Skull, Face and Cranium
Lab Summary
In this lab the skull, fetal skull, parotid gland, facial nerve (VII) and brain removal with encountered structures are taught. This volume includes facial nerve (VII) dissection through the parotid gland. Emphasis is made of the cranial nerves encountered in order along skull base from olfactory (I) to hypoglossal (XII) in the course of brain removal.
Lab Objectives
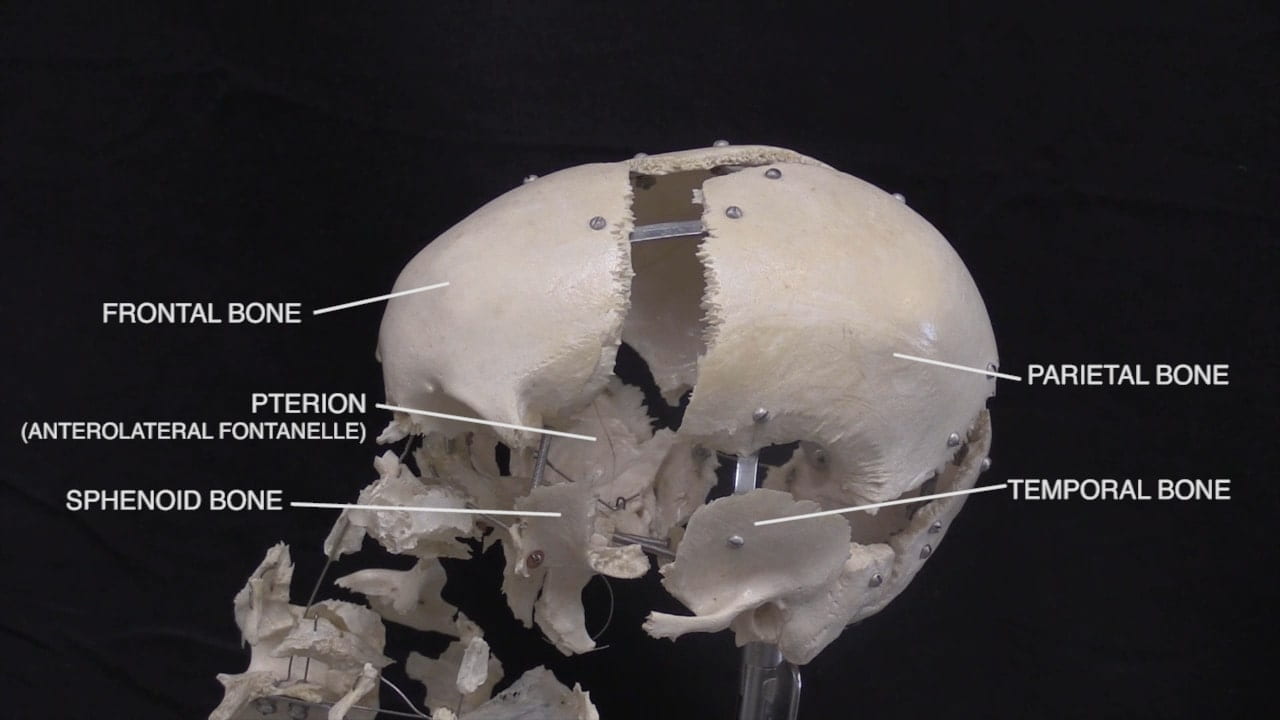
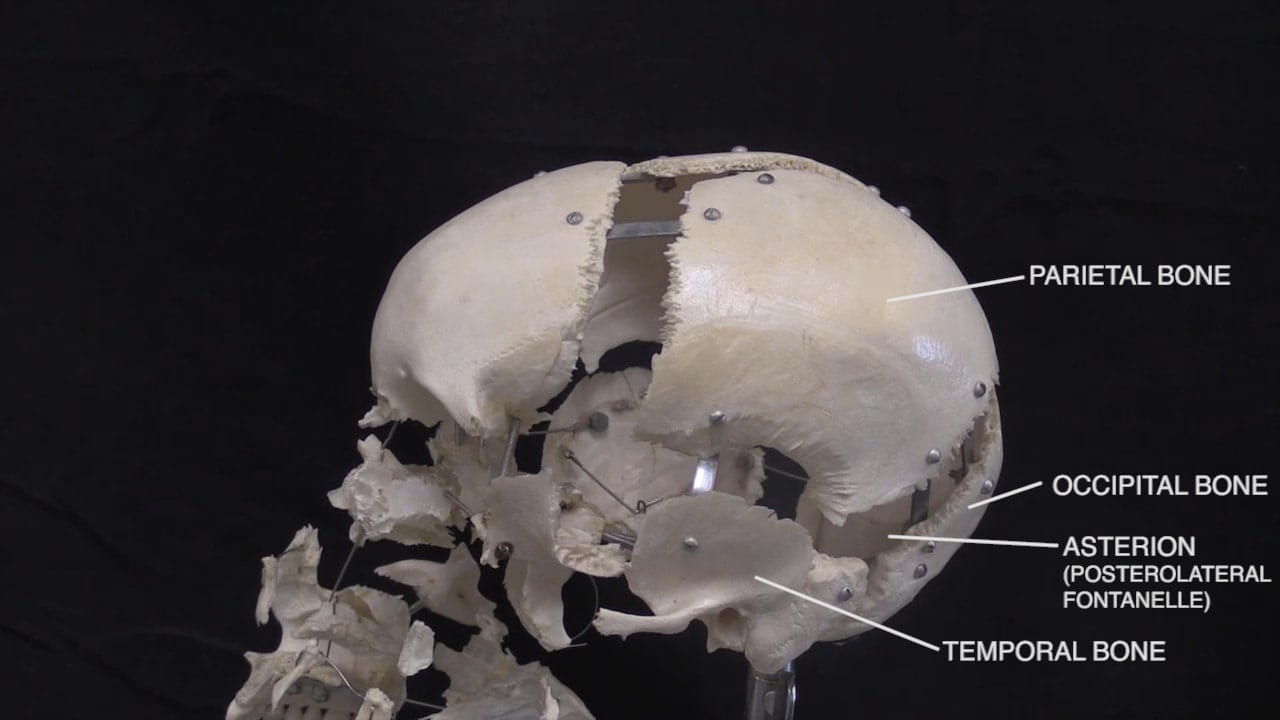
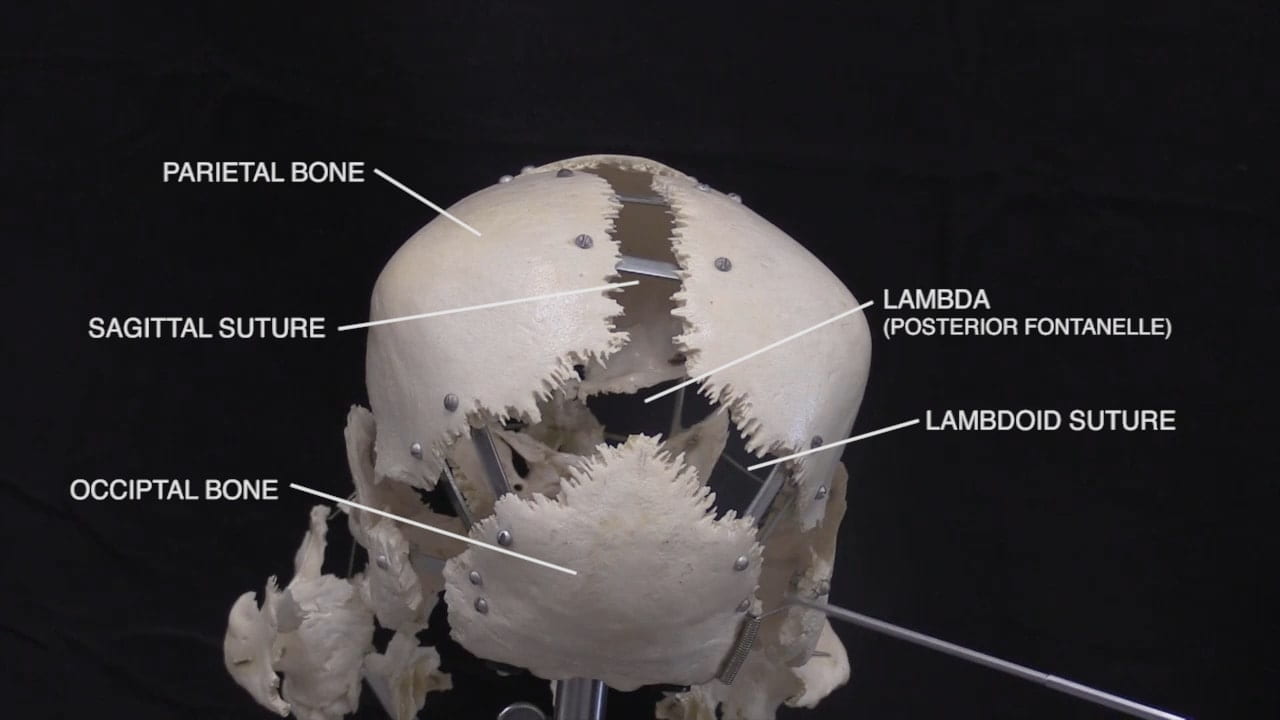
