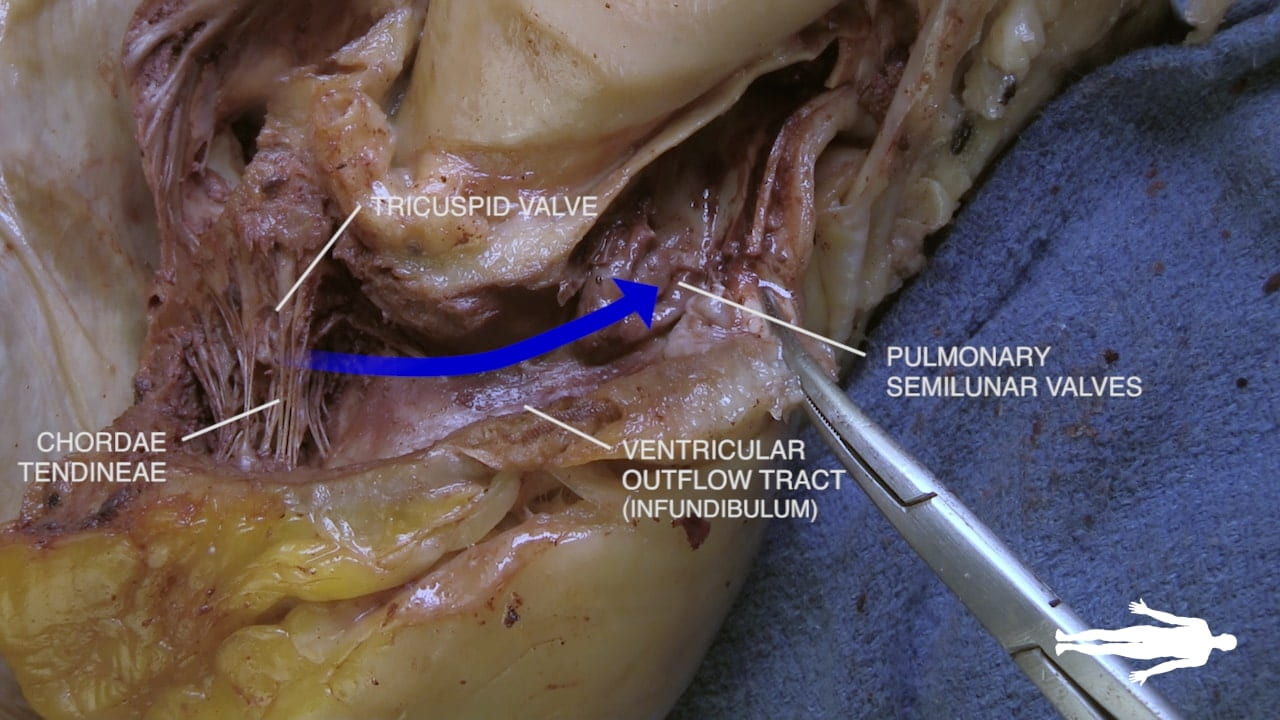
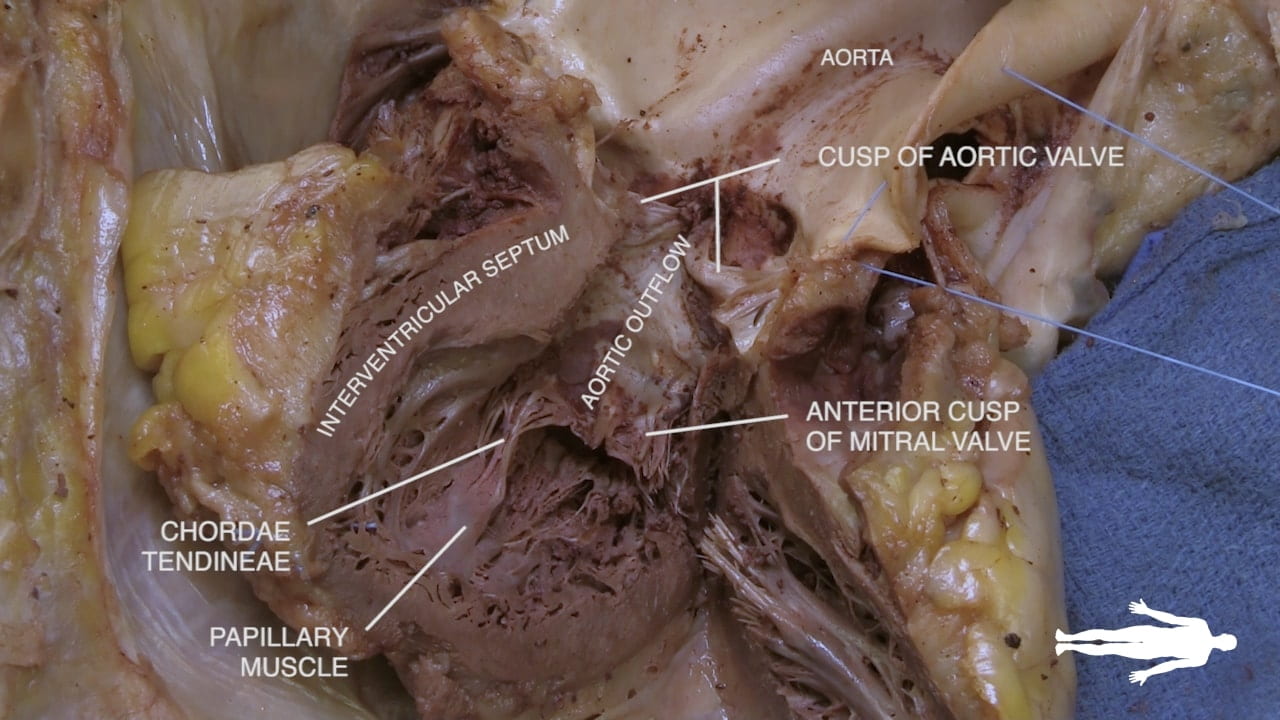
- Name the valves of the heart and the chambers / vessels they connect.
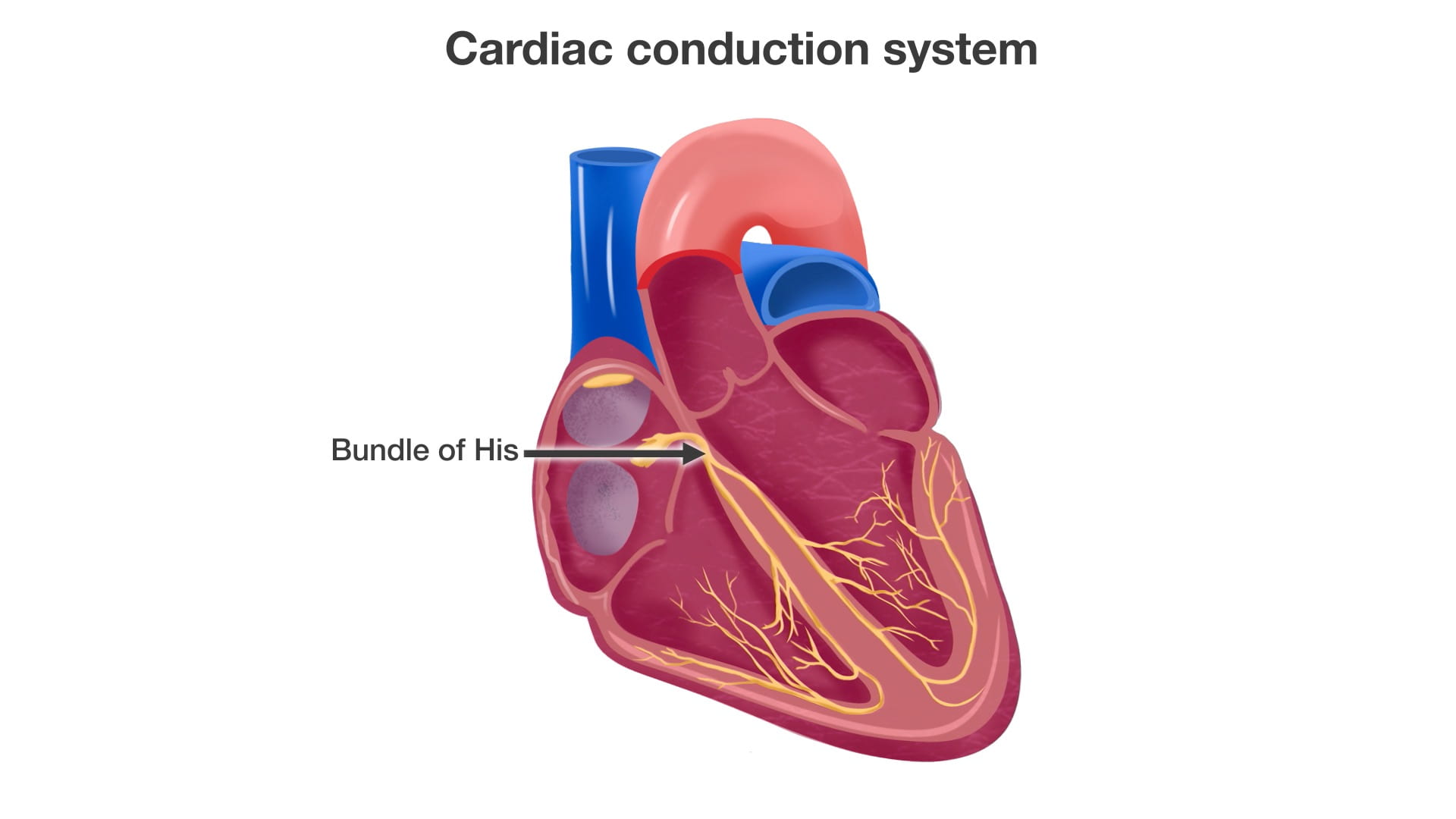
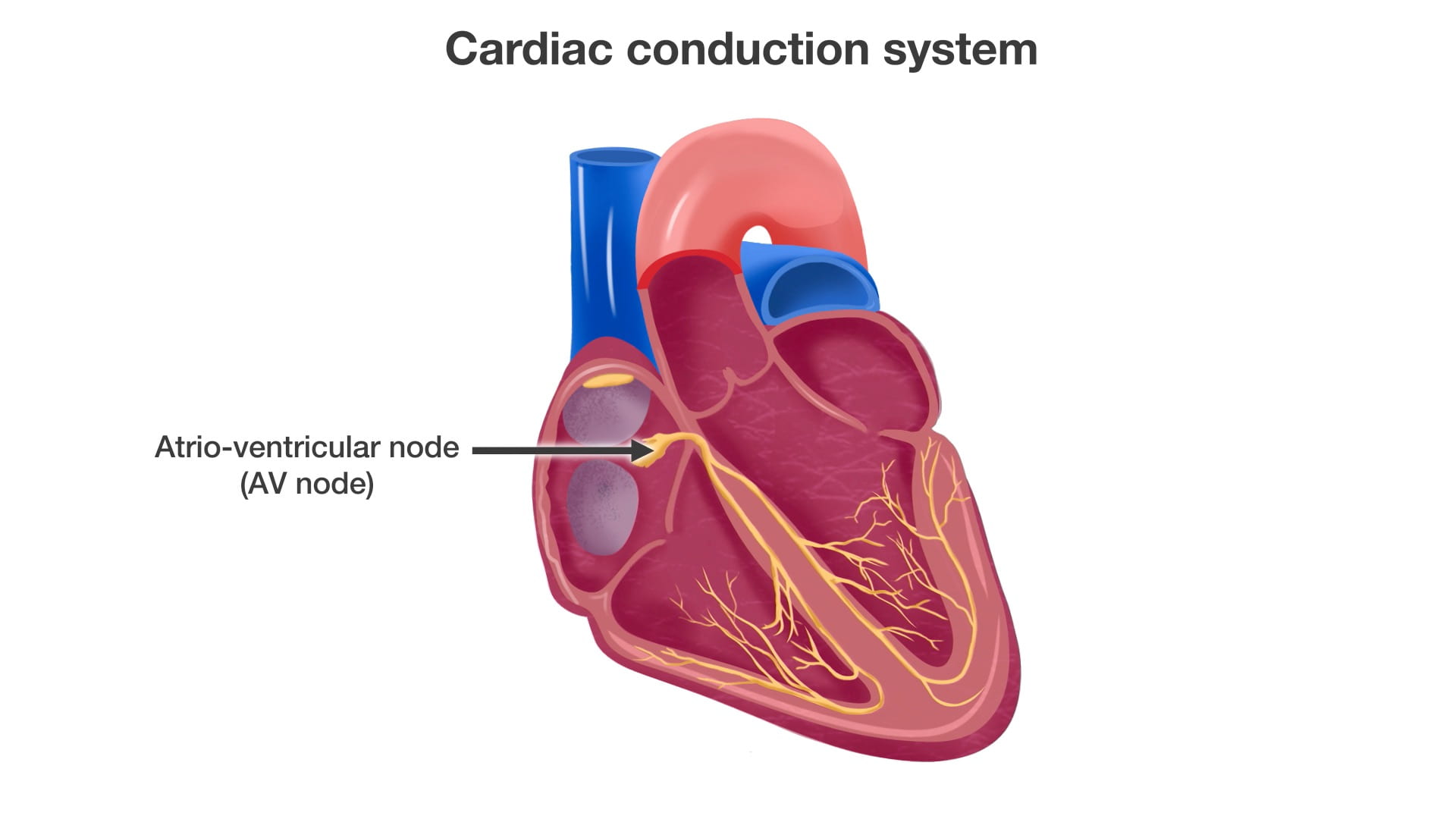