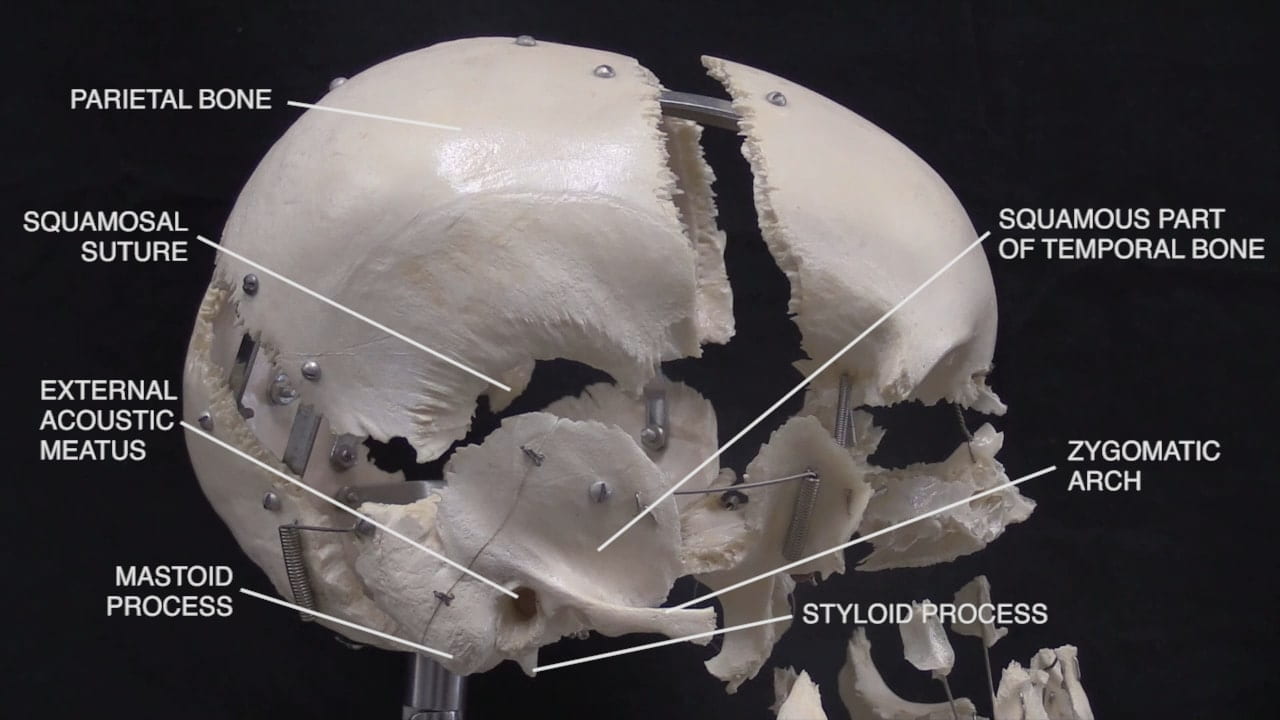
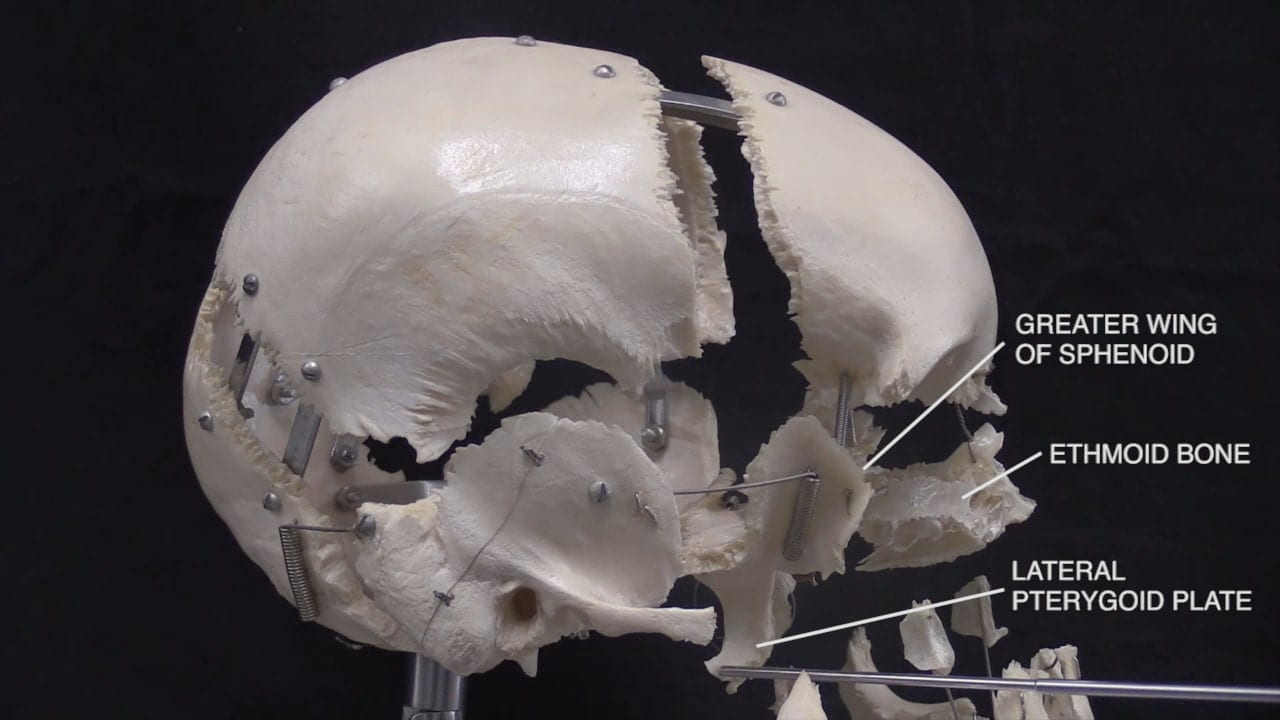
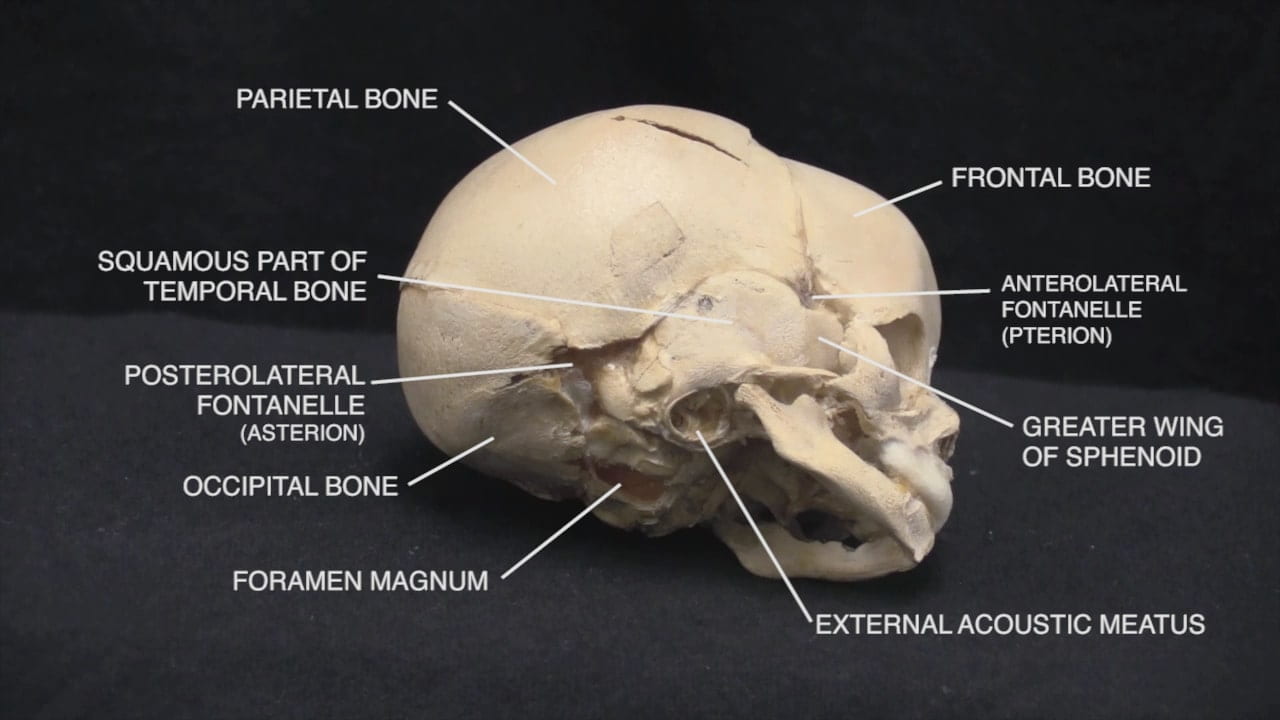
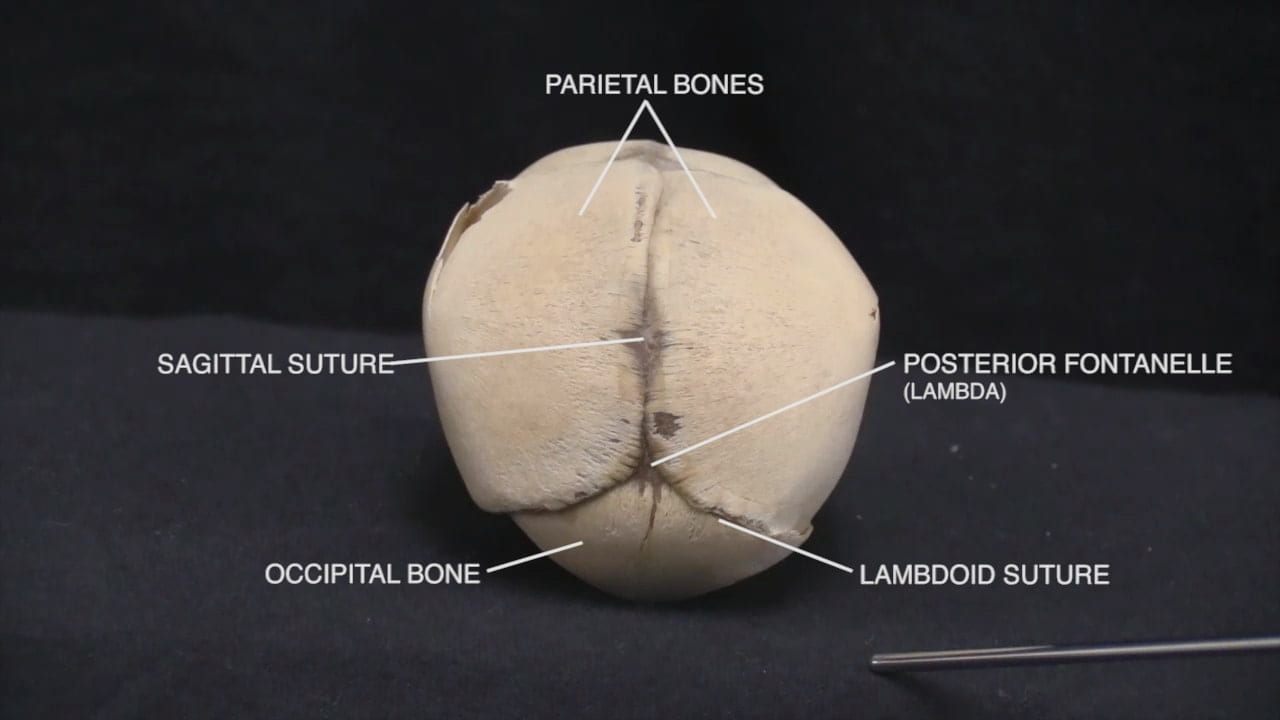
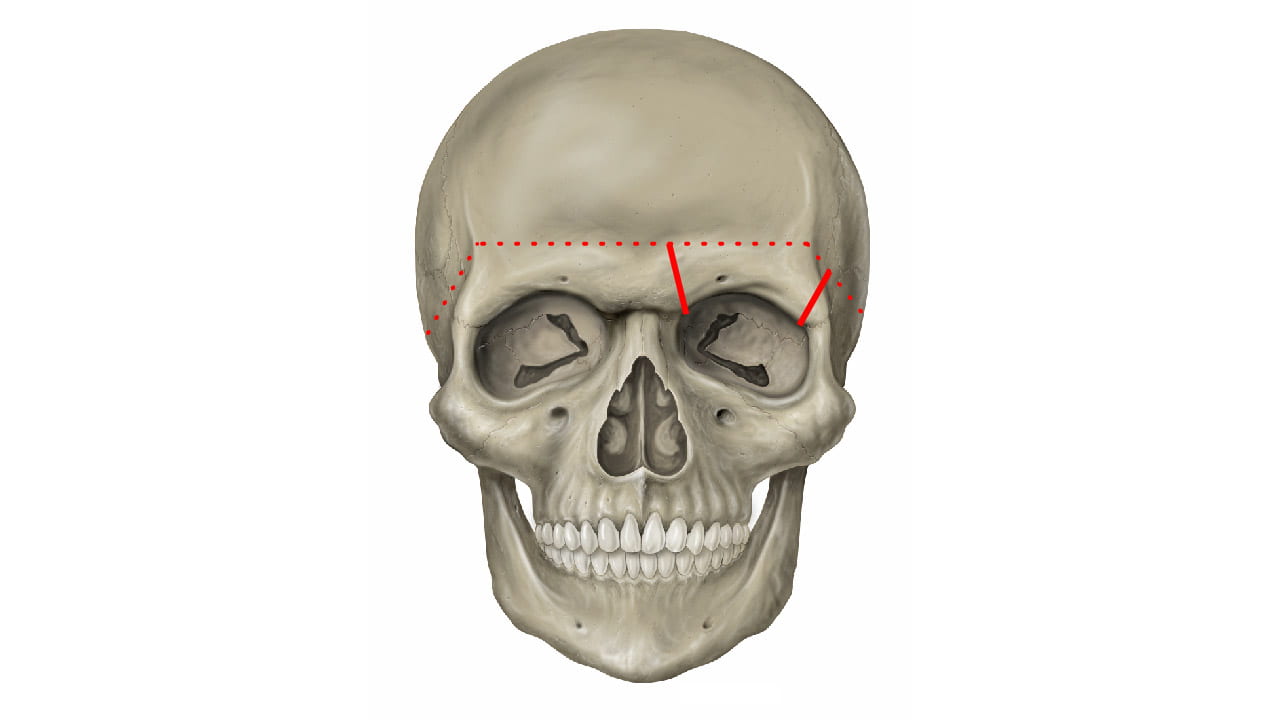
- Describe the bones of the cranial vault and sutures.
- Relate the cranial nerves to their position in the skull base.
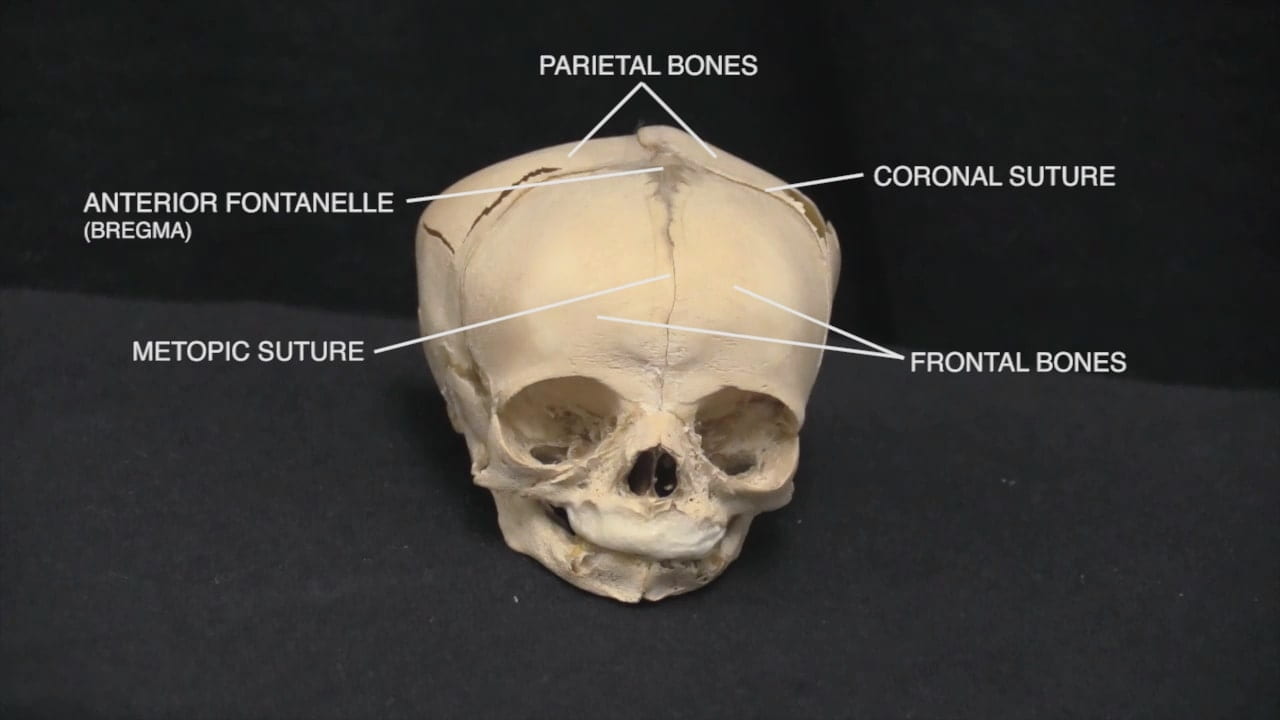
- Describe the position of the anterior fontanelle.
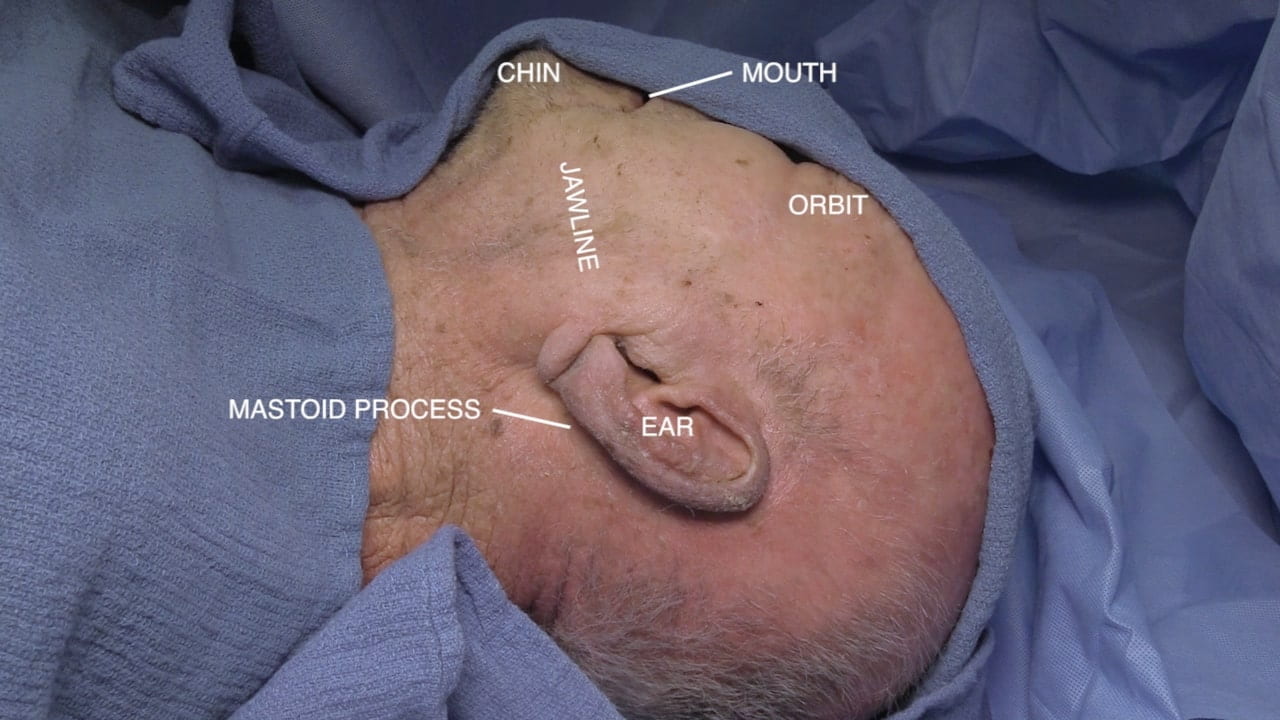
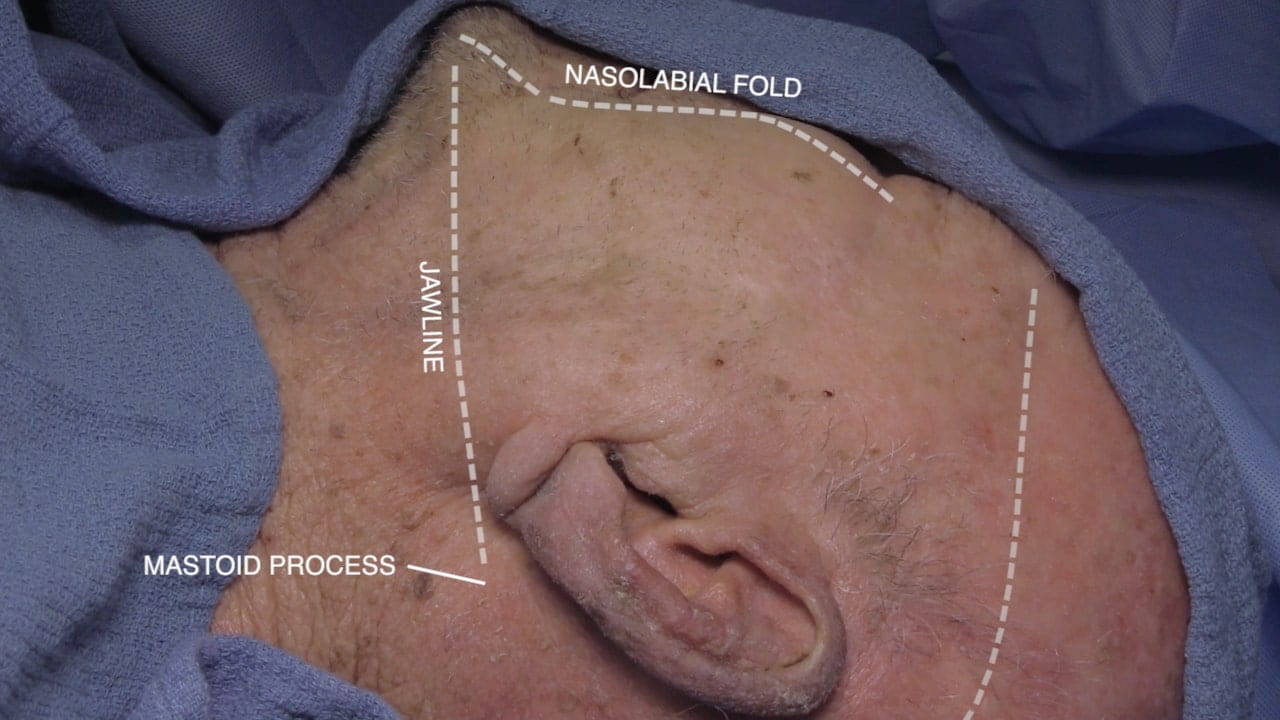
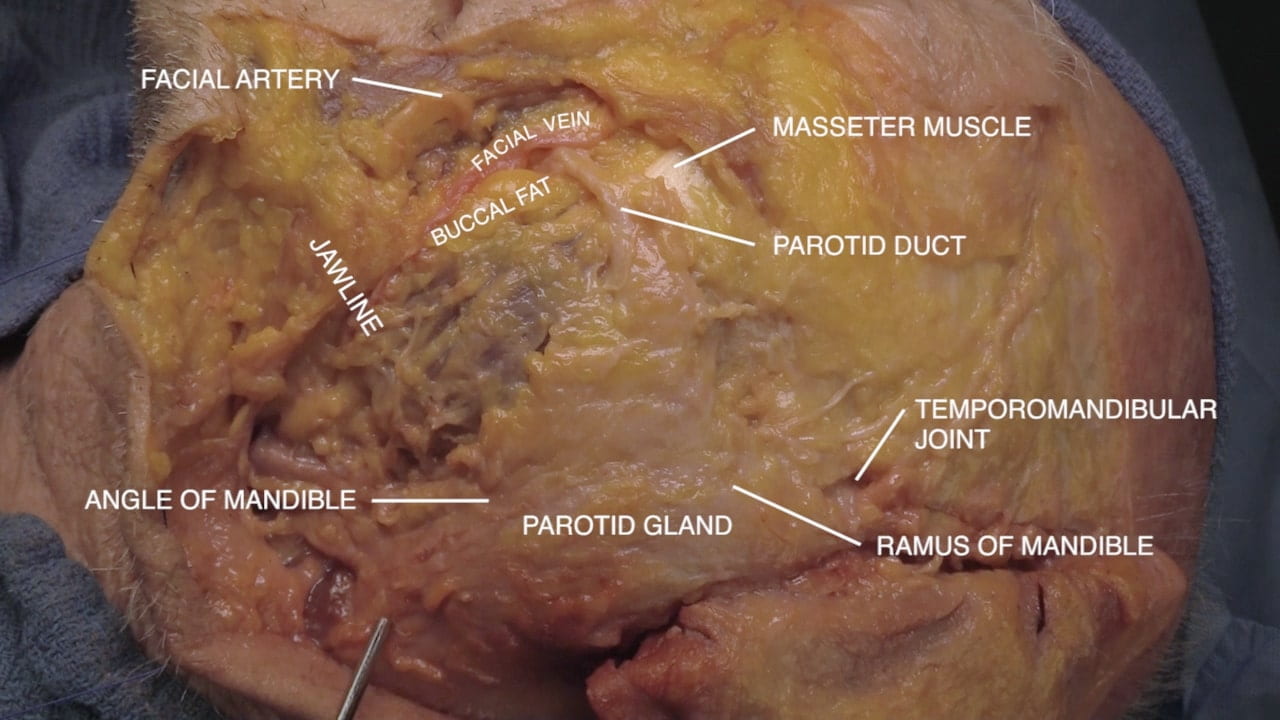
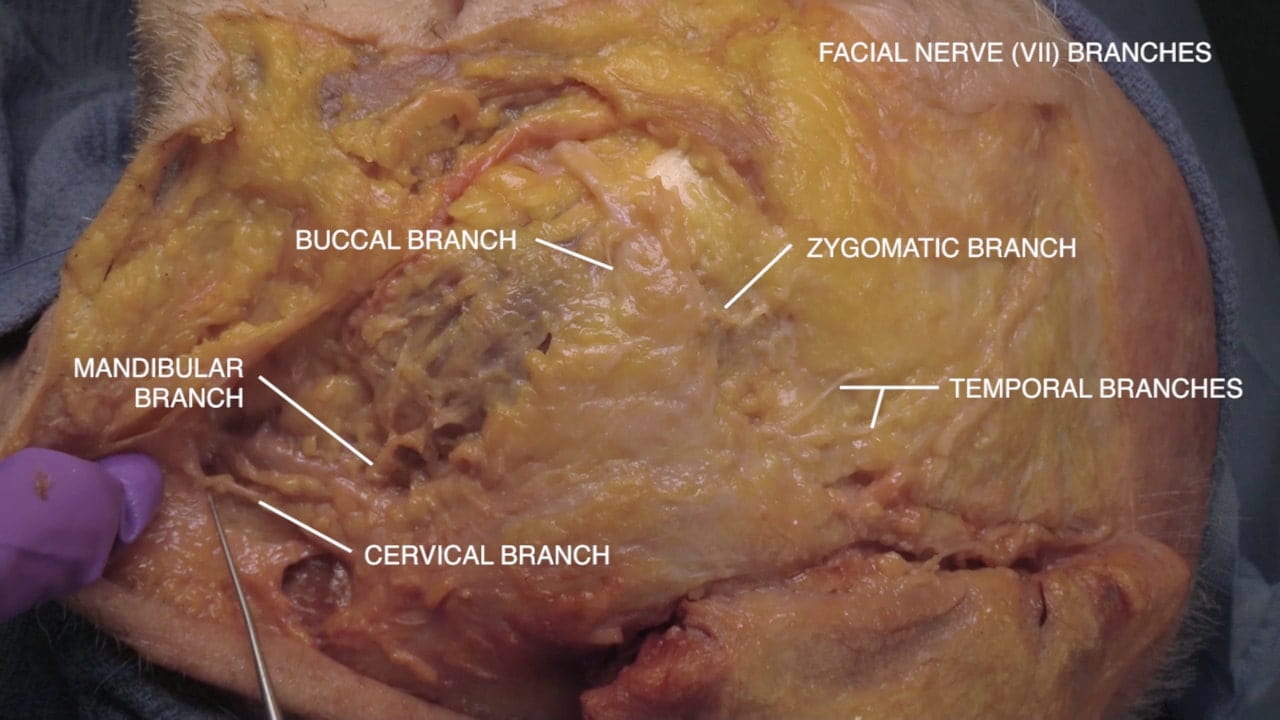
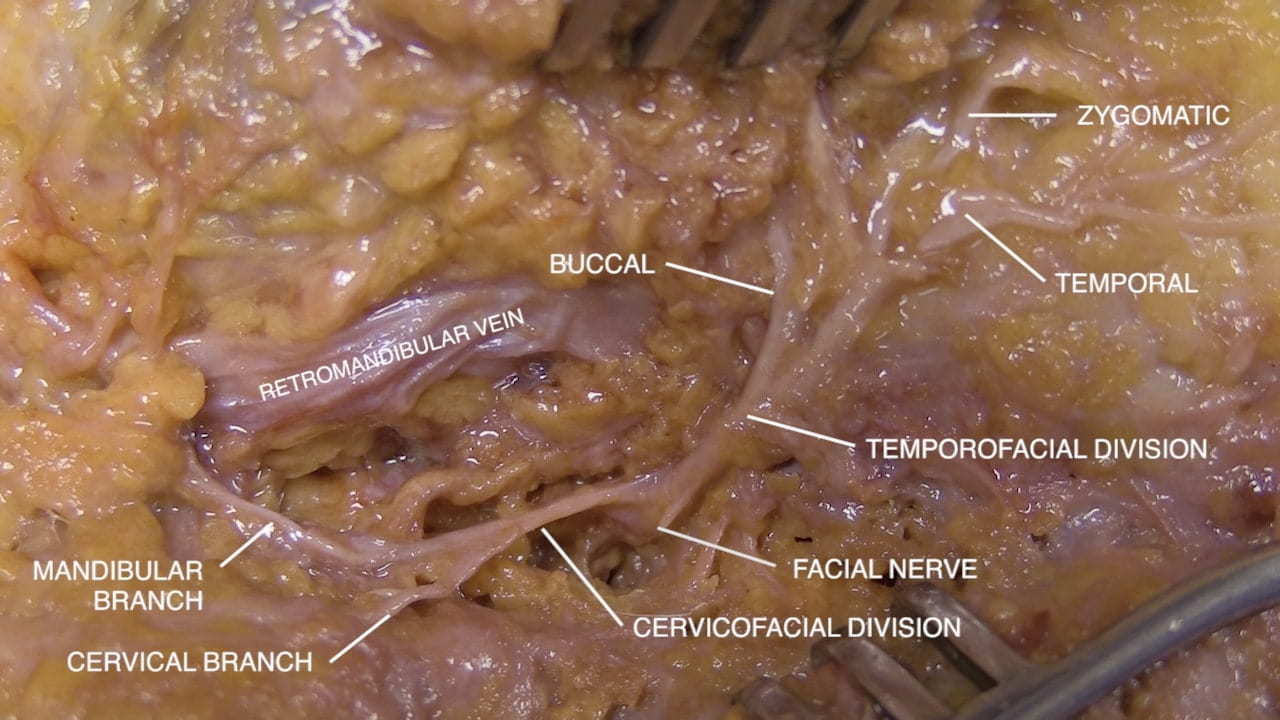
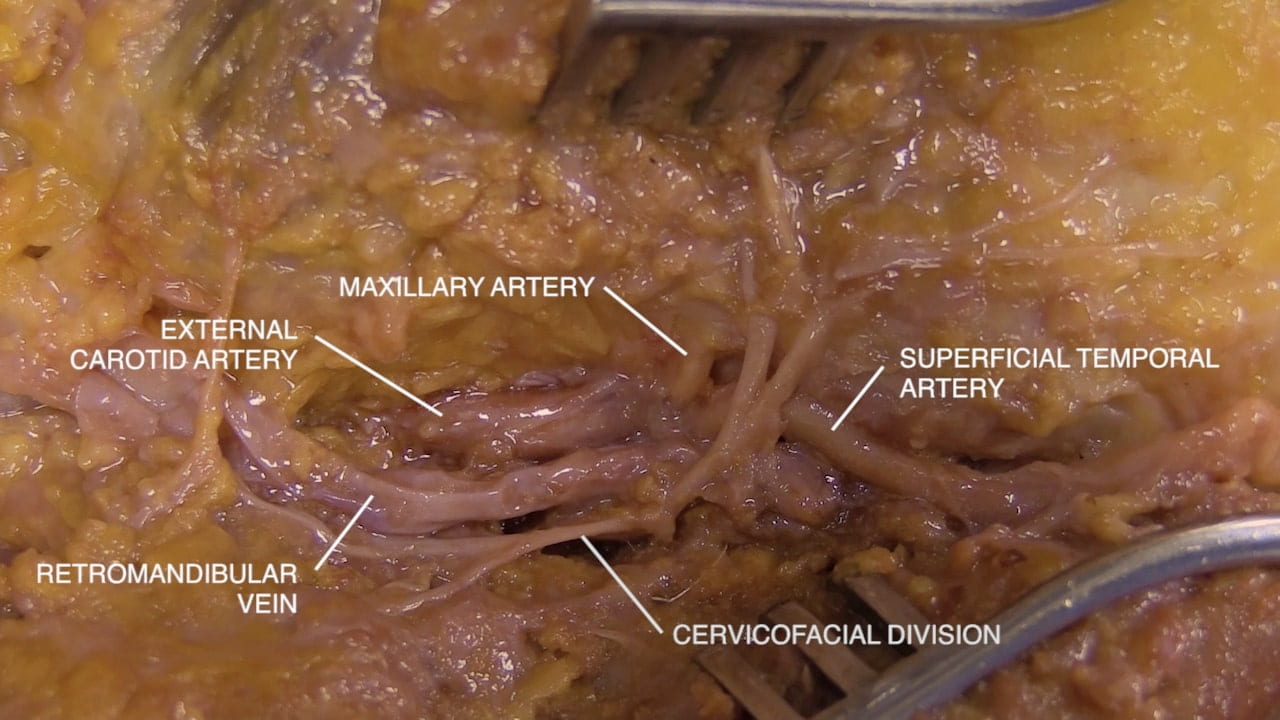
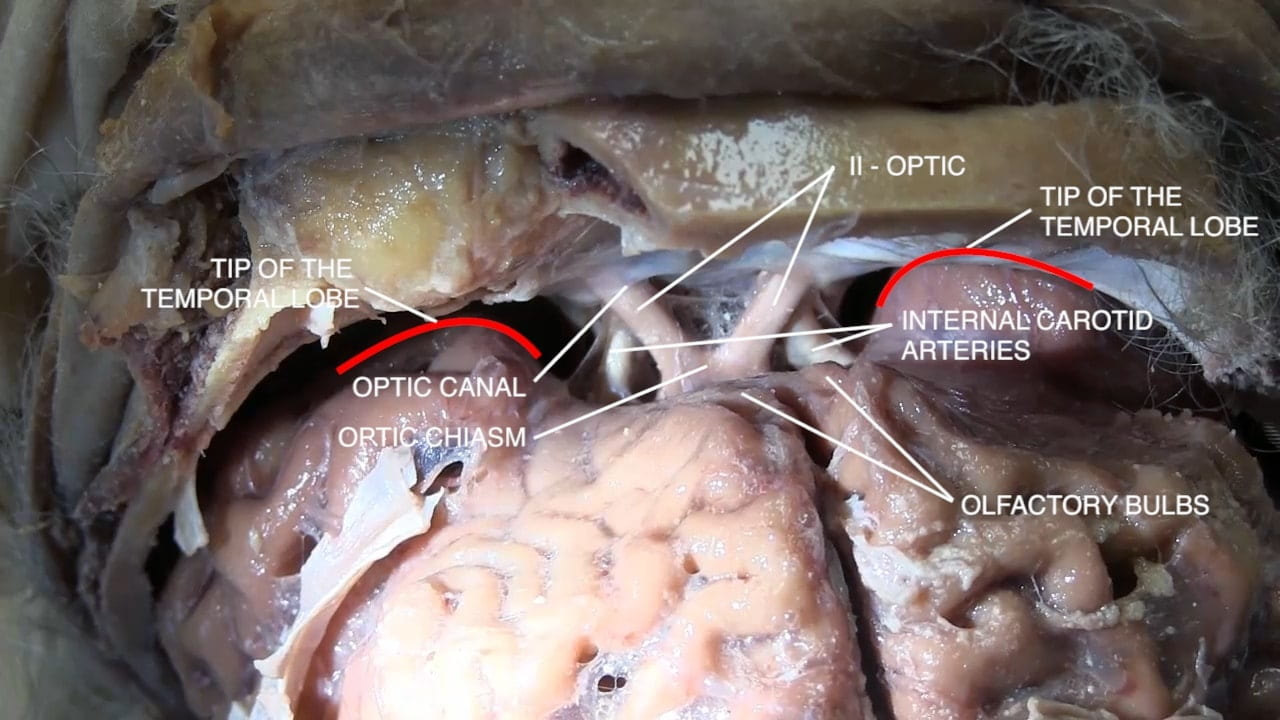
- Describe the location of the parotid gland, duct and branches of the facial nerve (VII). 5) Describe the relationship of the internal carotid artery and the optic nerve.
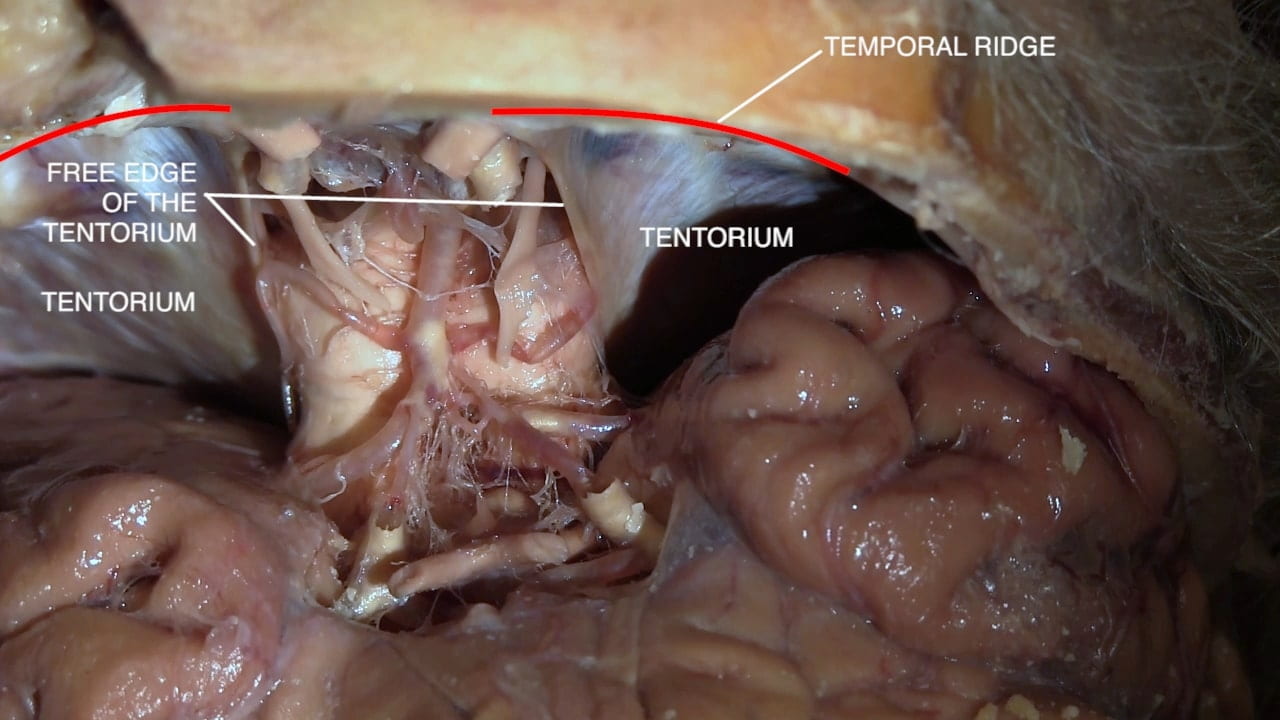
- Be able to describe the position of the major dural folds.
- Describe the positions of the cranial nerves at the base of the brain.