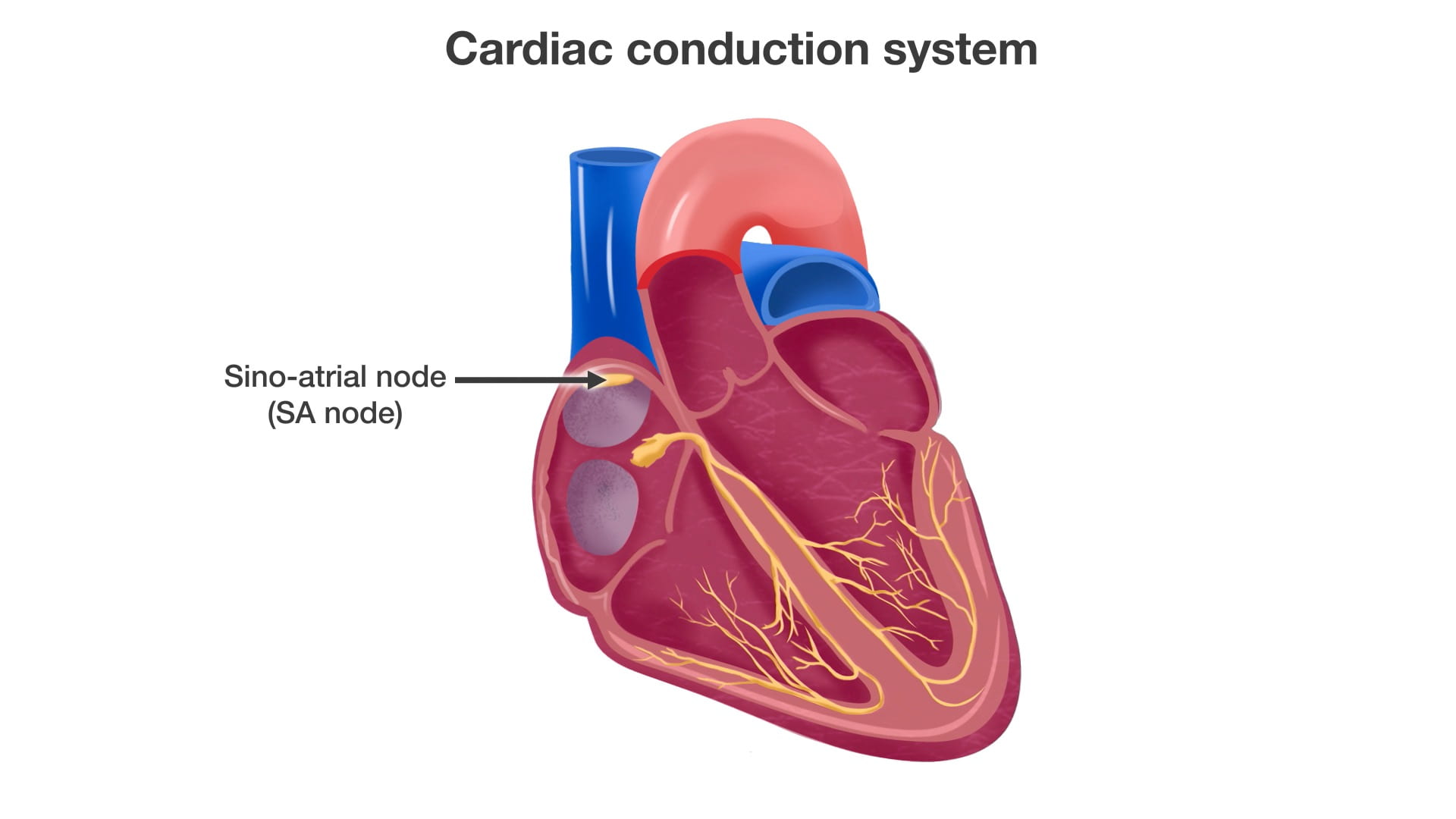
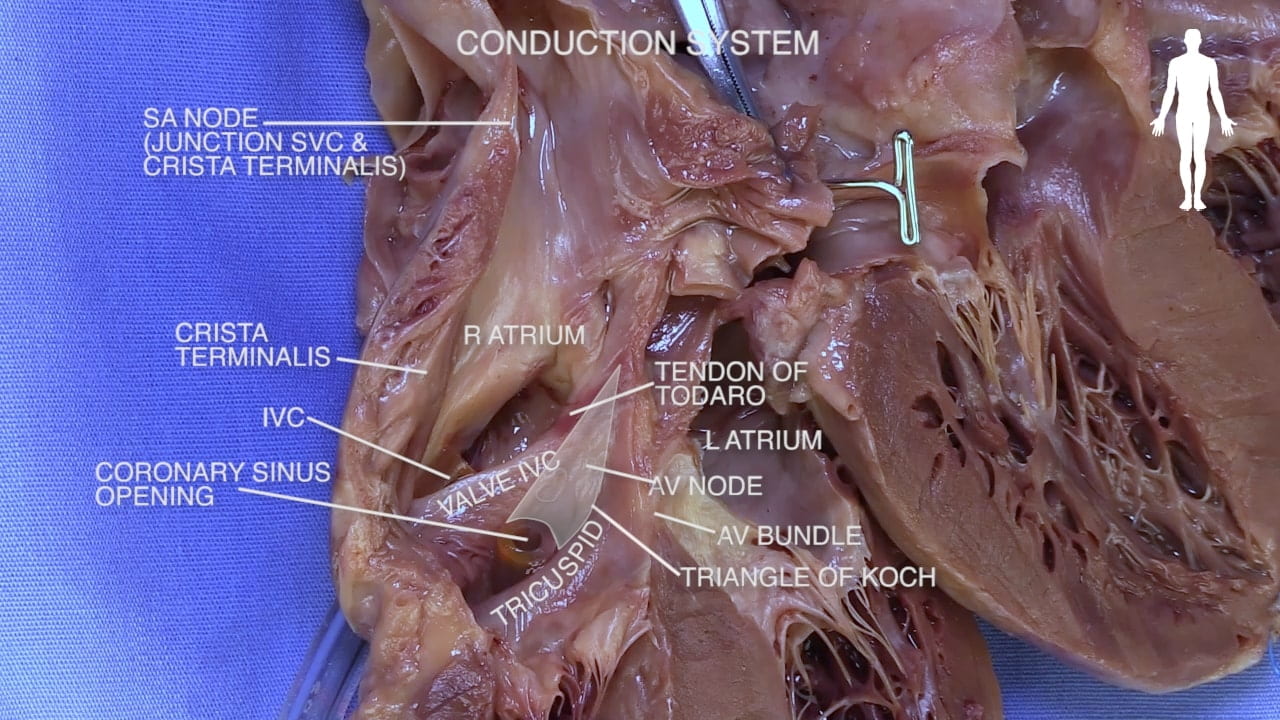
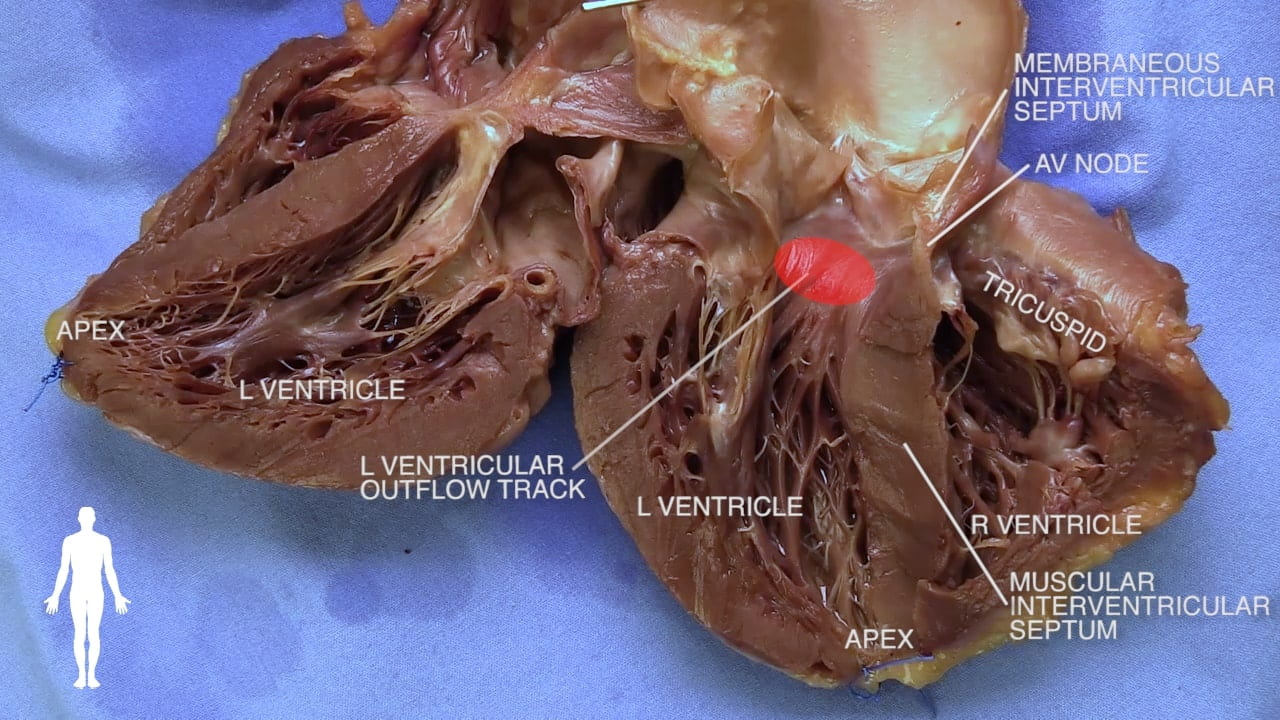
- Describe the approximate location of the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes.
- Describe the conduction system of the heart.
- Describe the functional importance of papillary muscles and chordae tendineae.
Lecture List
The Heart, Exposure of the Heart, Coronary Vessels, Removal of the Heart, Bisecting the Heart, In Situ Dissection of the Heart
Anatomy of the Heart
The Heart Gallery
Exposure of Heart
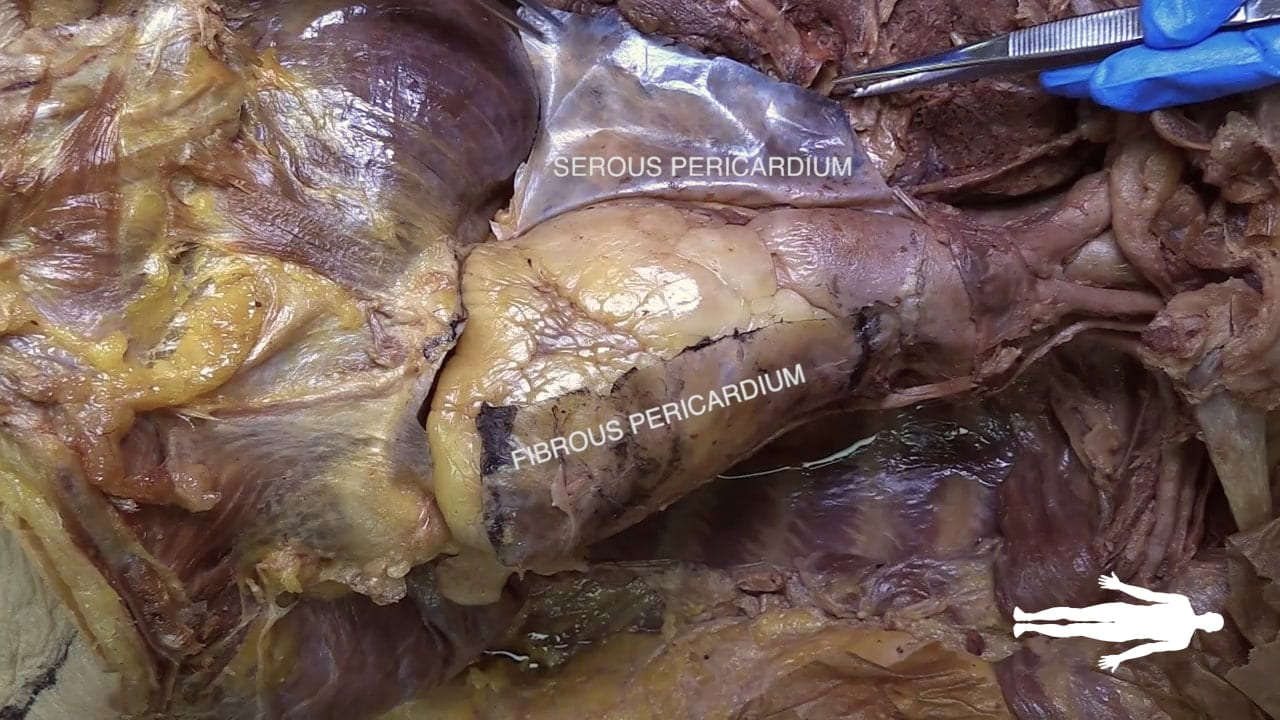
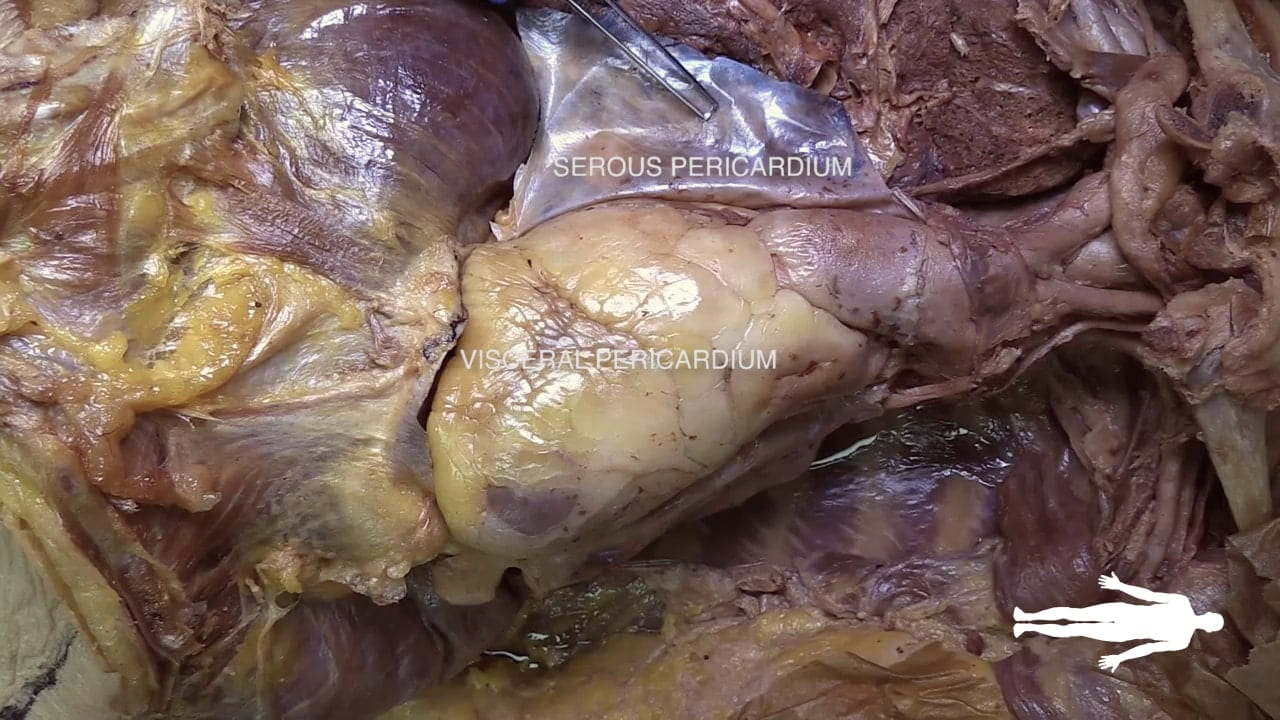