Lecture List
Skull, Disarticulated Skull, Fetal Skull, Parotid Gland and Facial Nerve, Brain Removal
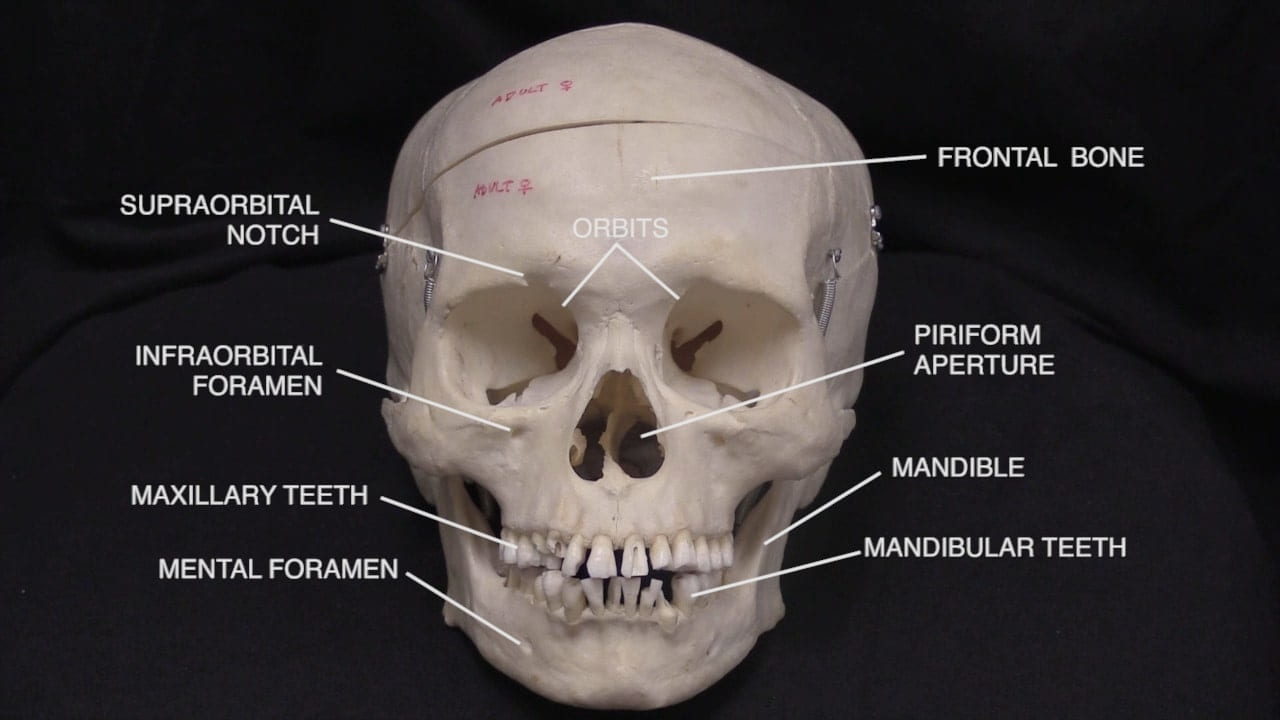
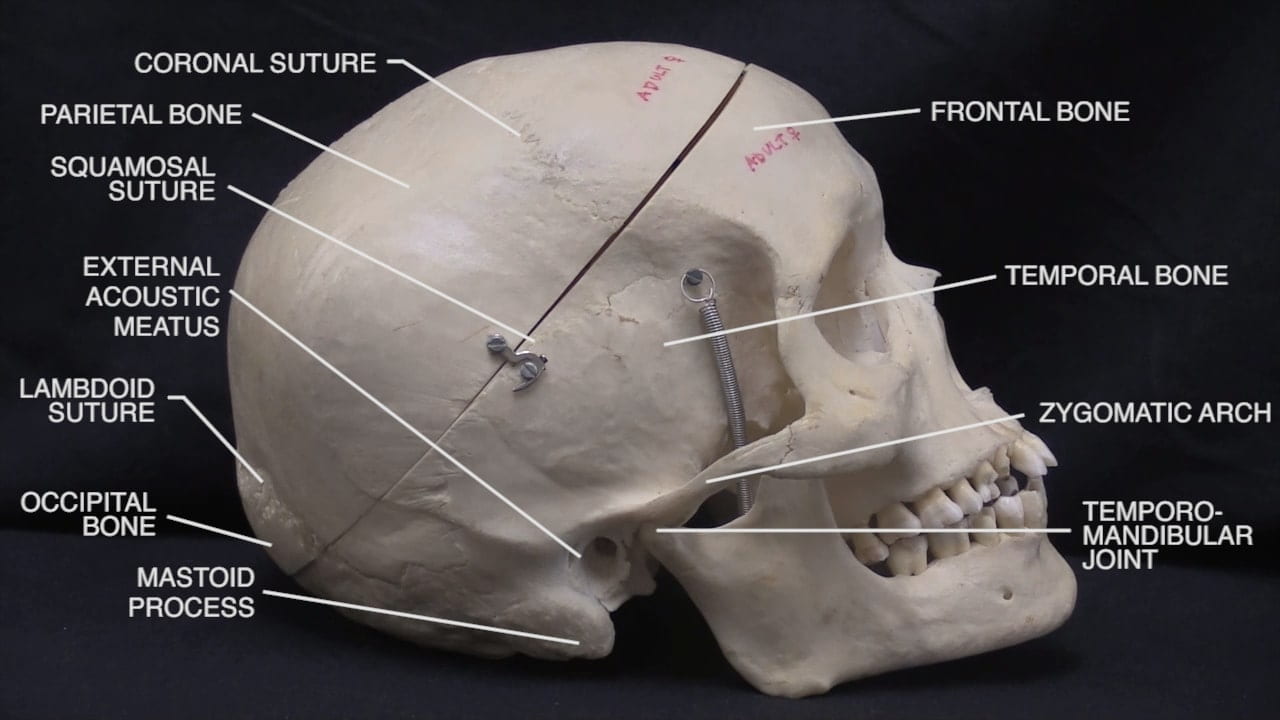
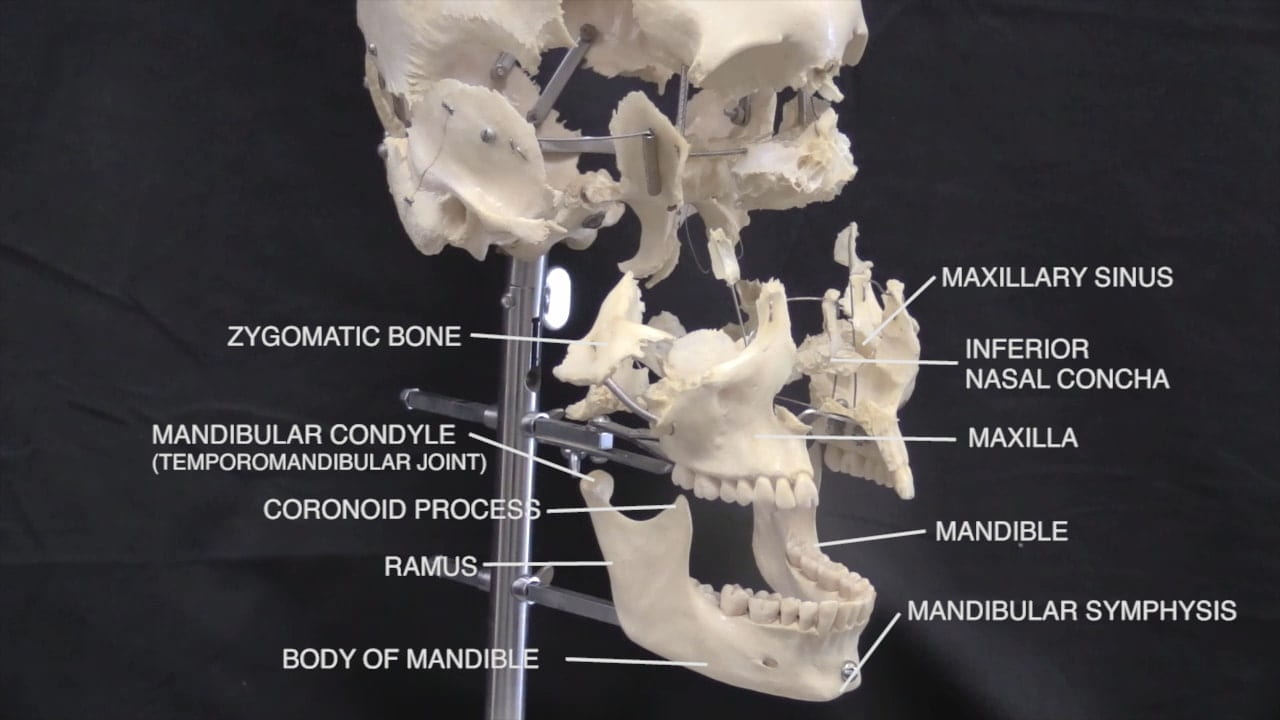
Examination of the Skull
Skull Gallery
Disarticulated Skull
Expanded Skull Gallery
Fetal Skull
Fetal Skull Gallery
Parotid Gland and Facial Nerve