Pericardium
Incise the pericardium in the anterior midline. Open further with transverse incisions at the apex and base.
Identify the fibrous pericardium and the parietal and visceral (epicardium) layers of the serous pericardium.
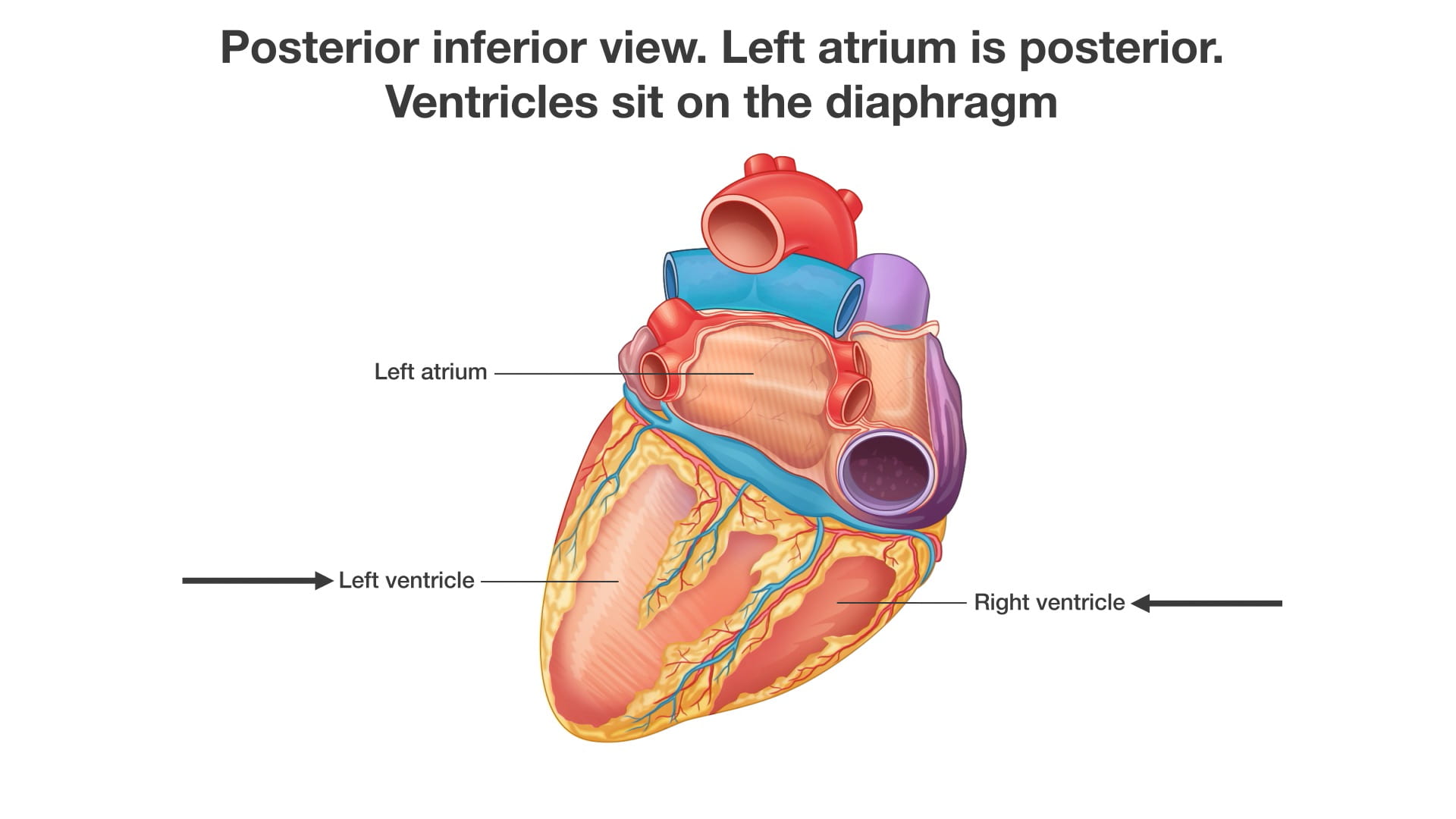
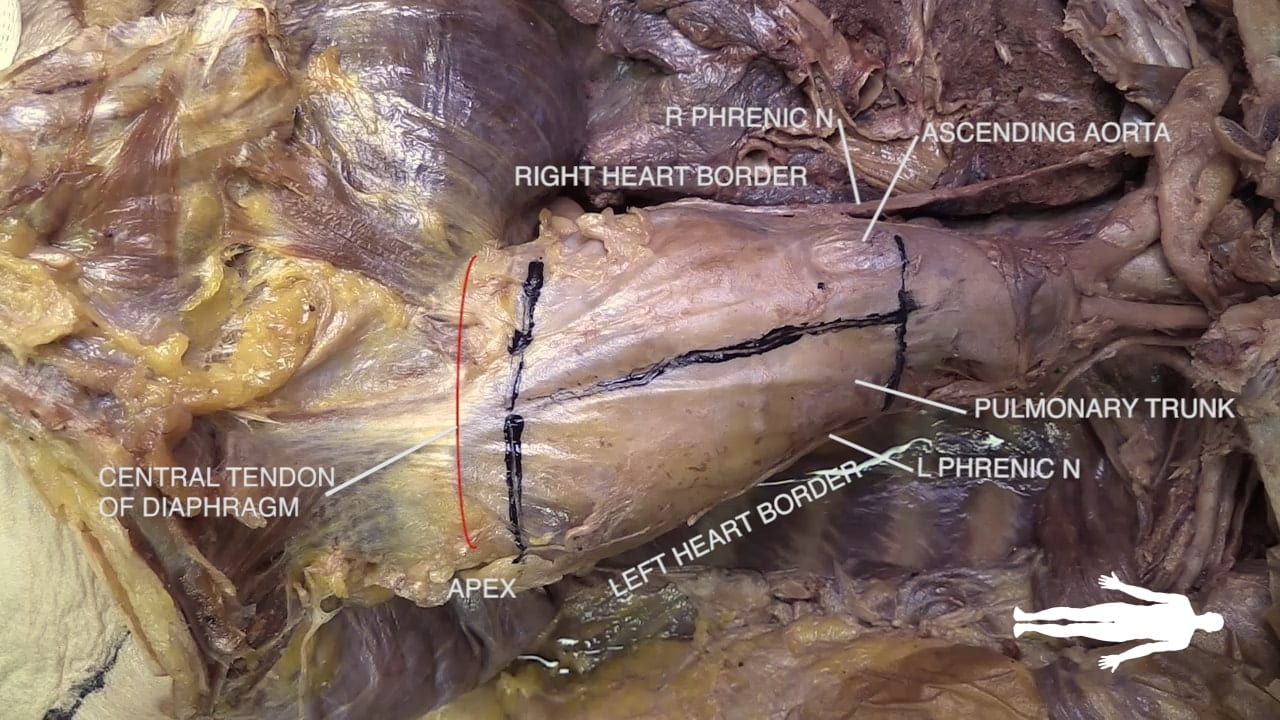
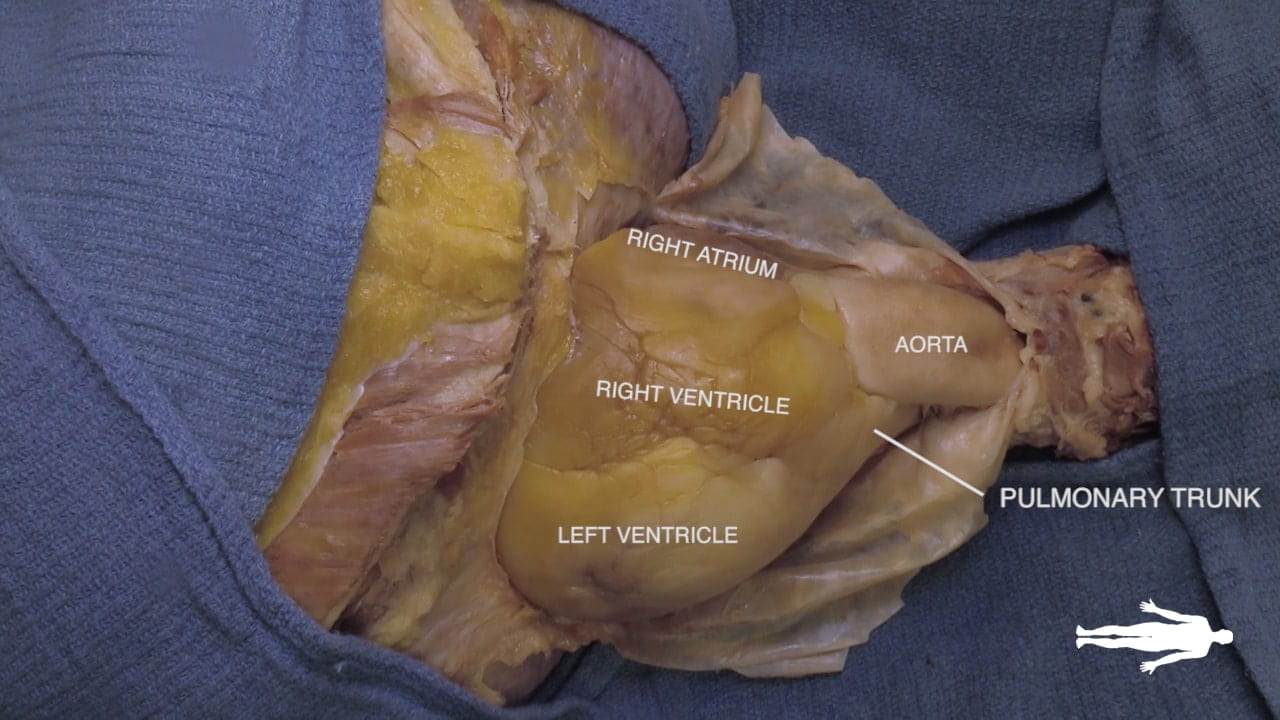
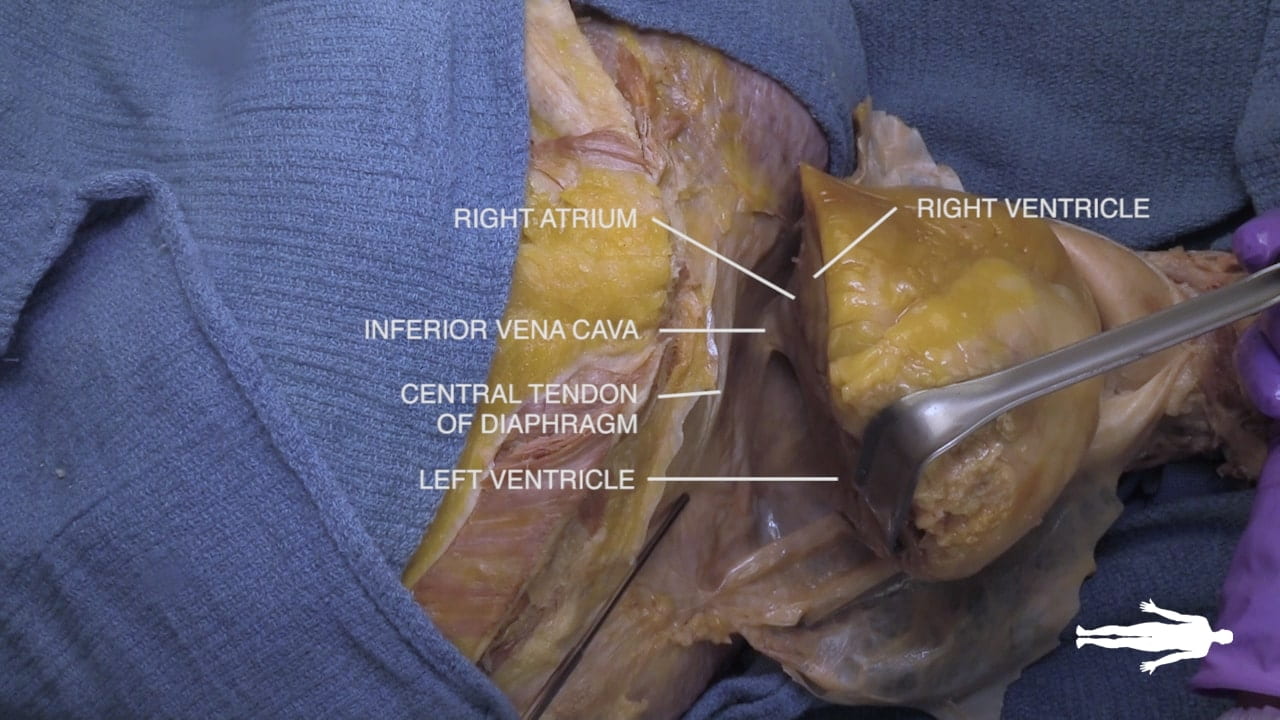
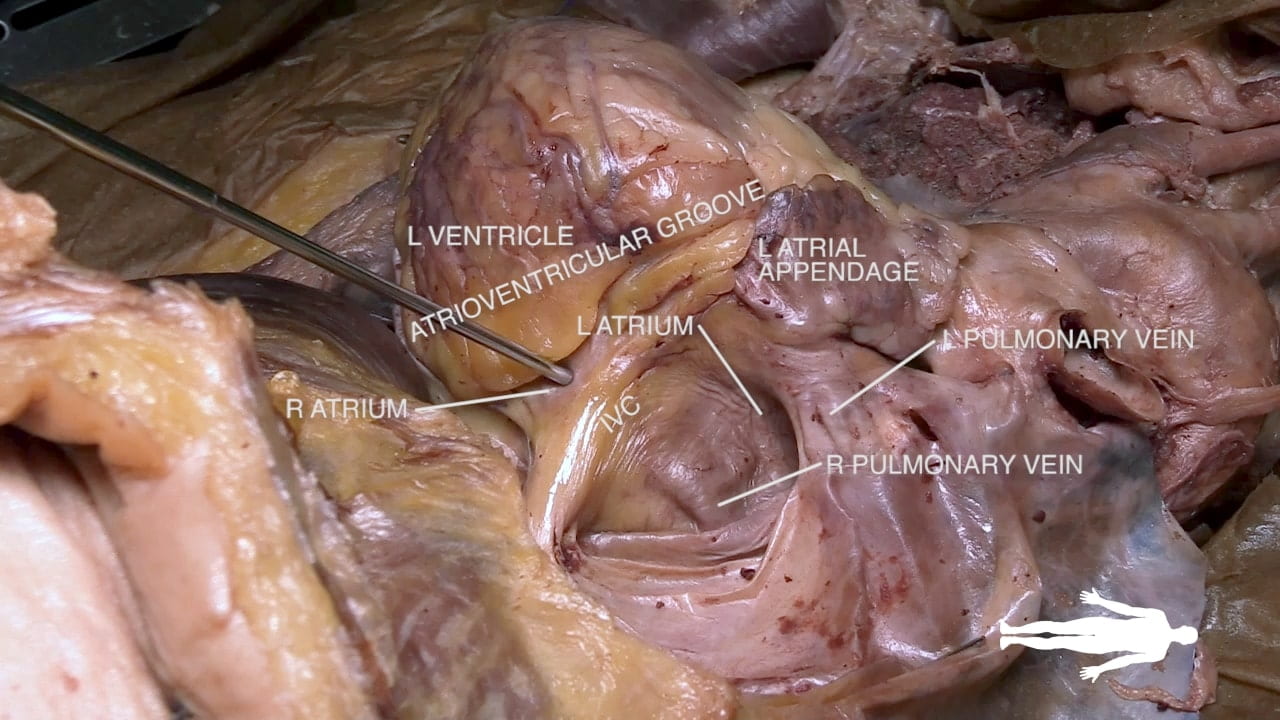
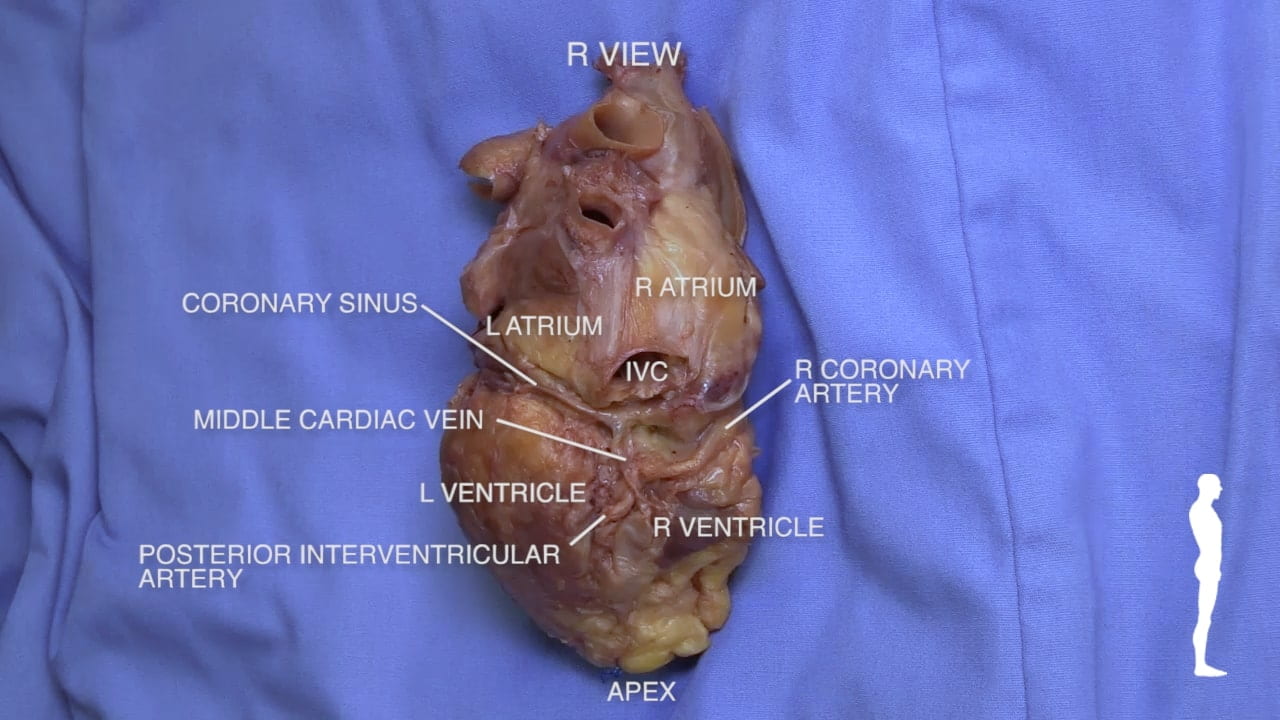
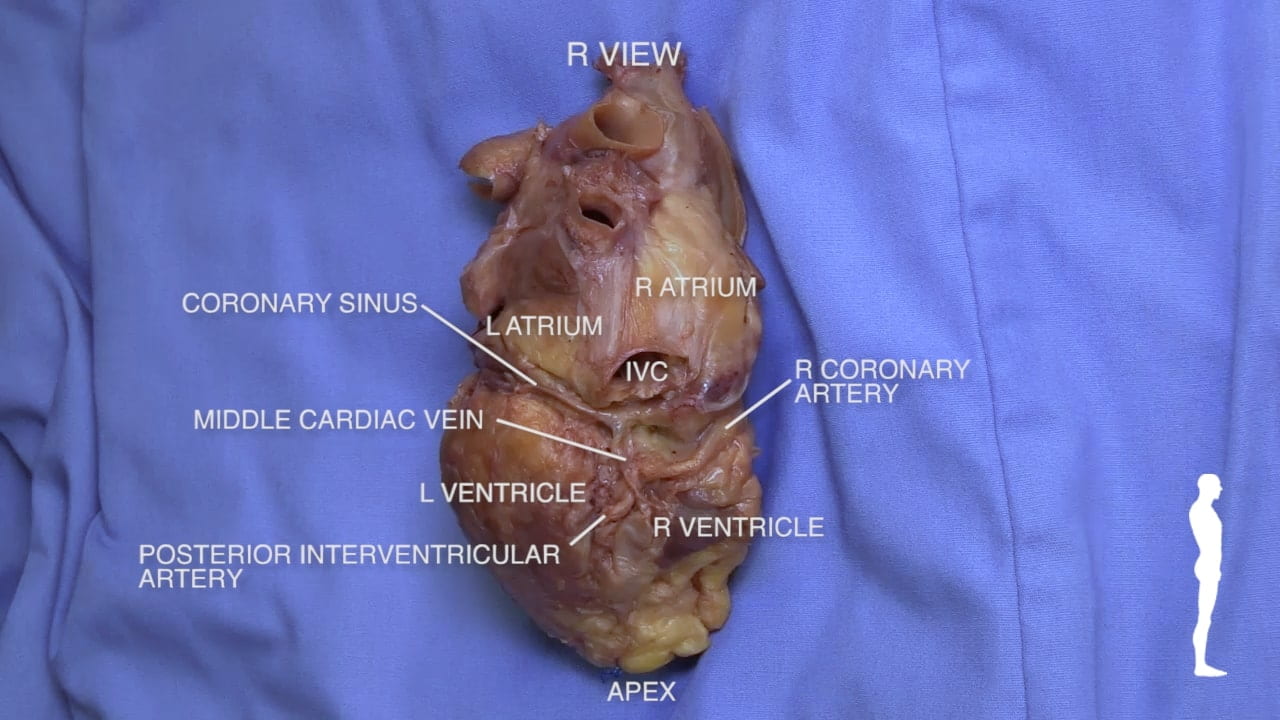
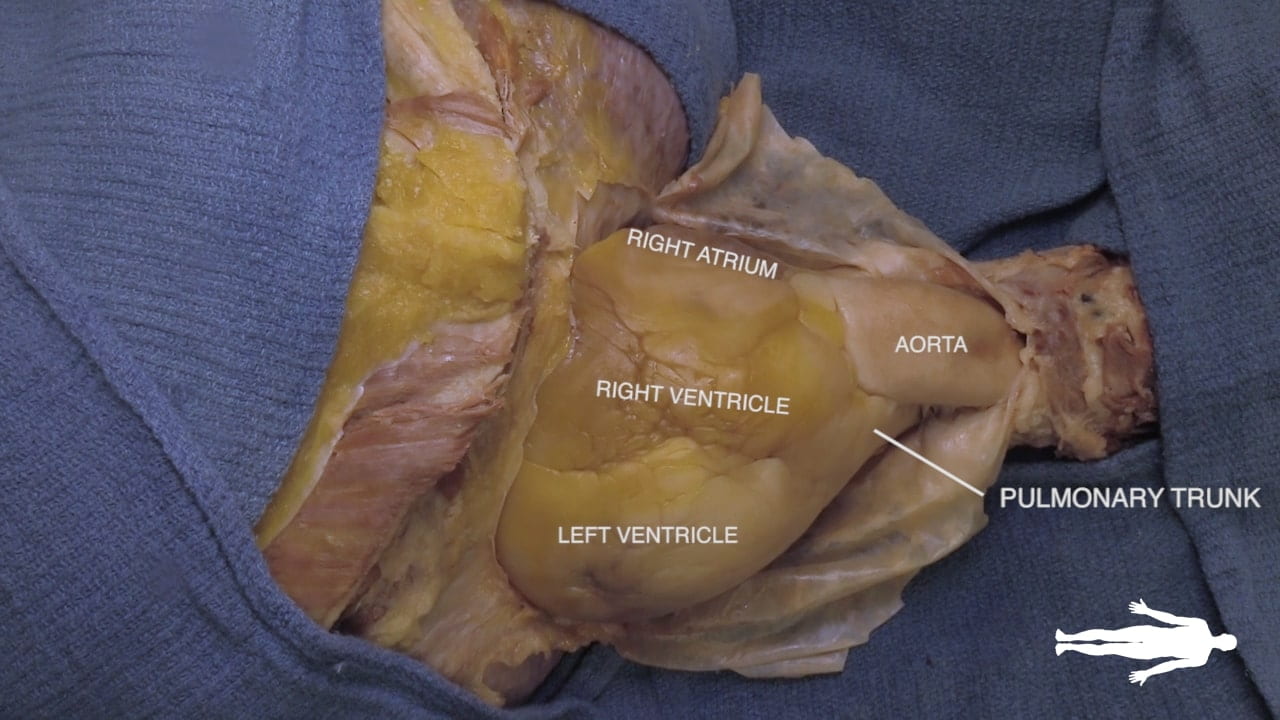
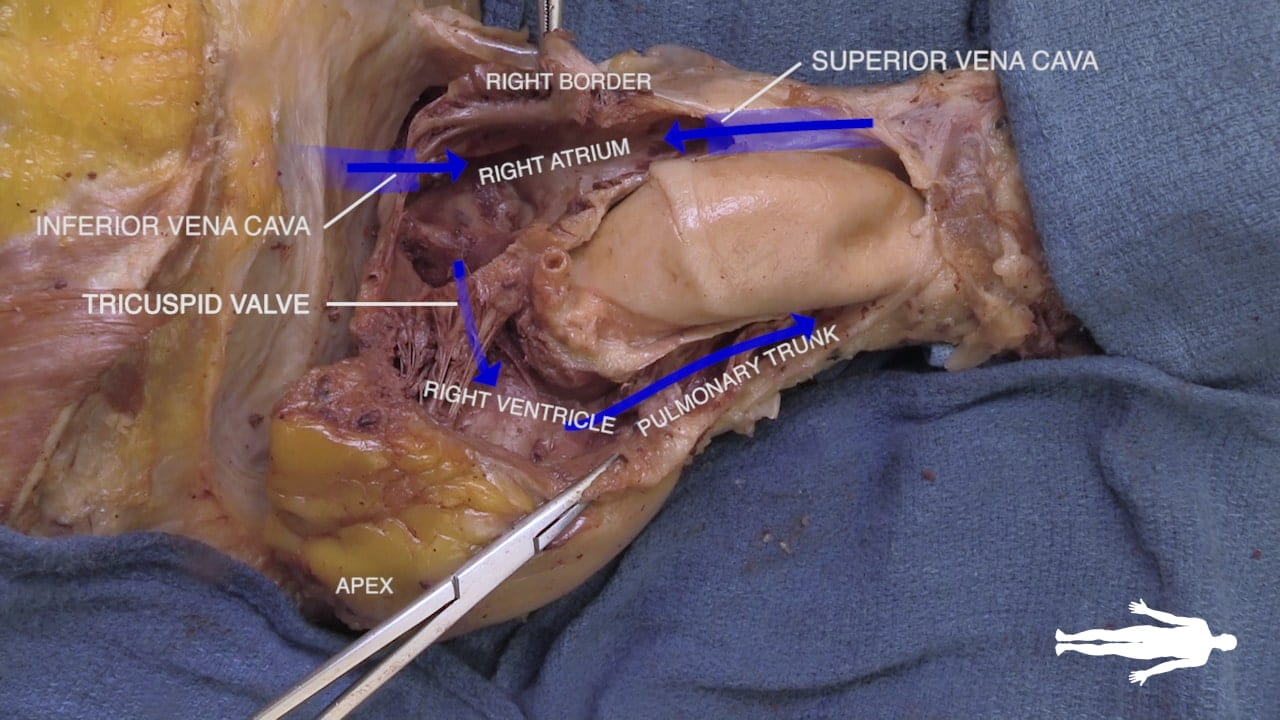
Cardiac Surfaces
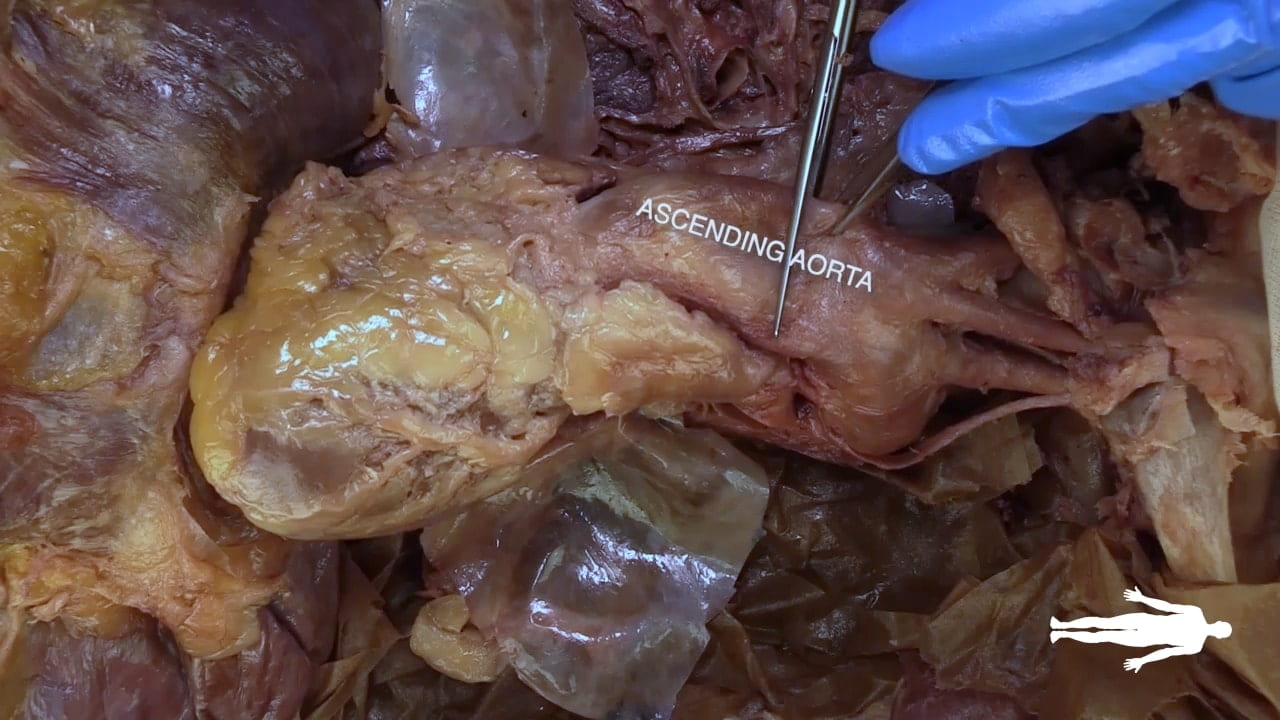
Identify the chambers of the heart, aorta, pulmonary trunk, superior and inferior vena cavae and pulmonary veins.