Facial Nerve and Parotid
Facial Nerve
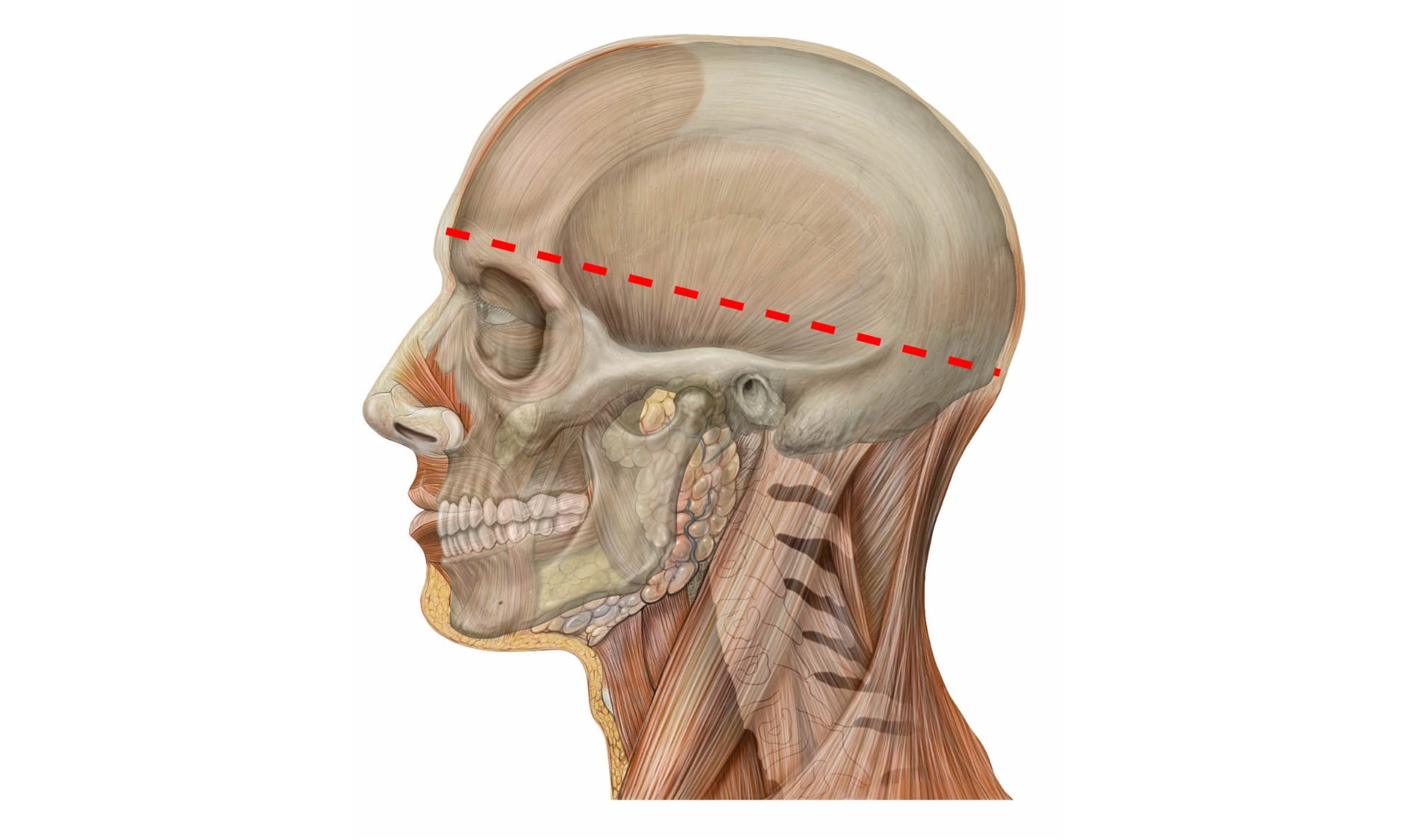
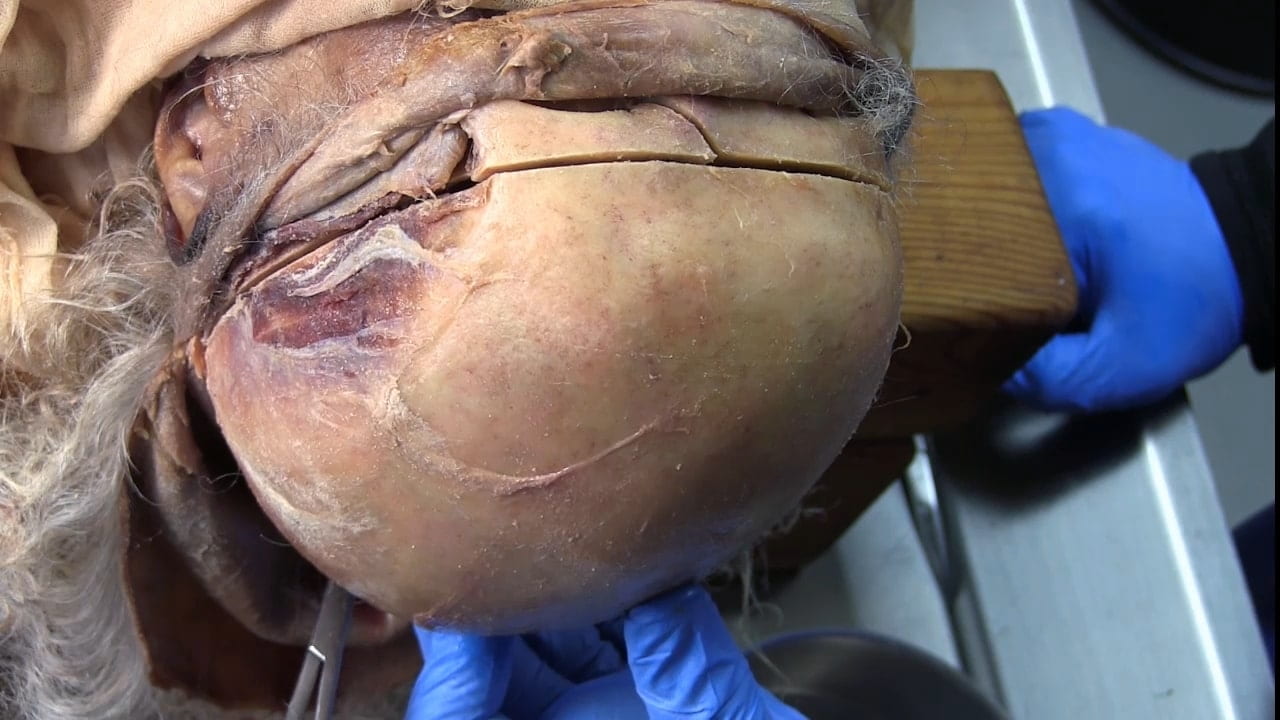
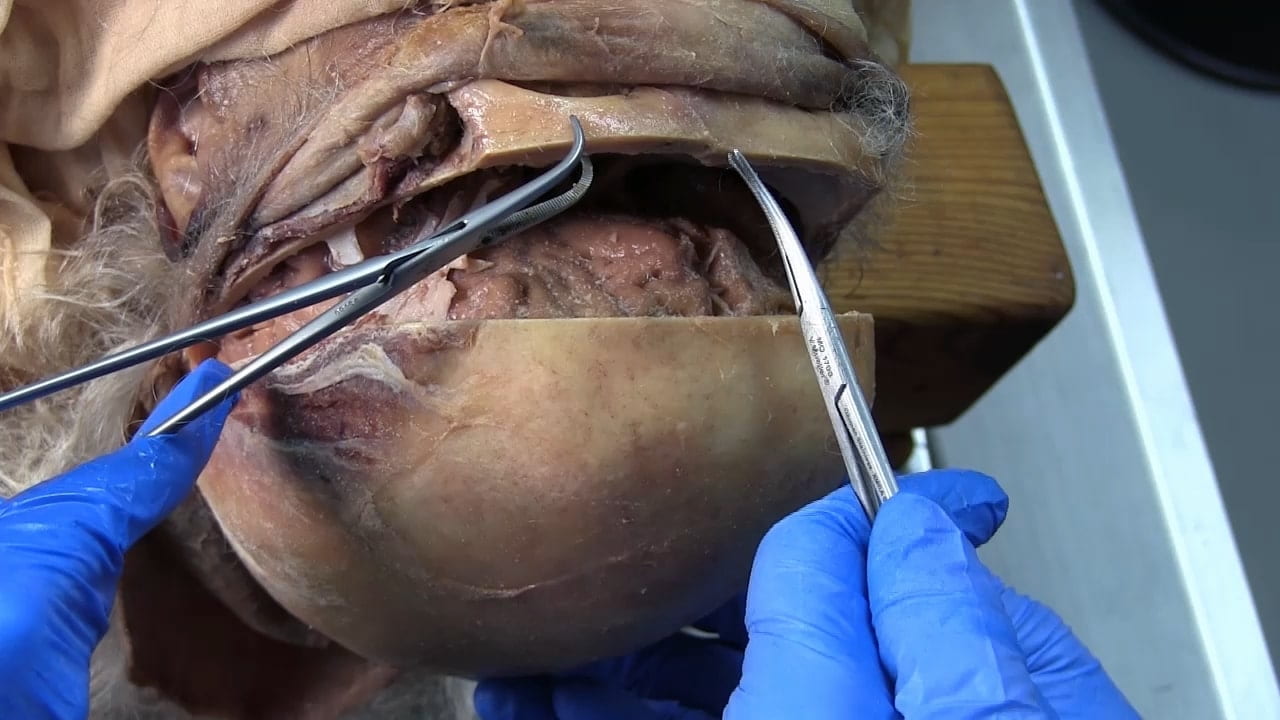
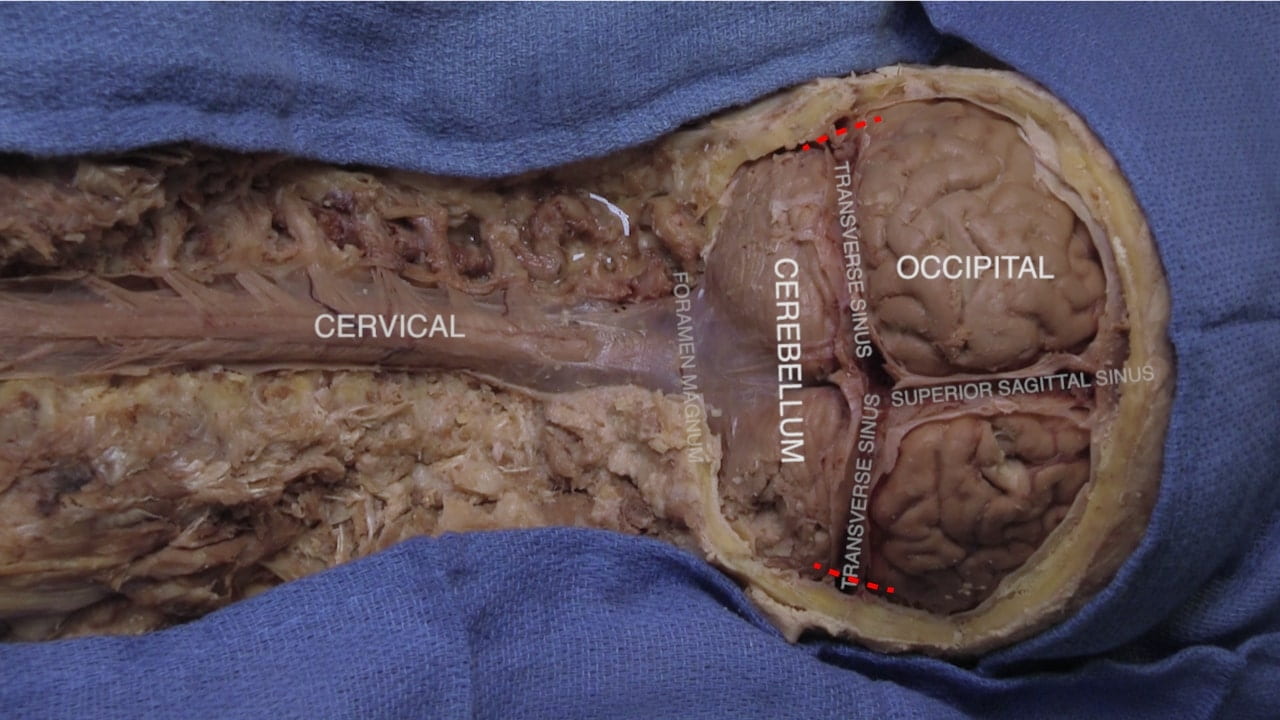
Remove Brain
Calvarial Vault Removal
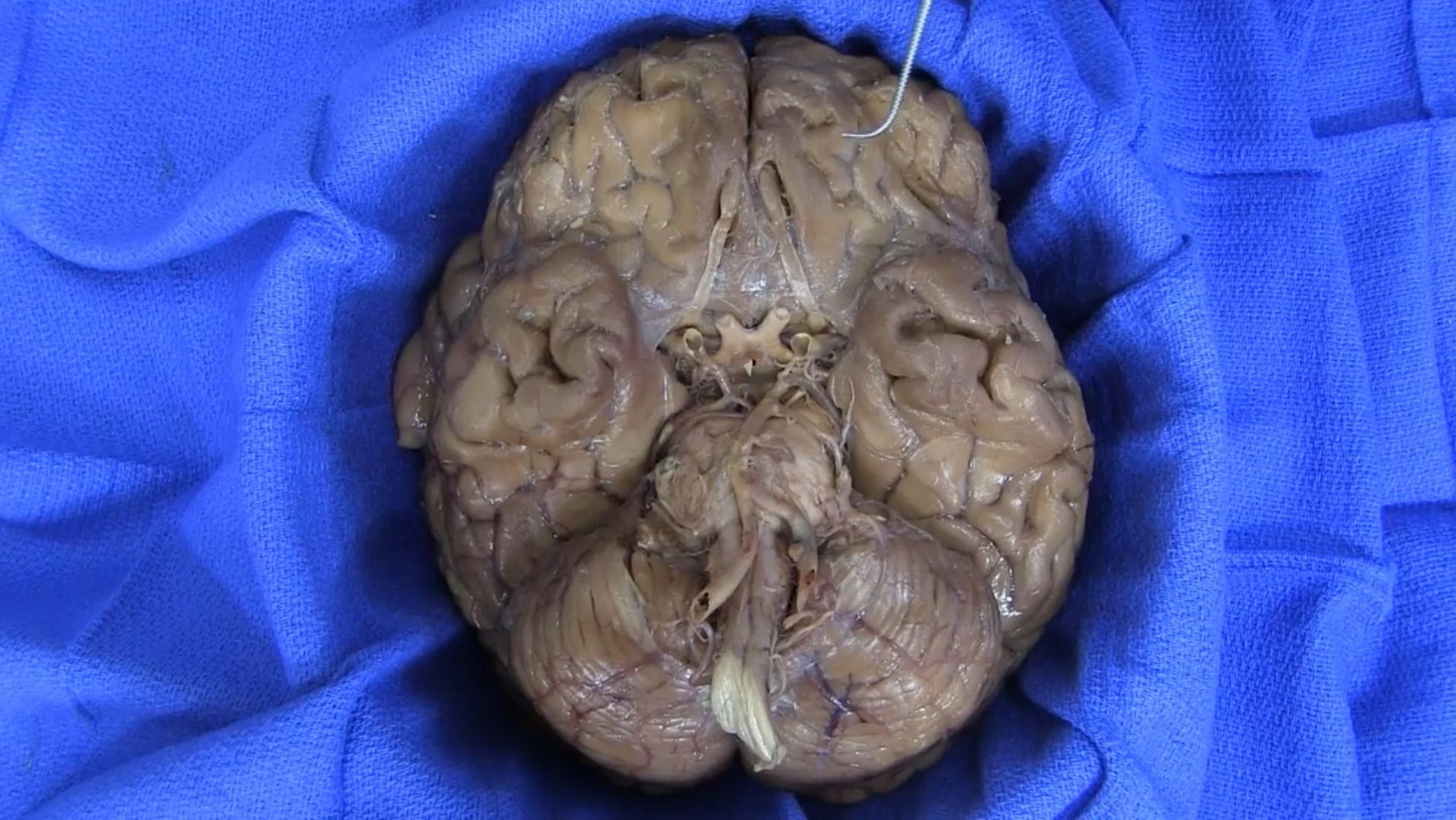
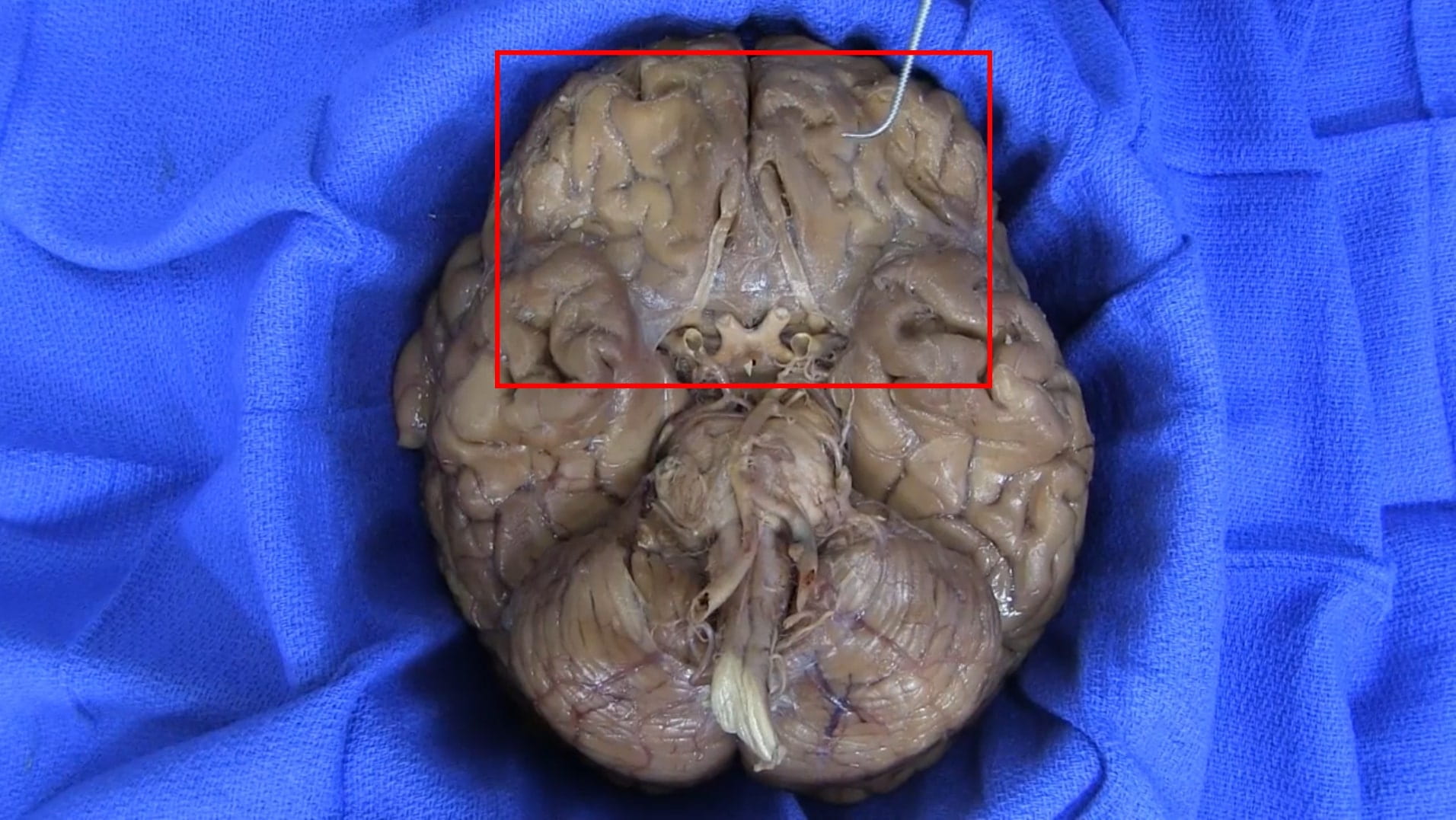
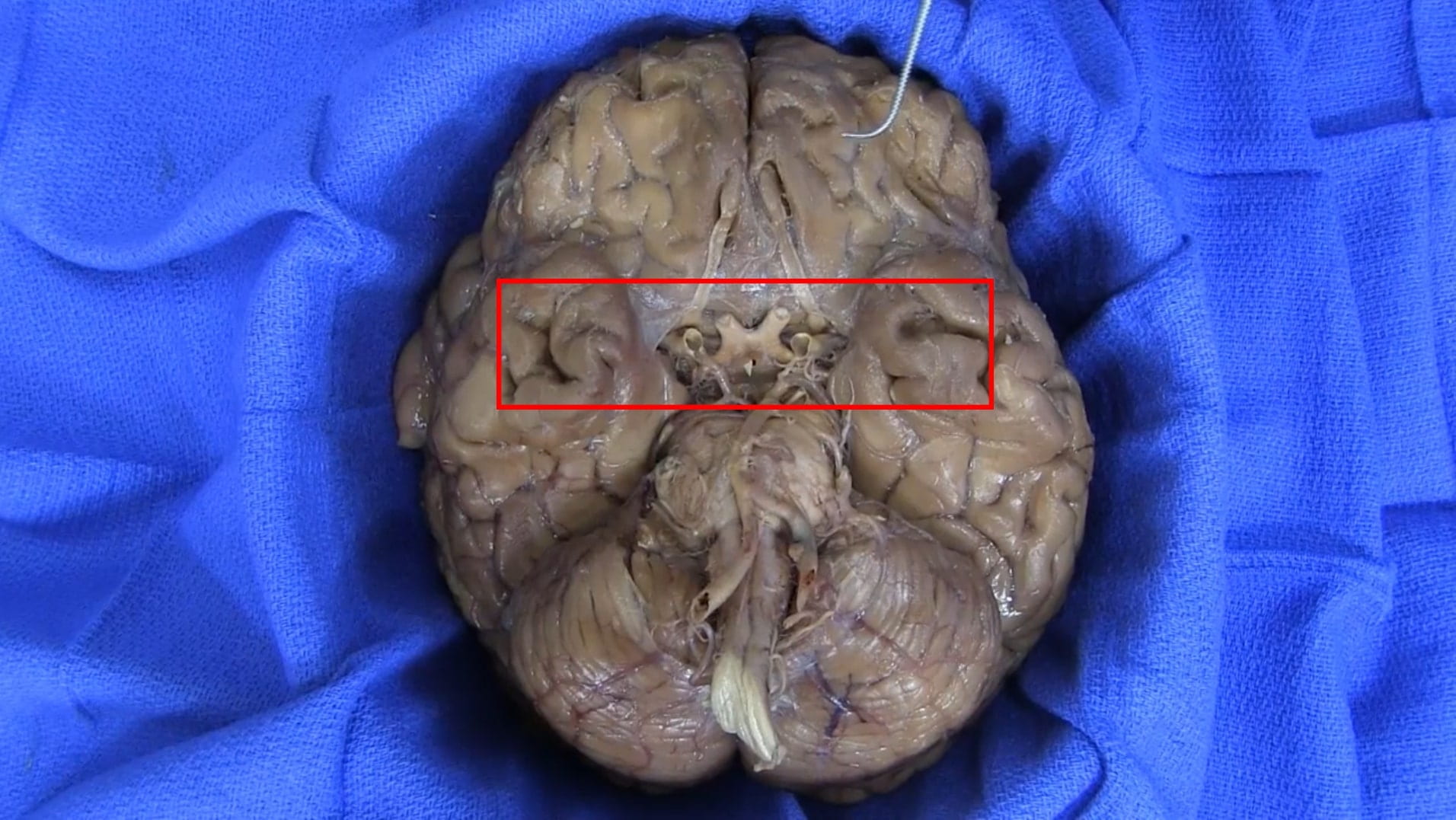
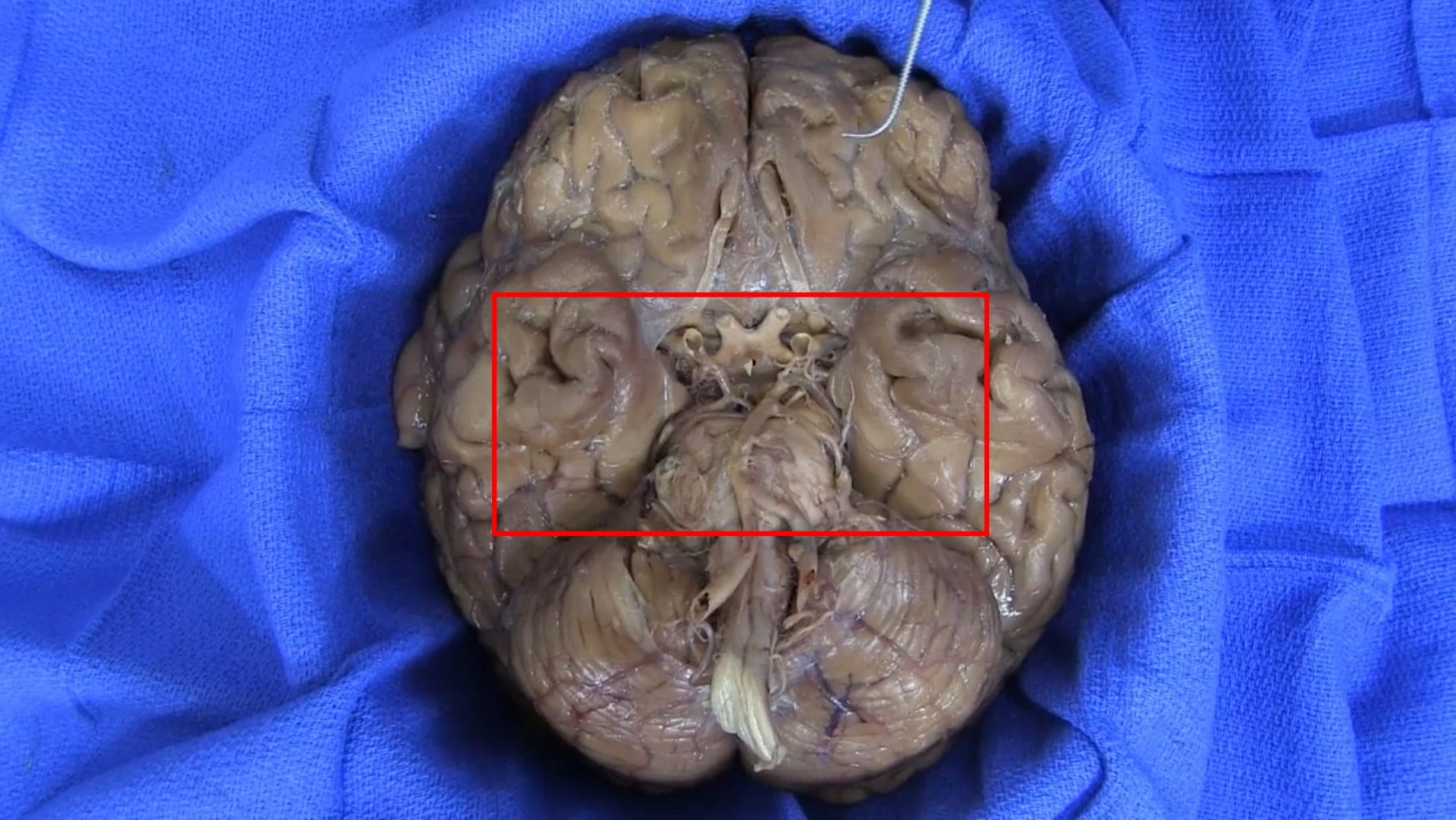
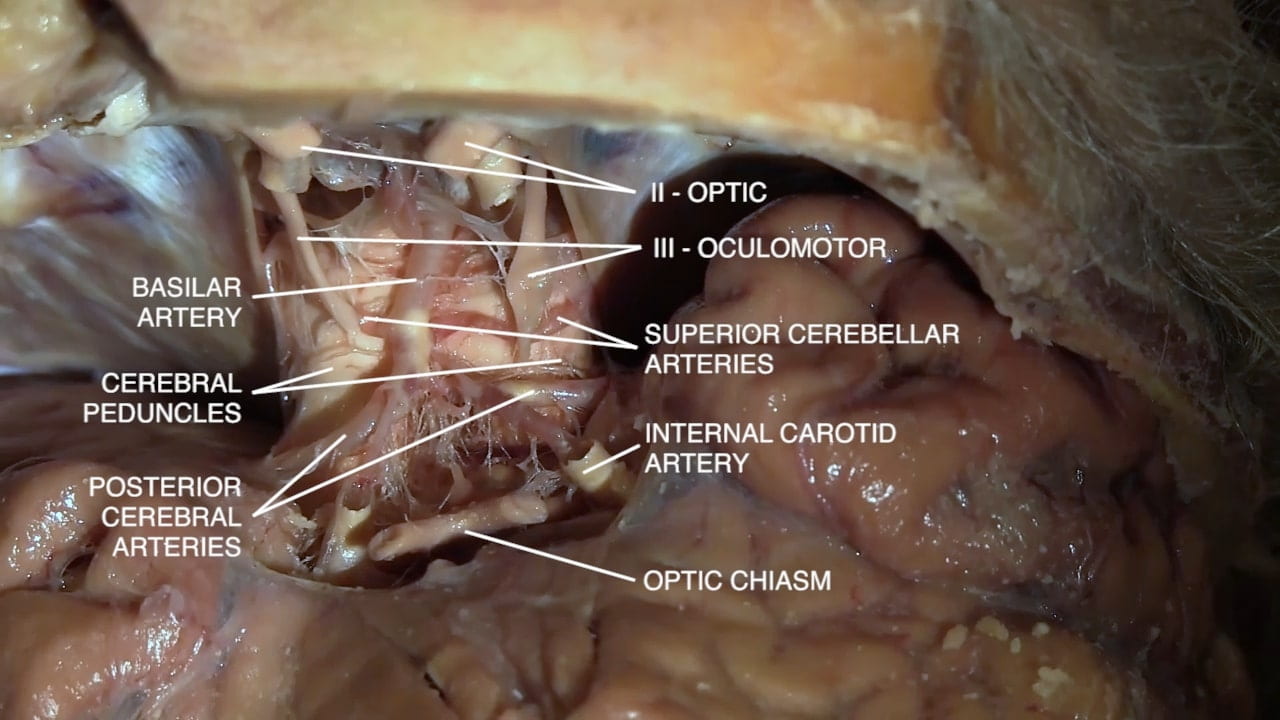
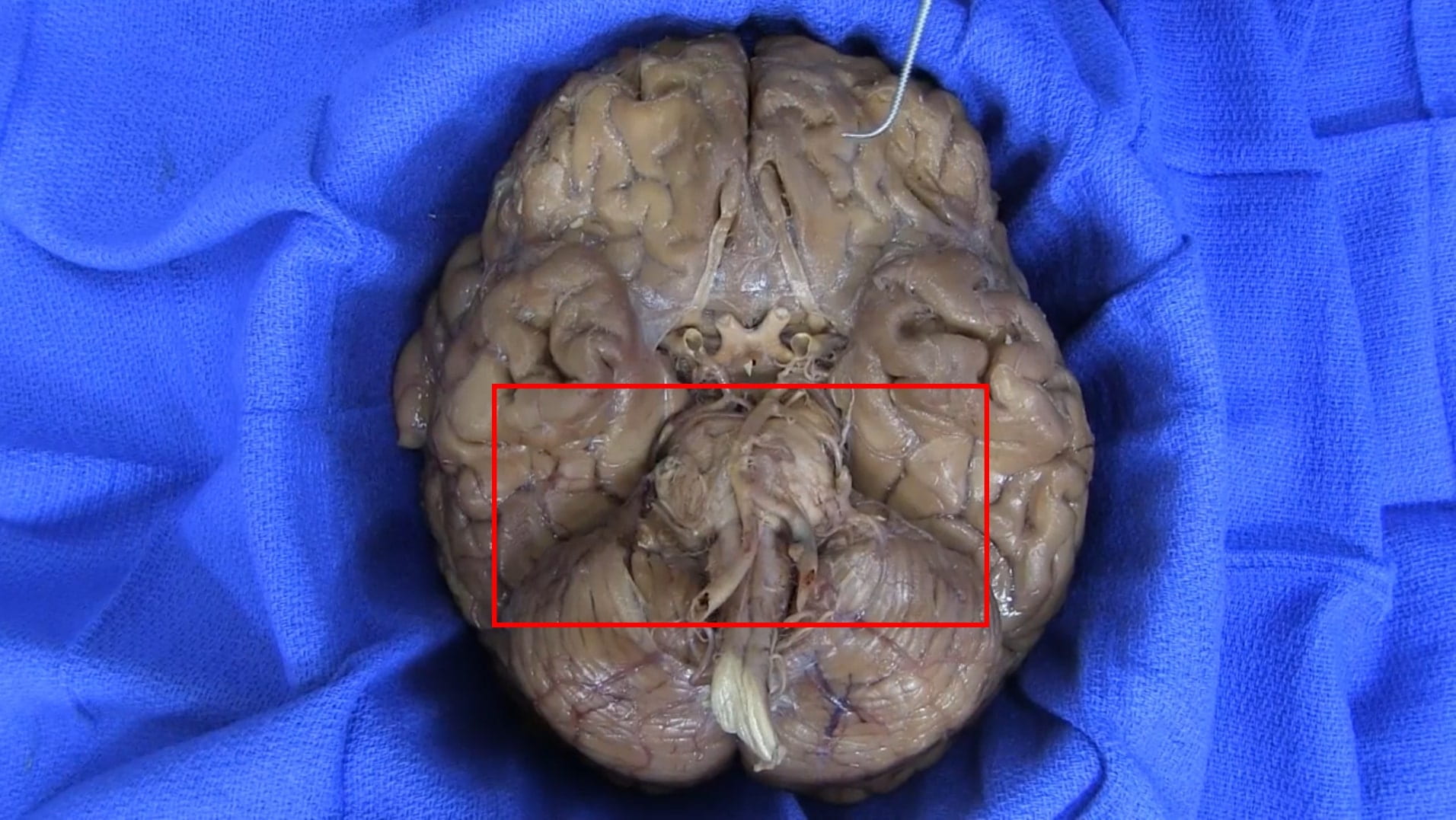
Base of Brain
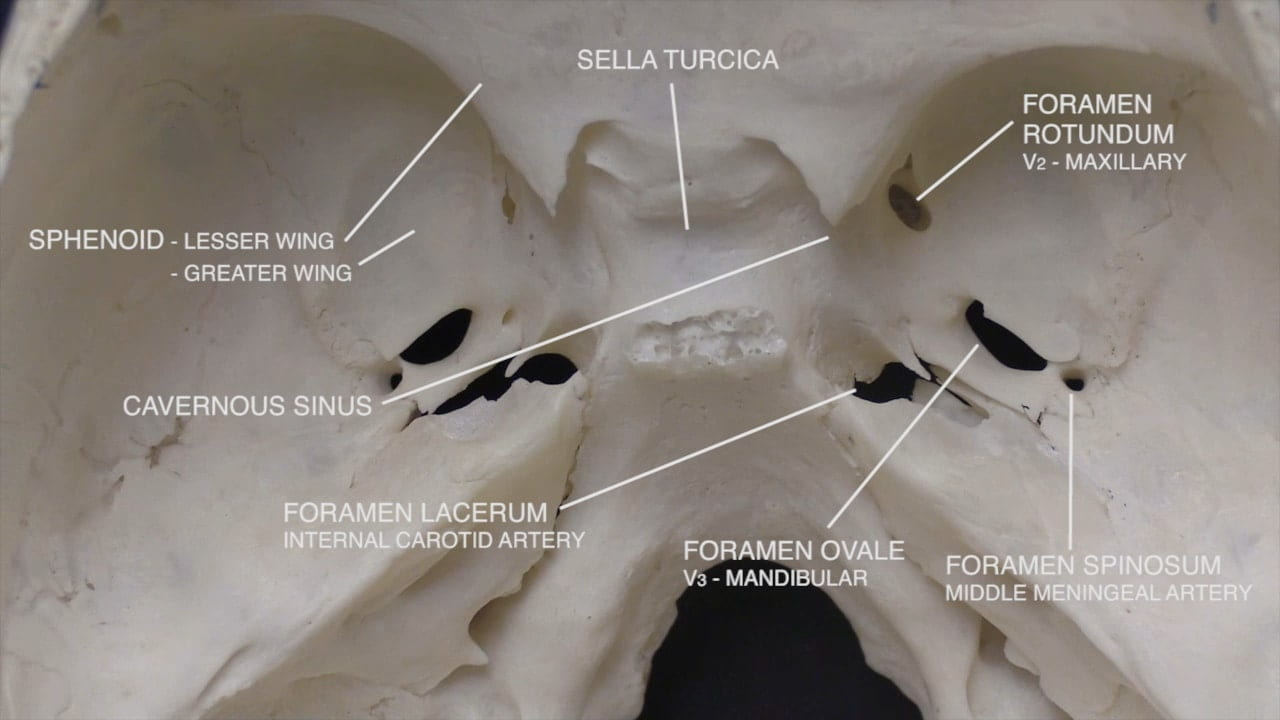
Parasellar Region
Tentorium
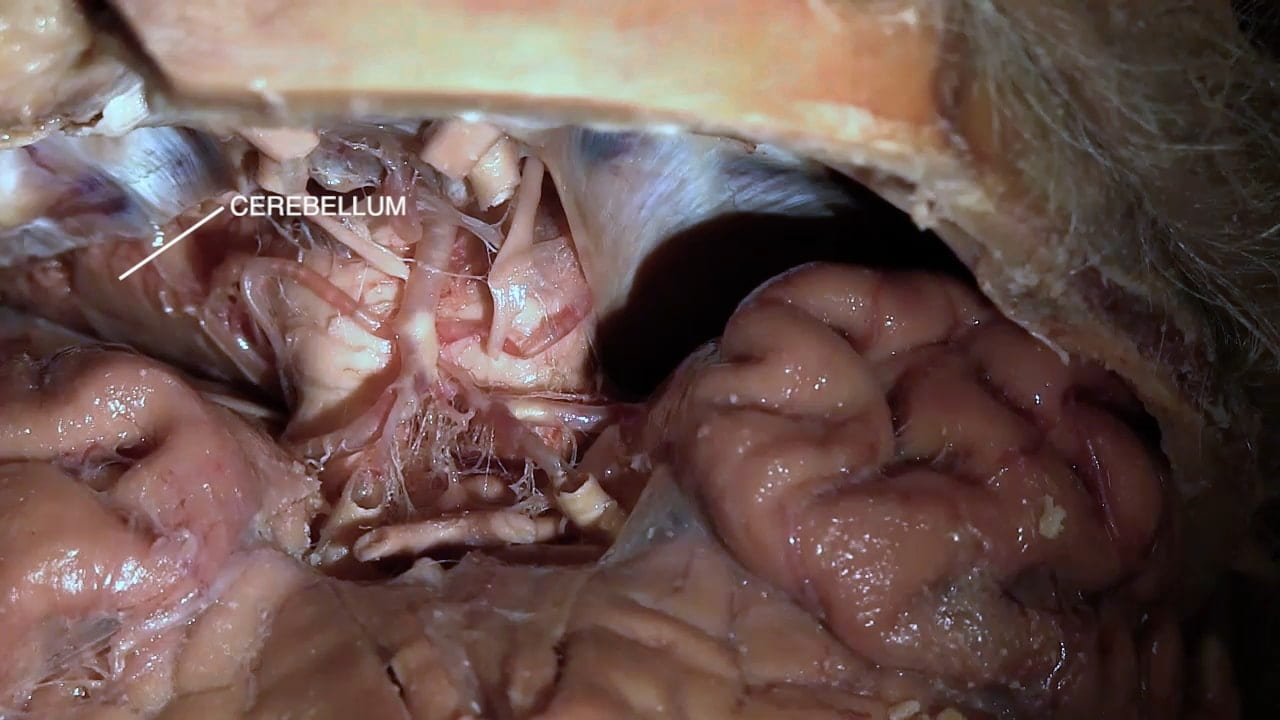
Pons and Medulla
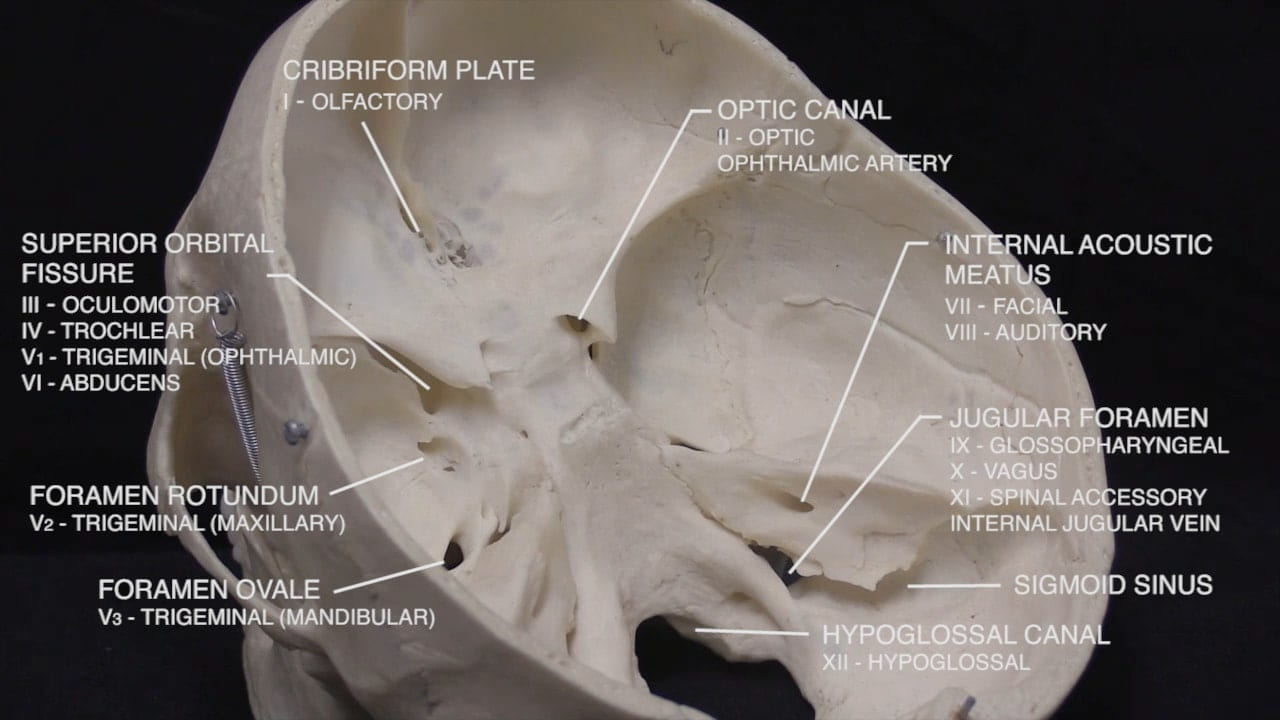
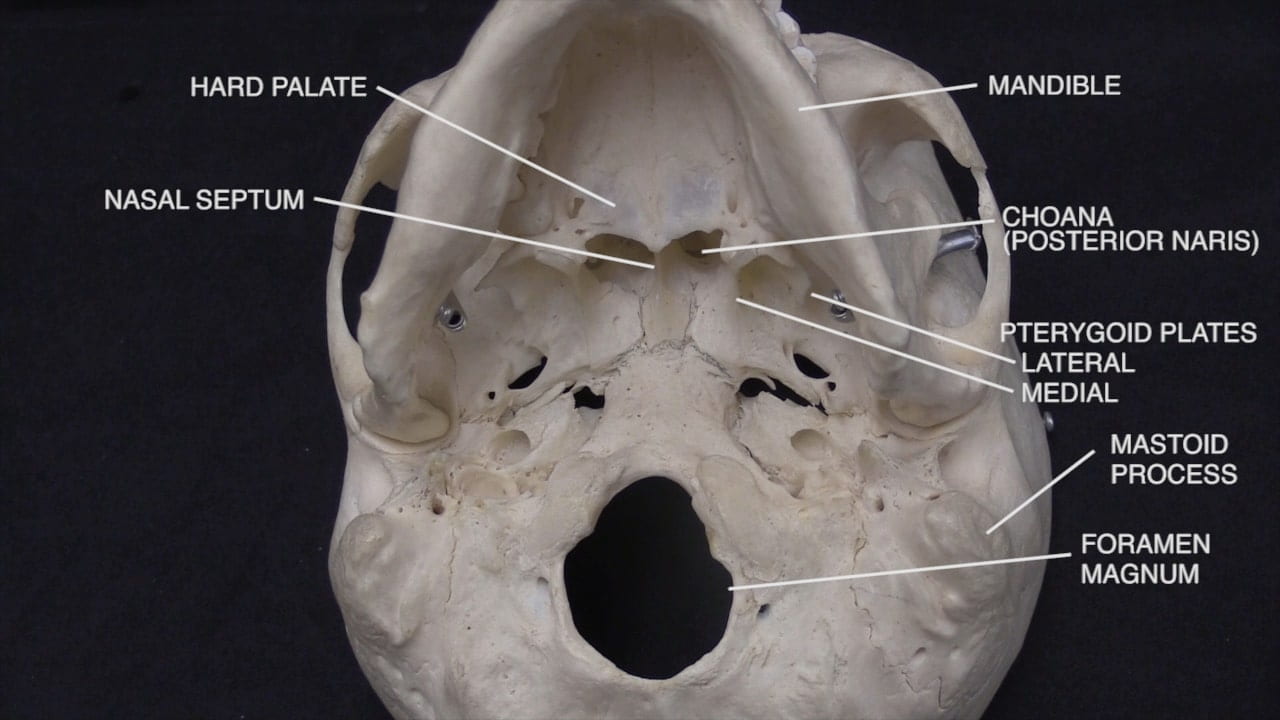
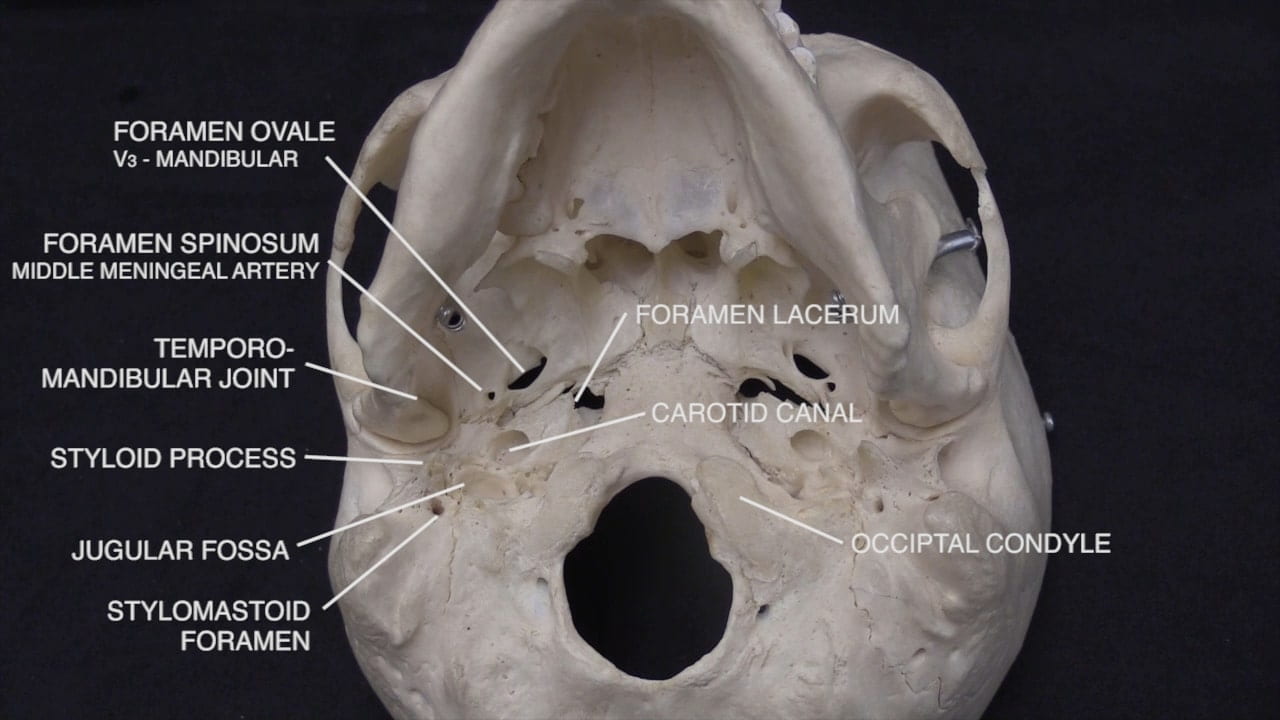