Lift the heart to view its diaphragmatic surface.
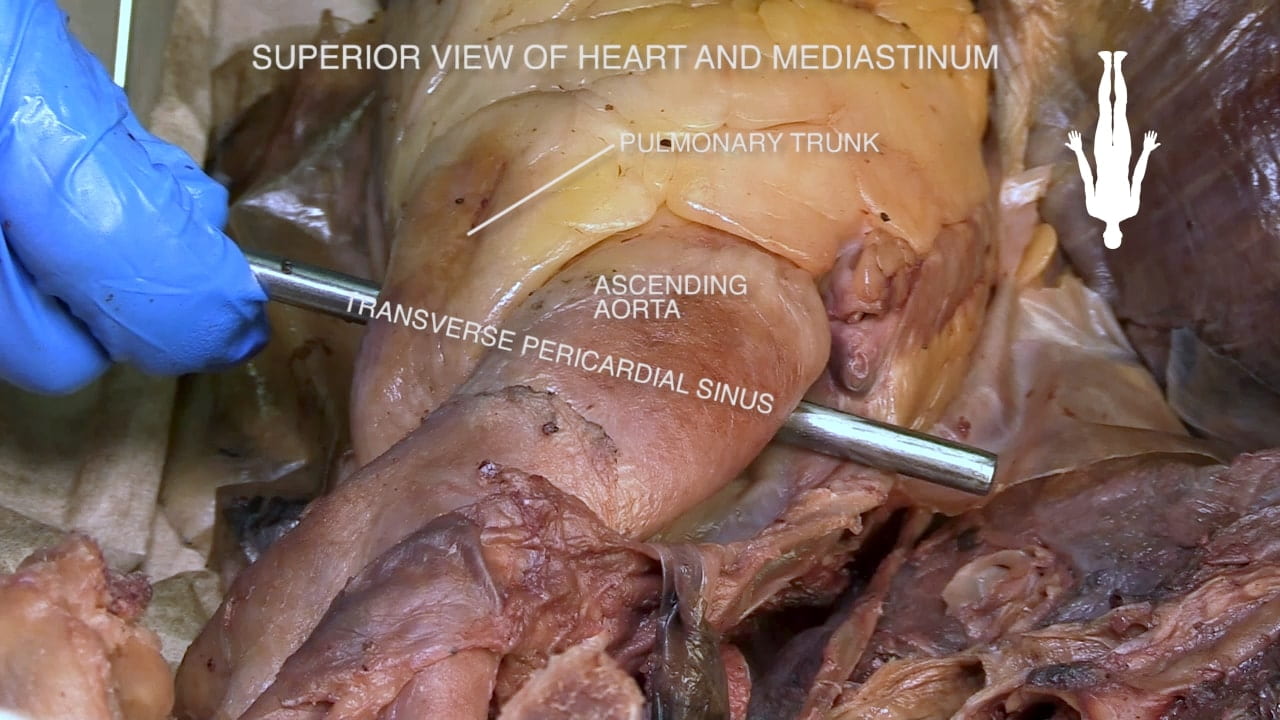
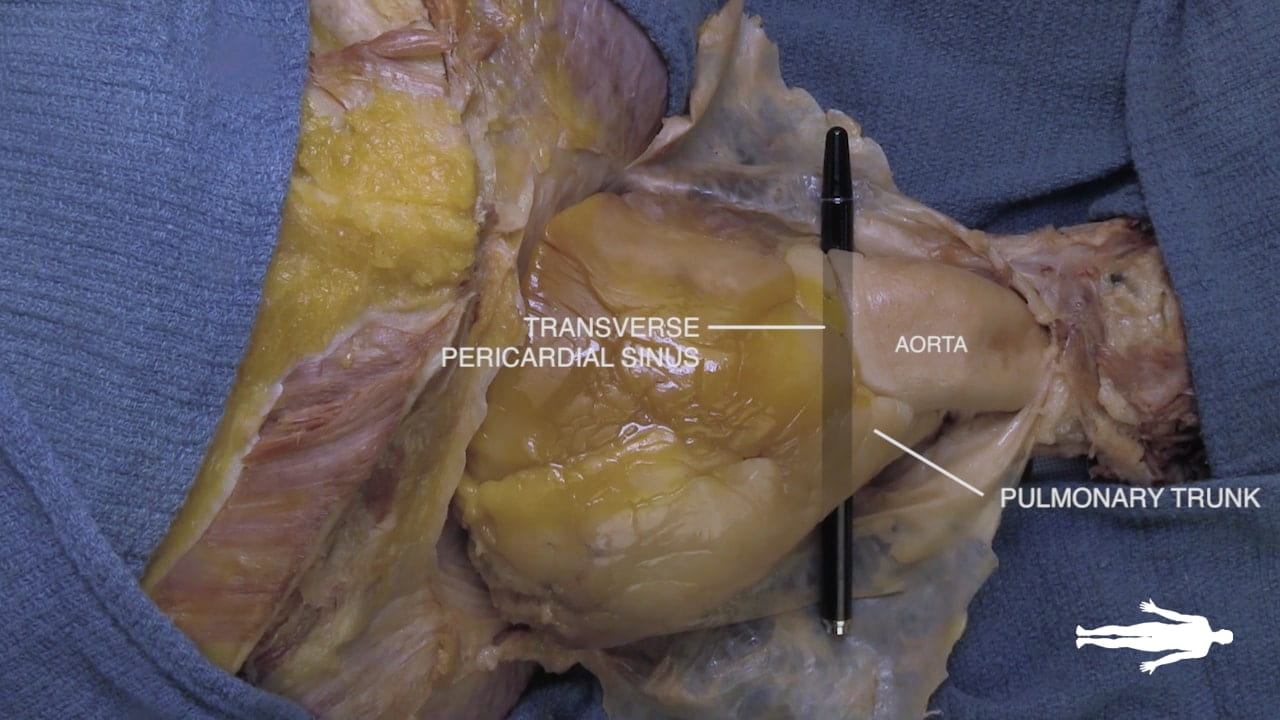
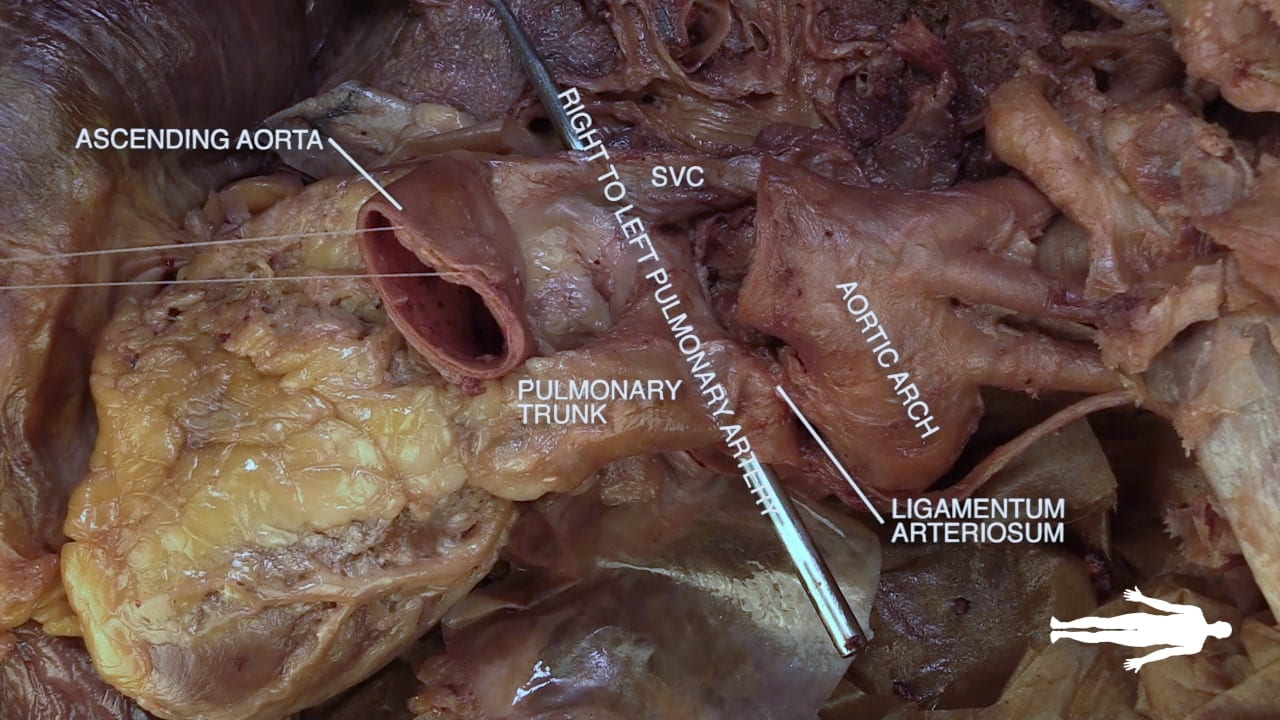
Transverse Pericardial Sinus
Place an instrument posterior to the pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta. Note that cardiac output is anterior to the probe and the venous inflow is posterior. This space is the transverse pericardial sinus and an important landmark in cardiac surgery.