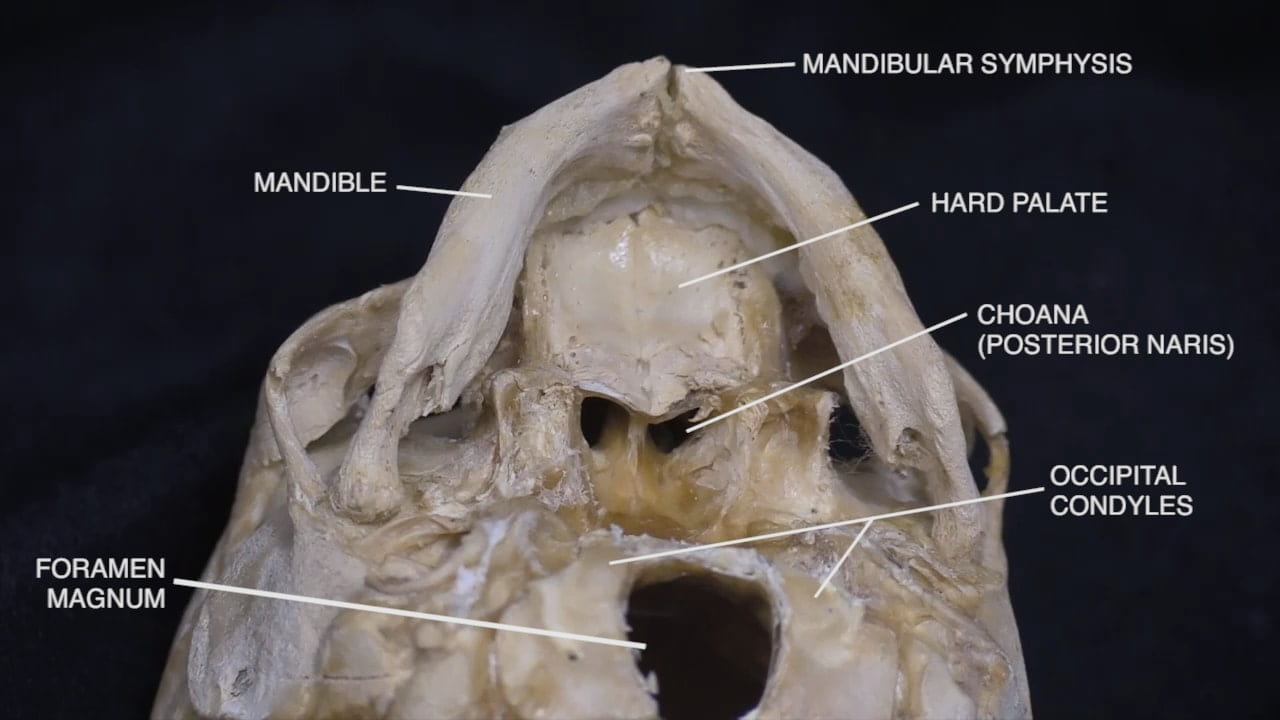
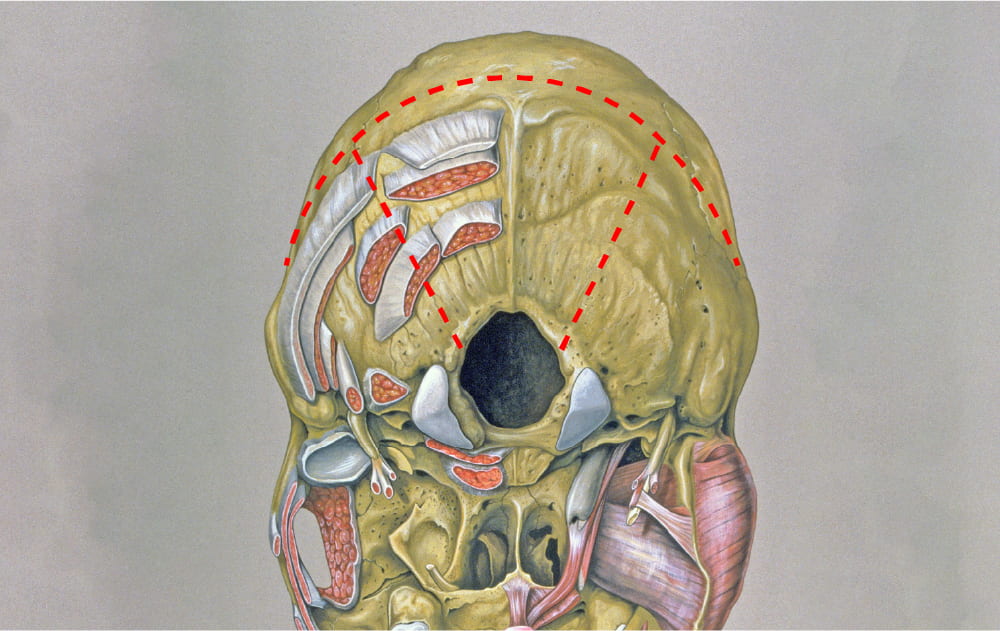
Interior Skull Base
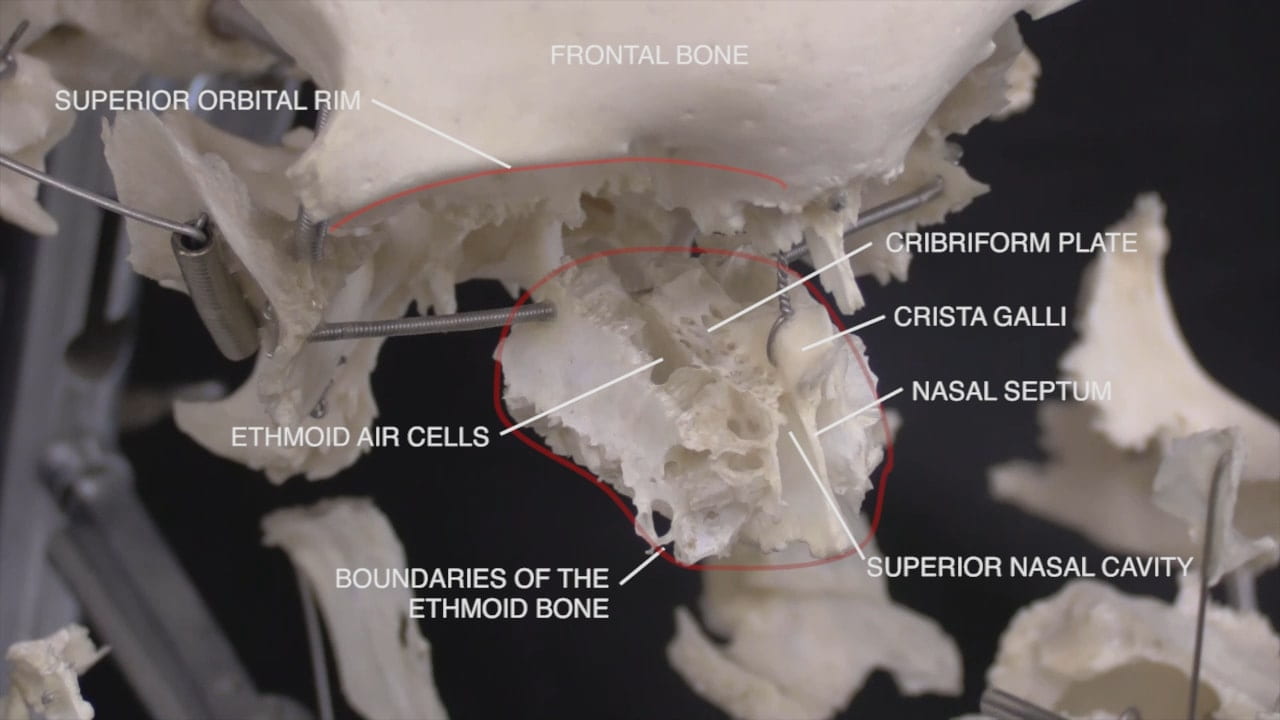
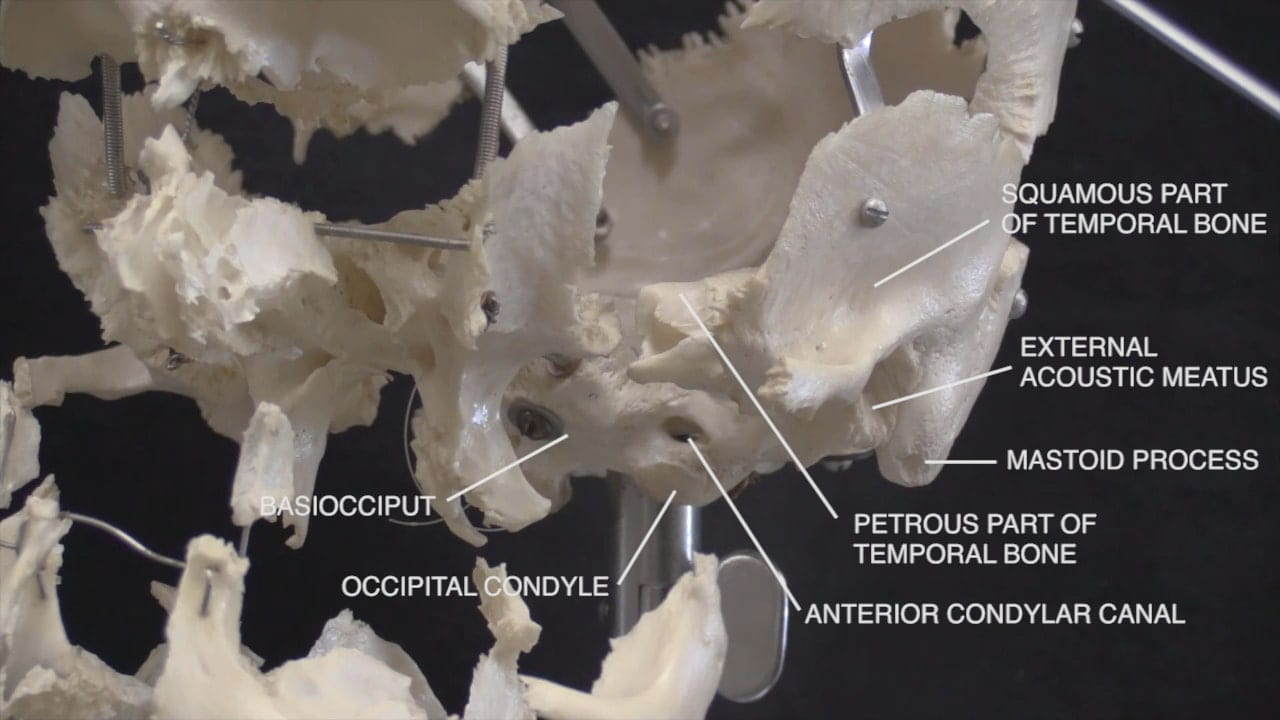
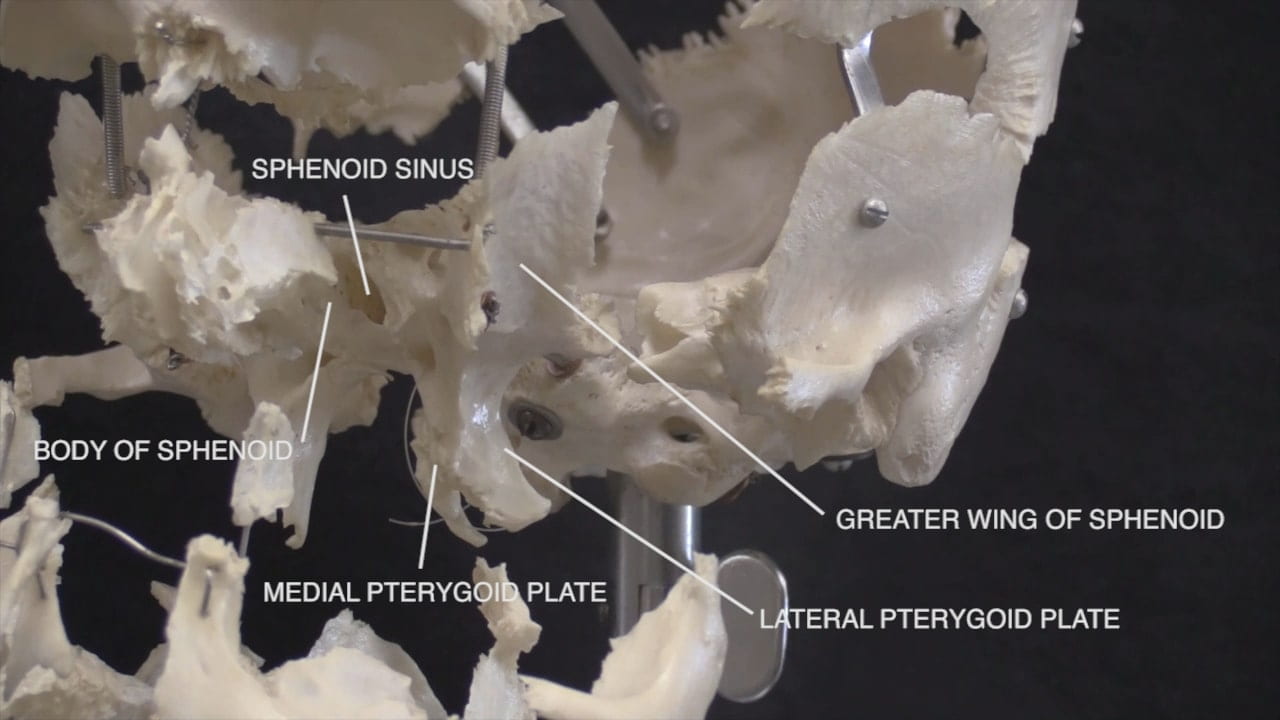
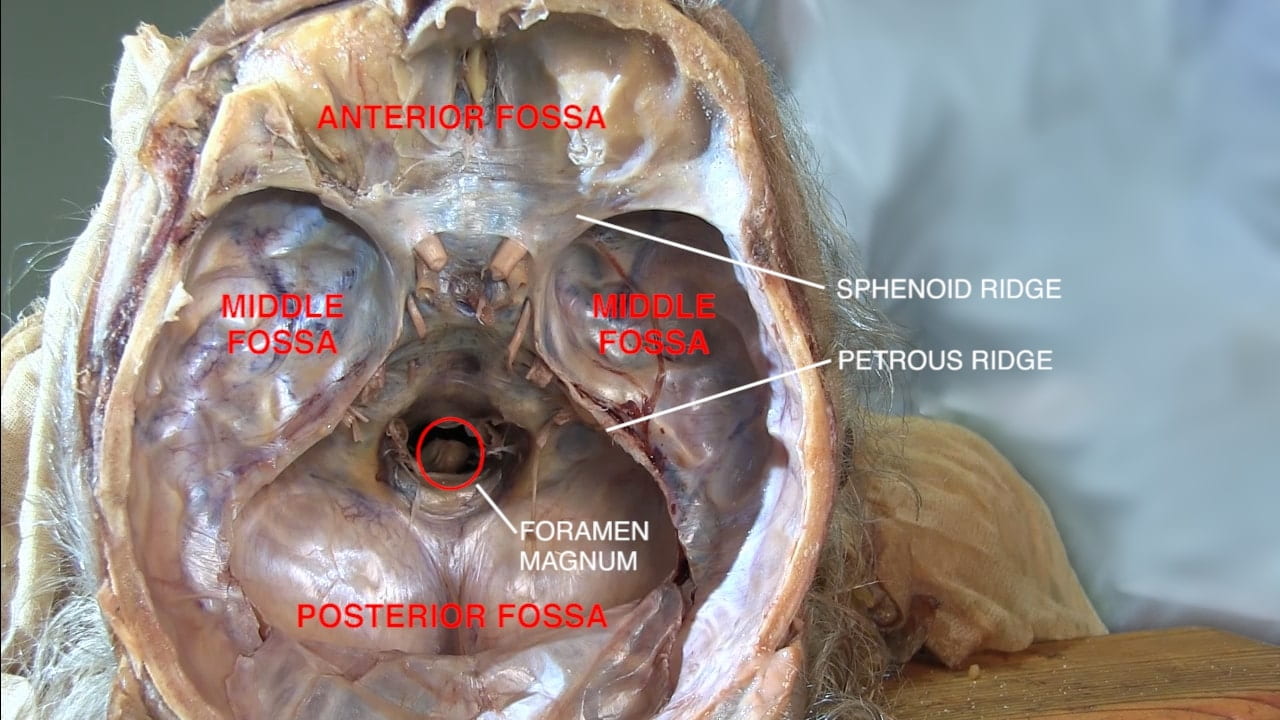
On the interior of the base of the skull, locate the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae.
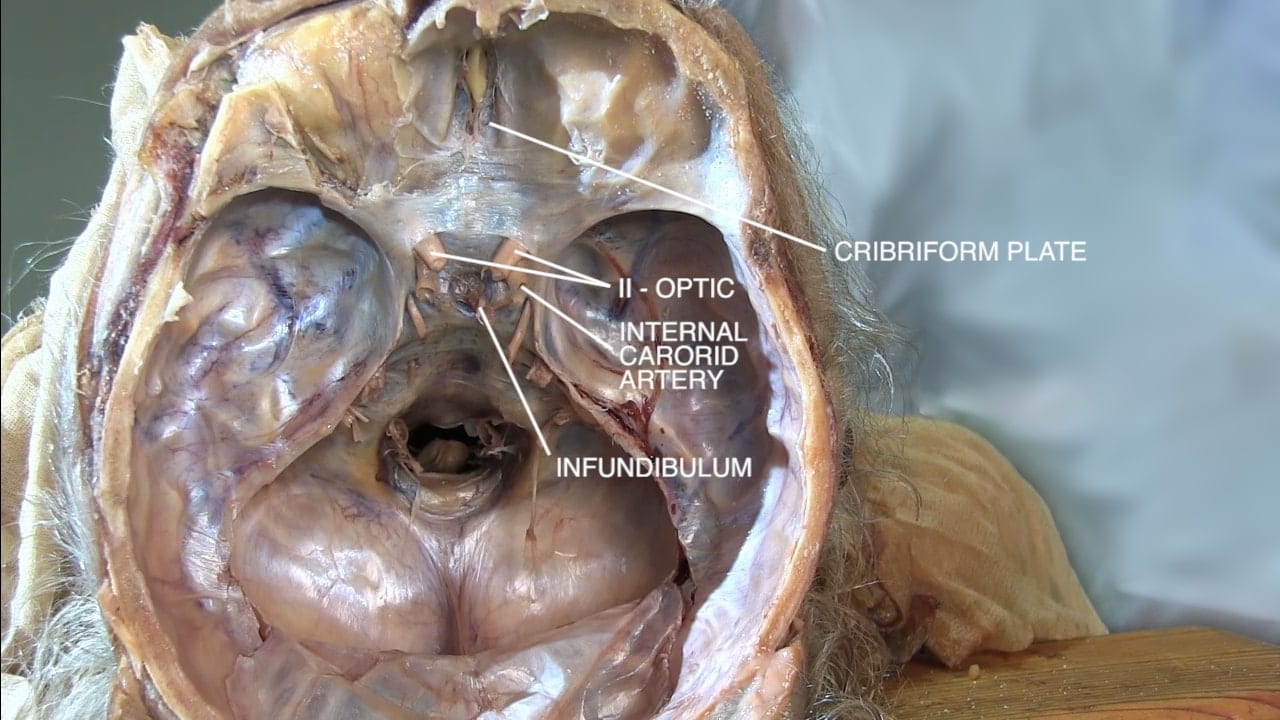
Locate the:
- Cribriform plate
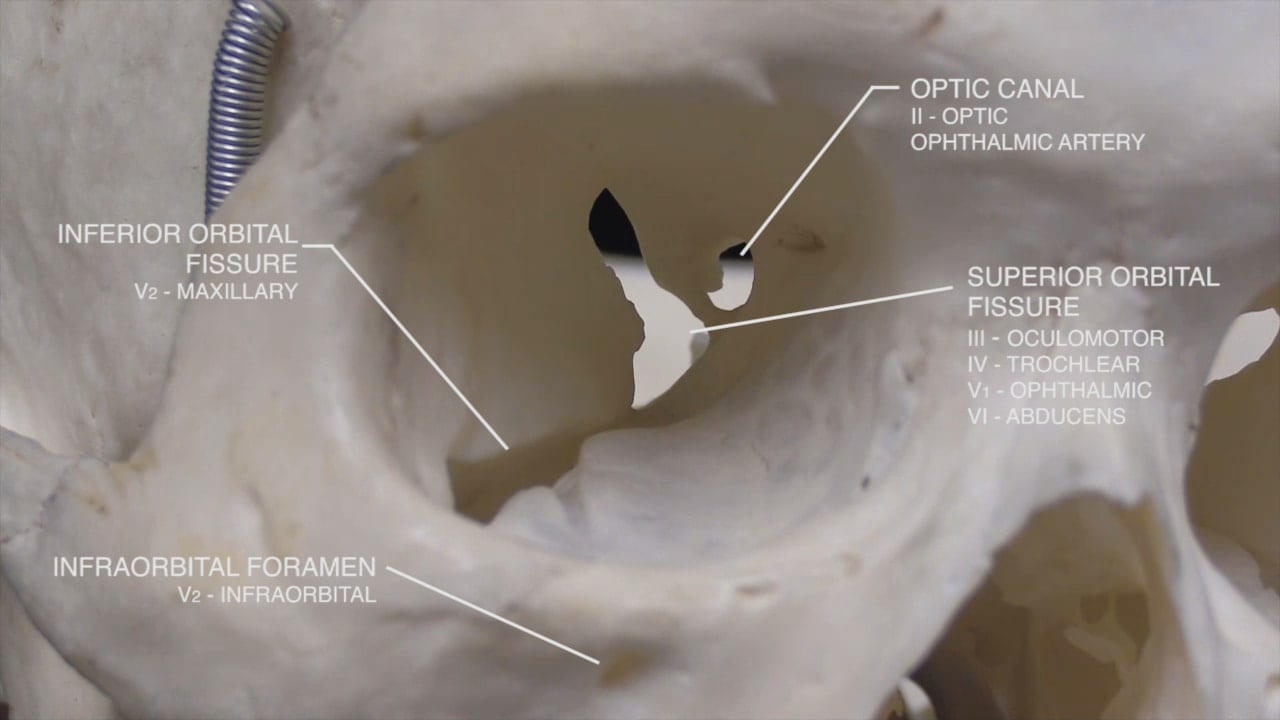
- Optic nerve (II)
- Internal carotid artery
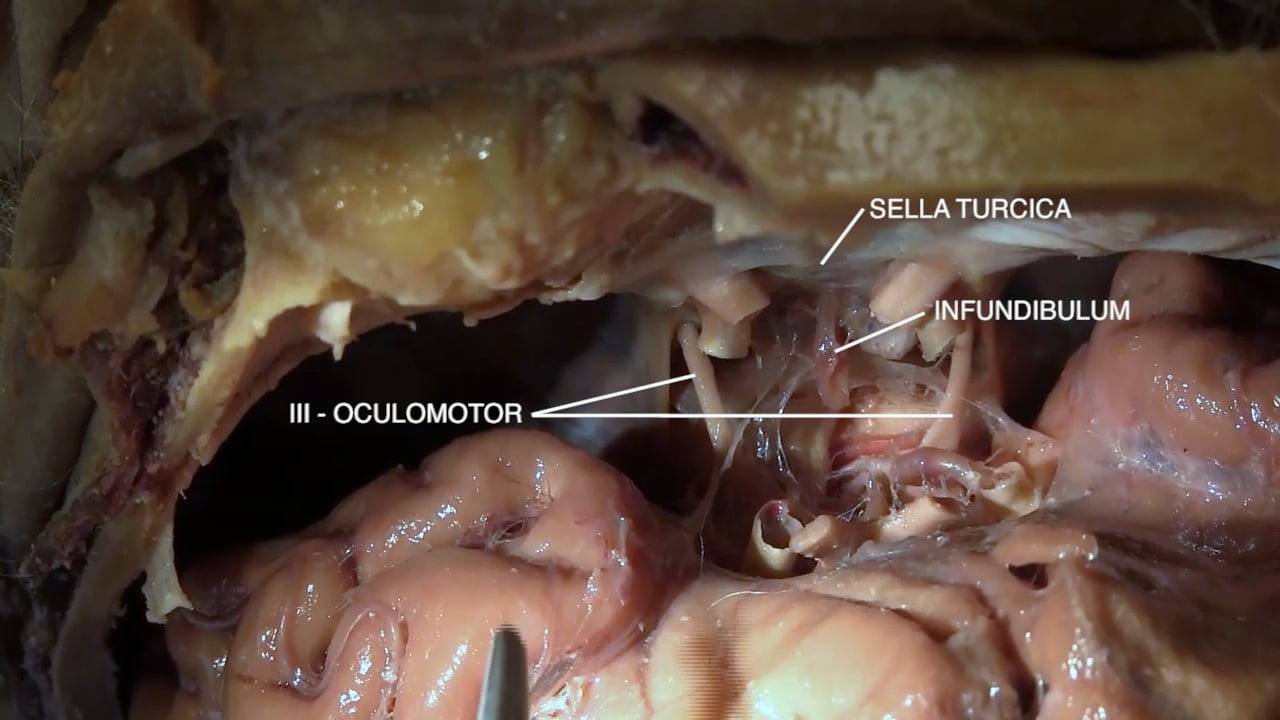
- Infundibulum
- Sella turcica
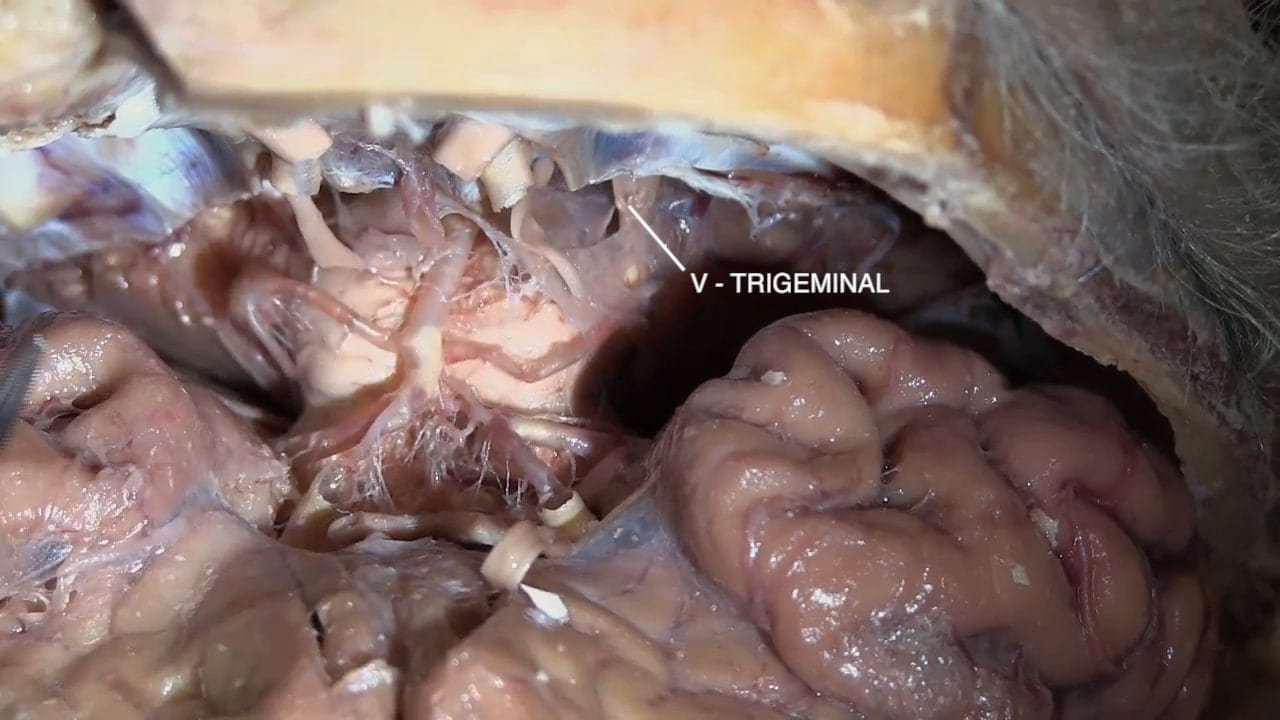
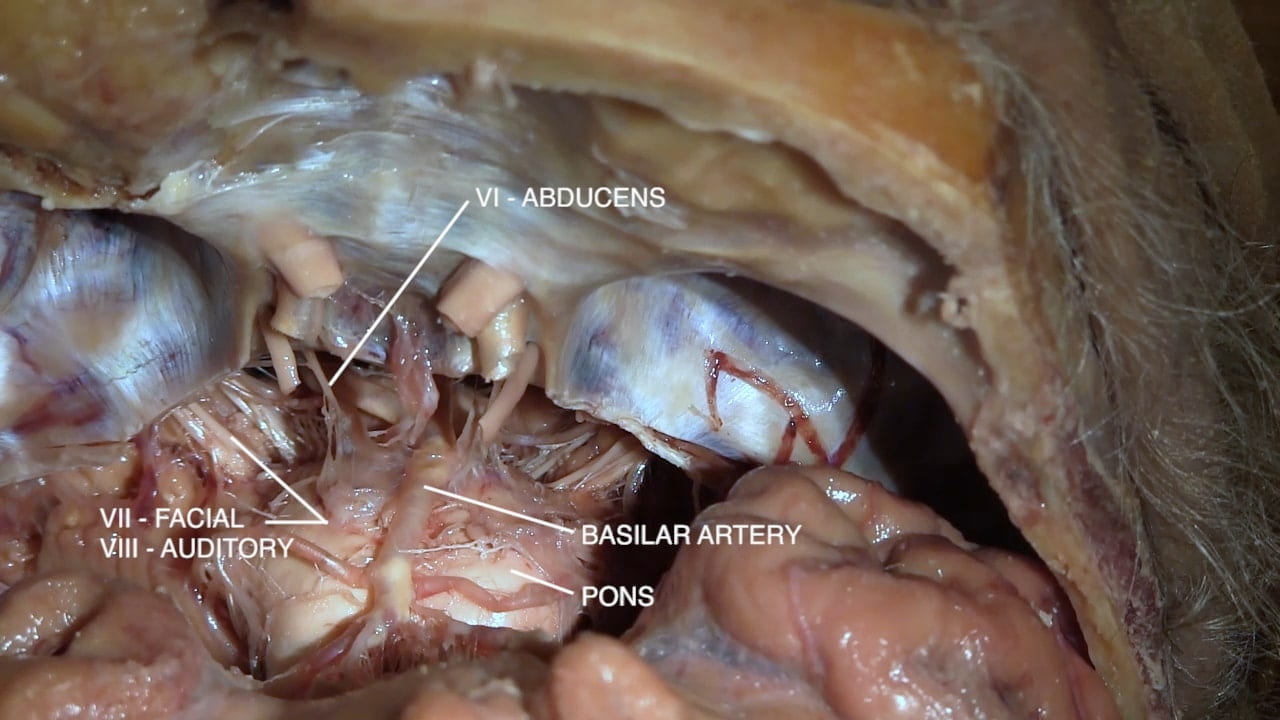
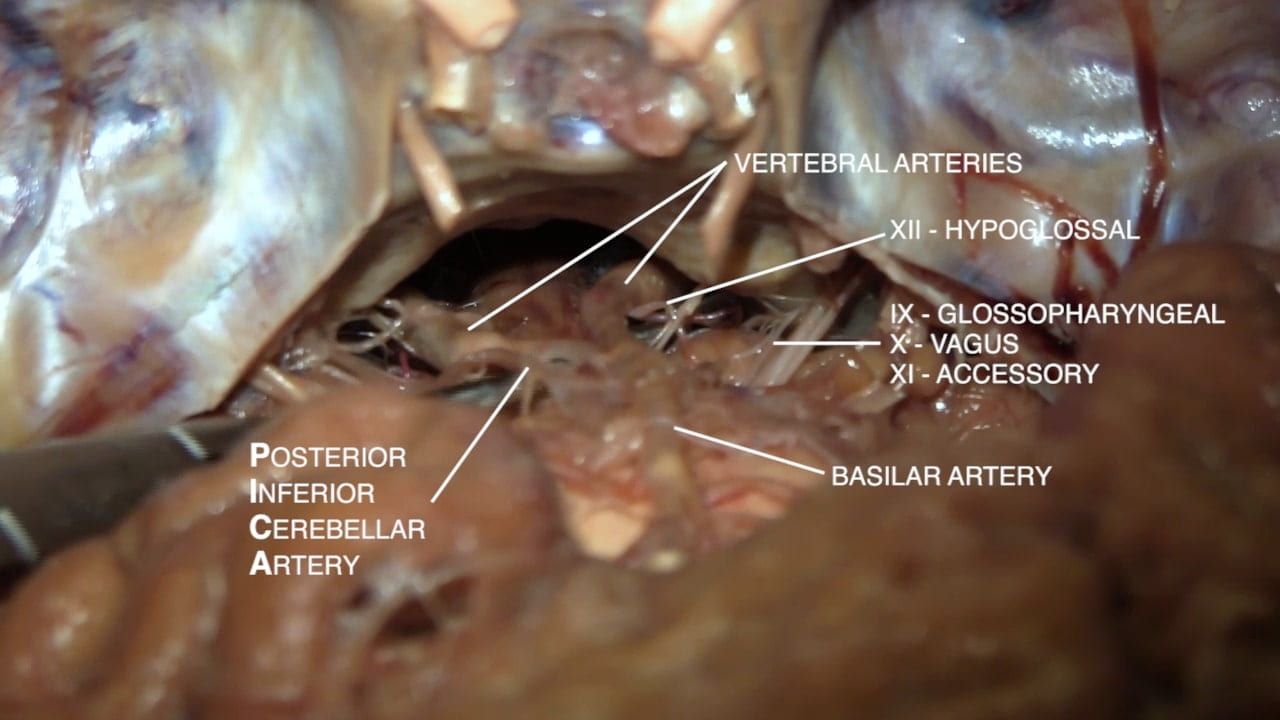
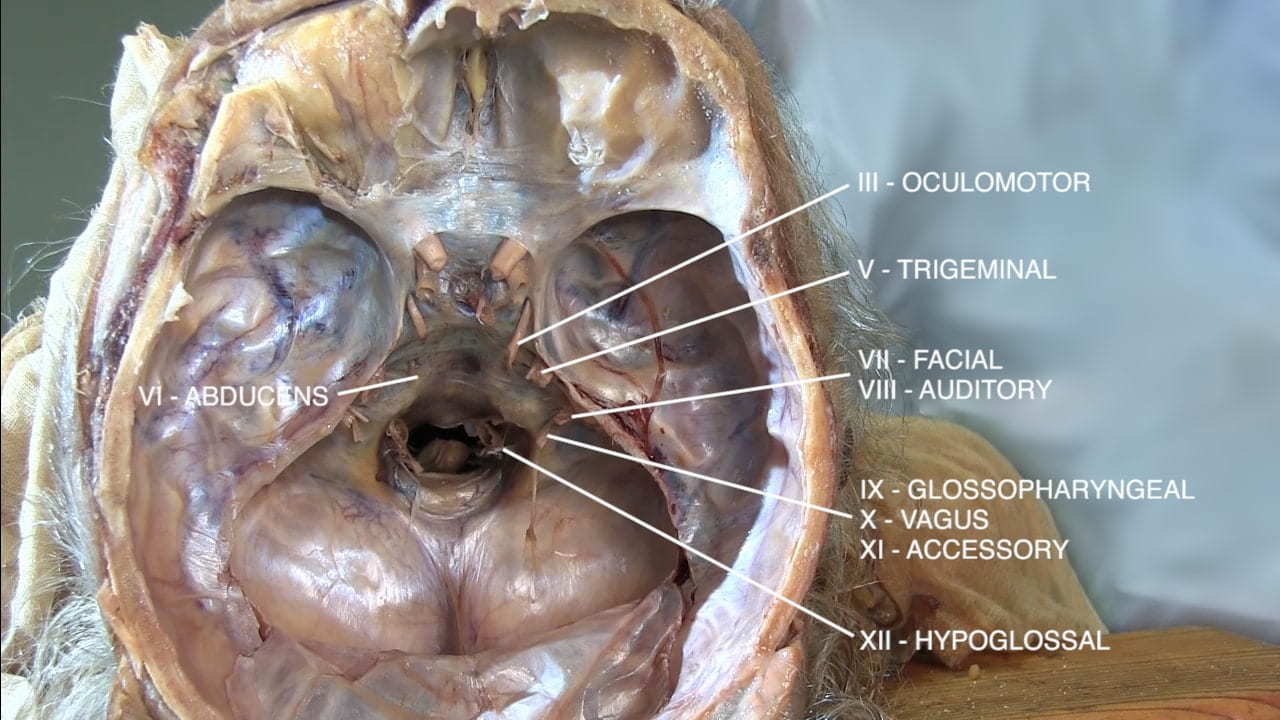
Continuing posteriorly identify the:
- Oculomotor (III)
- Trigeminal (V)
- Abducens (VI)
- Facial (VII)
- Auditory (VIII)
- Glossopharyngeal (IX)
- Vagus (X)
- Accessory (XI)
- Hypoglossal (XII)