Left Cardiac Surface
On the left side of the heart, locate vagus nerve (X), ligamentum arteriosum and left recurrent laryngeal nerve.
The vagus nerve lies along the aortic arch. The ligamentum arteriosum connects the left pulmonary artery and the arch of the aorta. The left recurrent laryngeal artery can be identified branching from the vagus nerve and passing posterior to the ligamentum arteriosum.

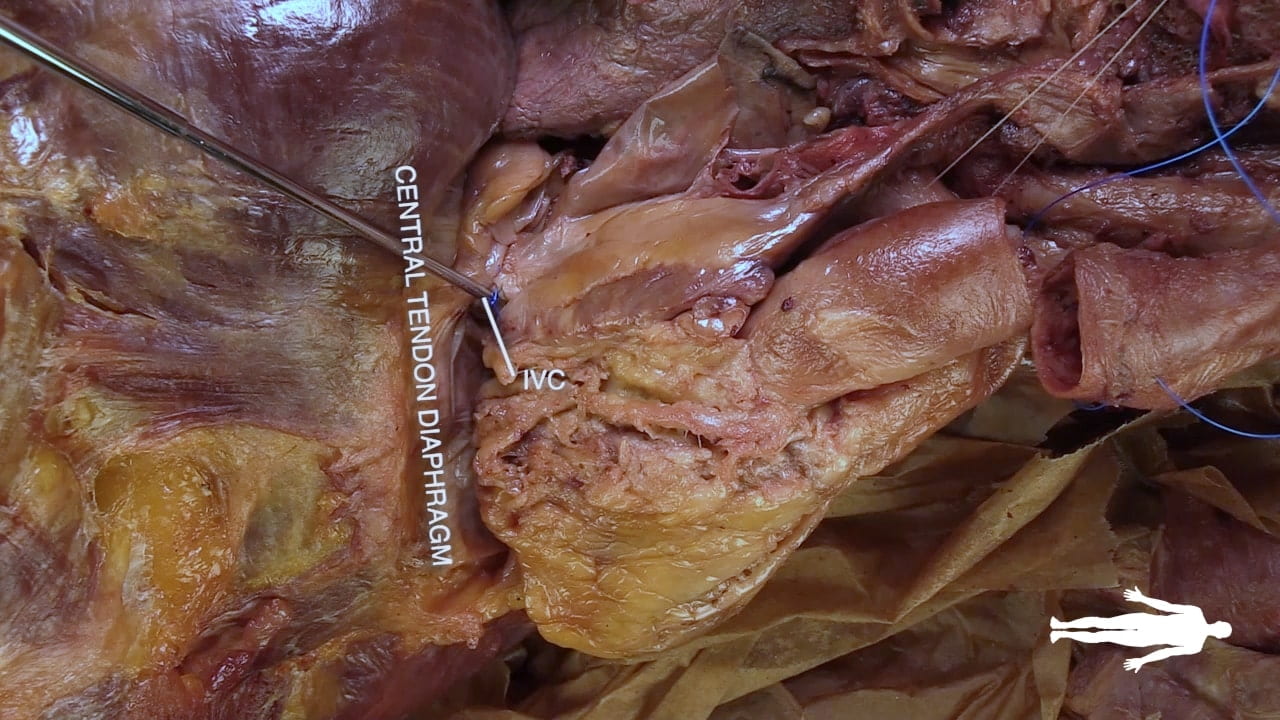
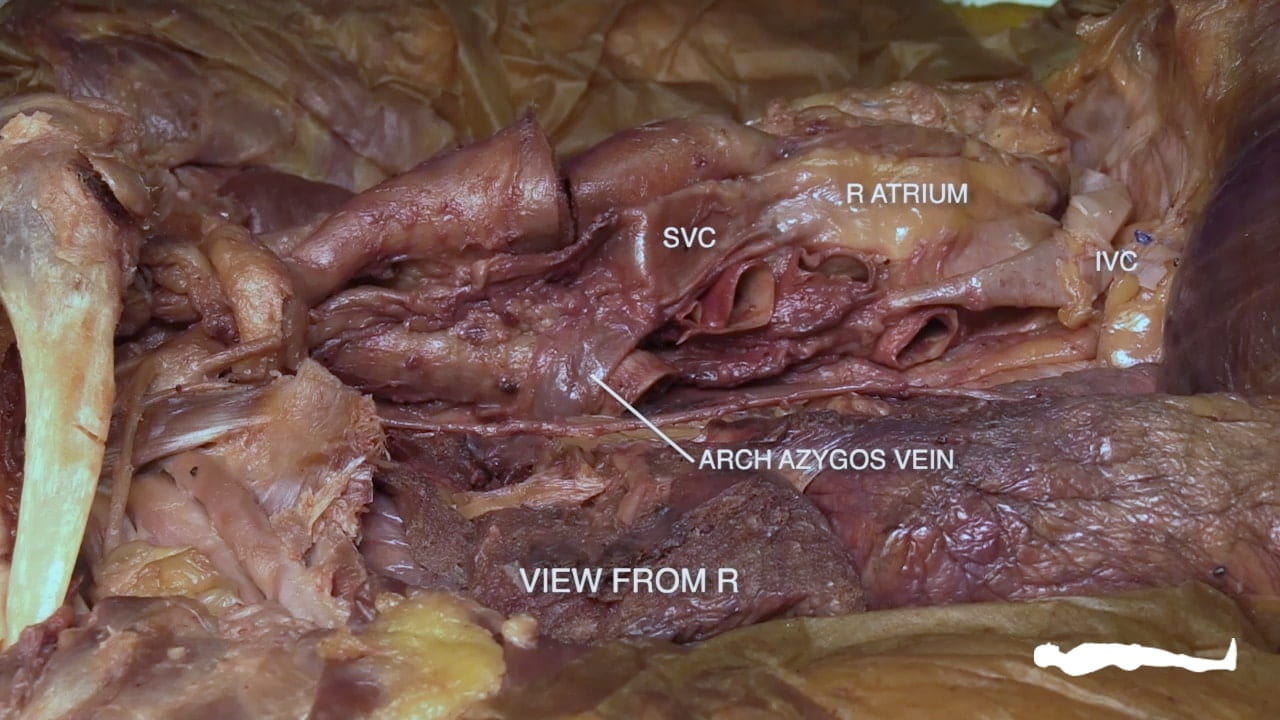
Right Cardiac Surface
On the right side of the heart, re-identify the hilus of the lung and find the arch of the azygos vein passing superior to the hilus of the lung to enter the superior vena cava.
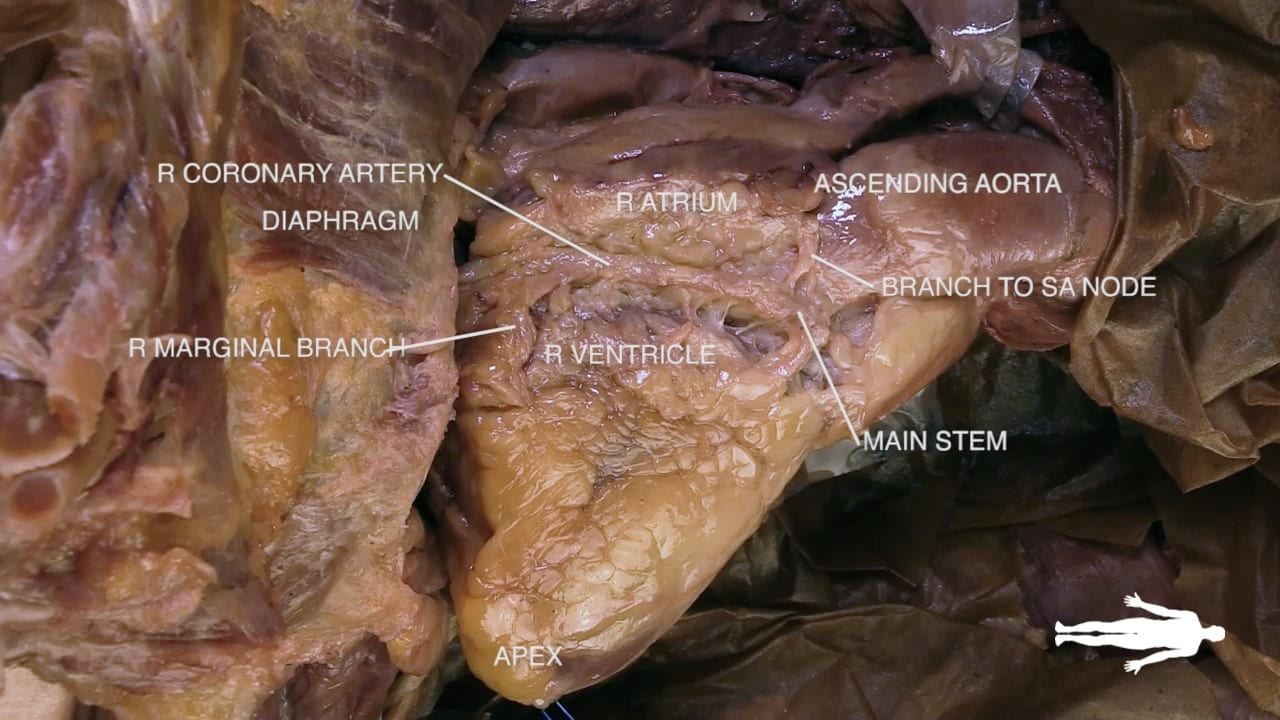
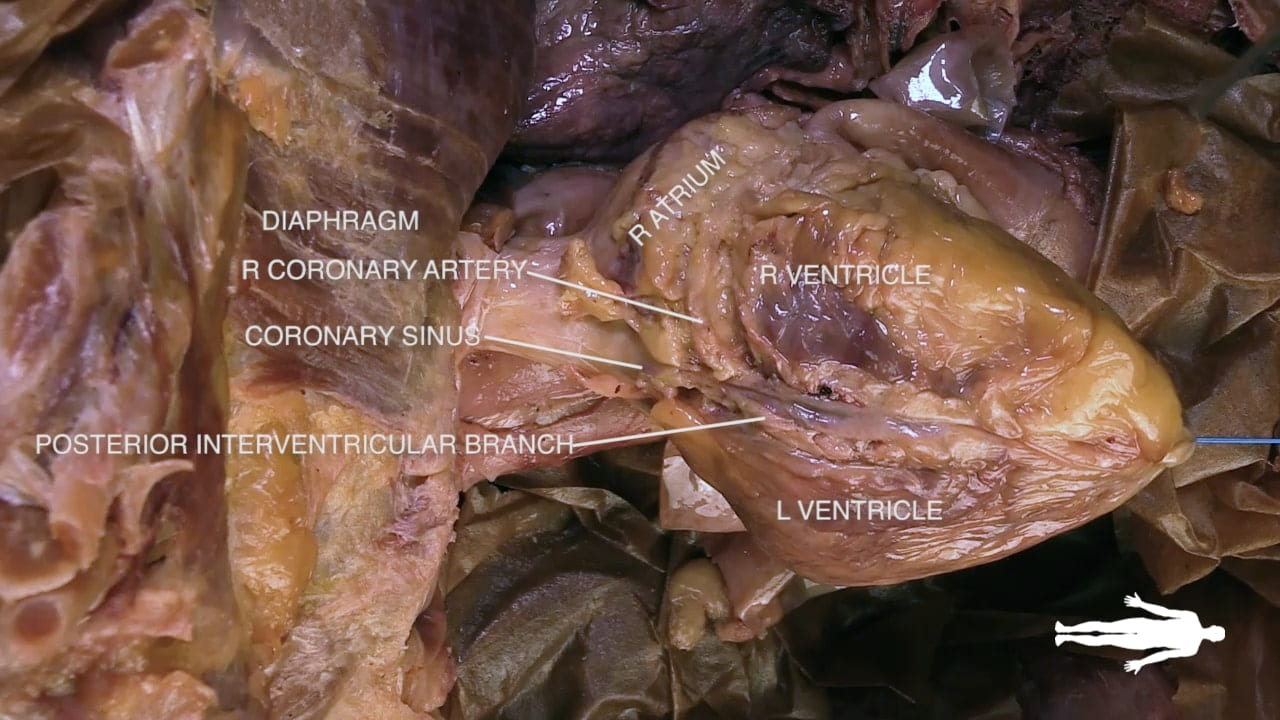
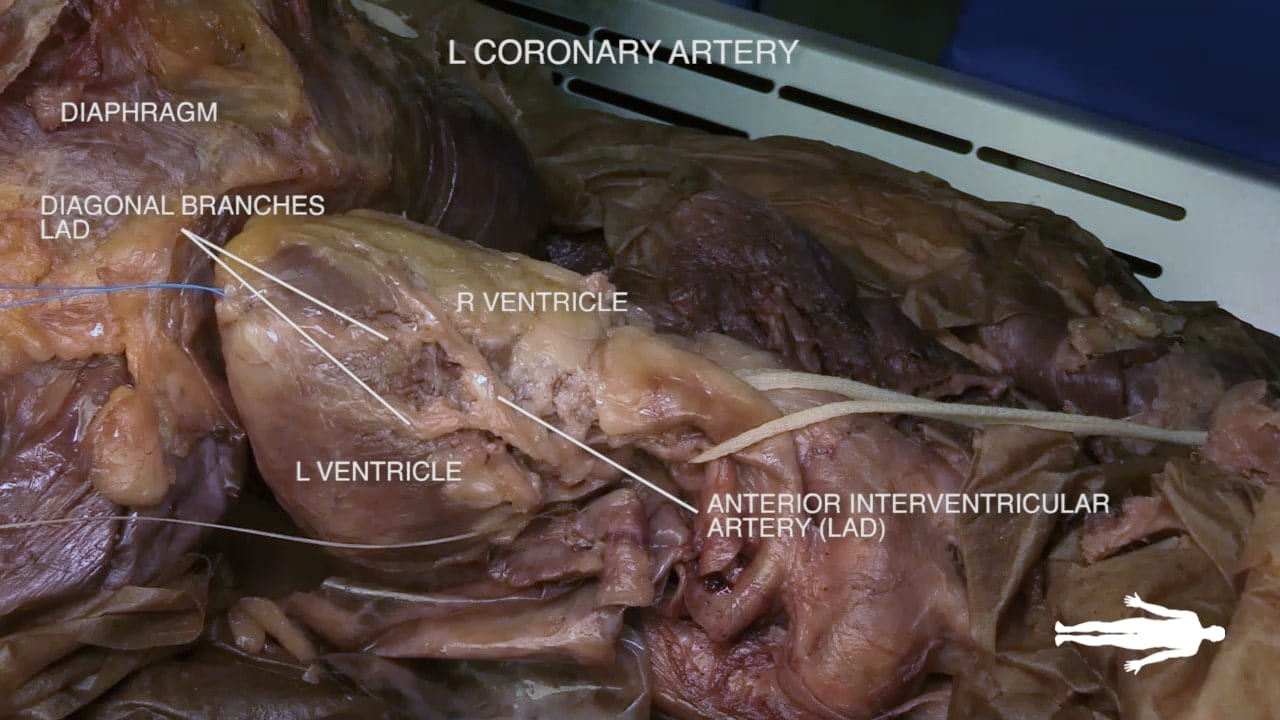
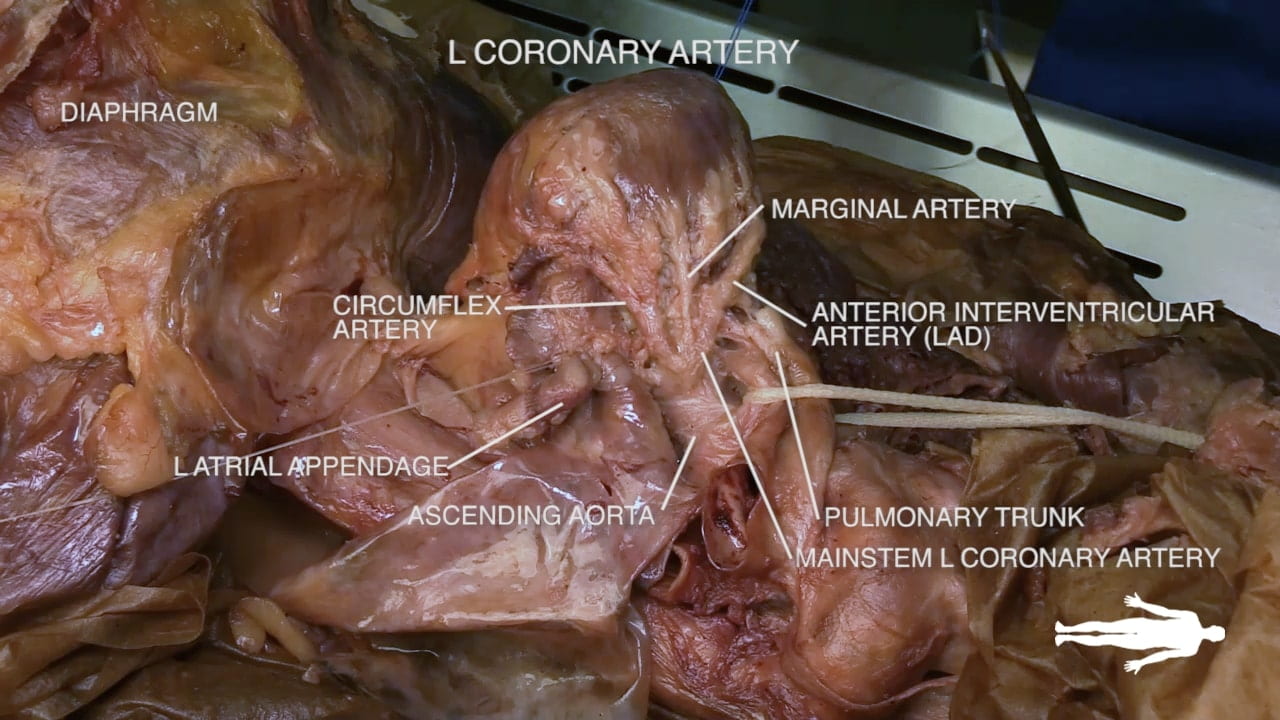
Identify the atrioventricular groove on the right side of the heart. The right coronary artery lies in this groove.

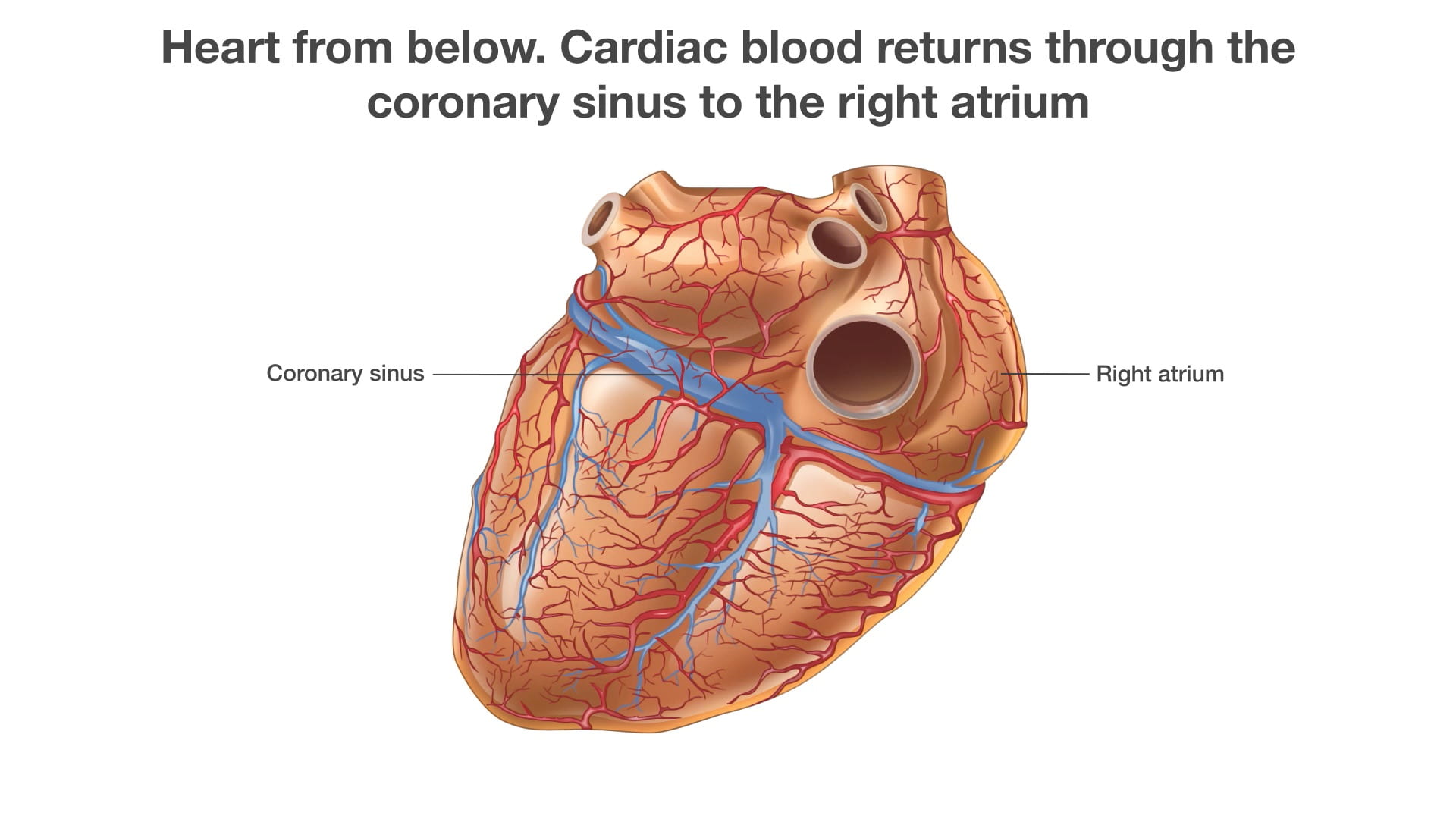
Coronary Vessels
Diagram of Coronary Vessels