Mediastinum
Lab Summary
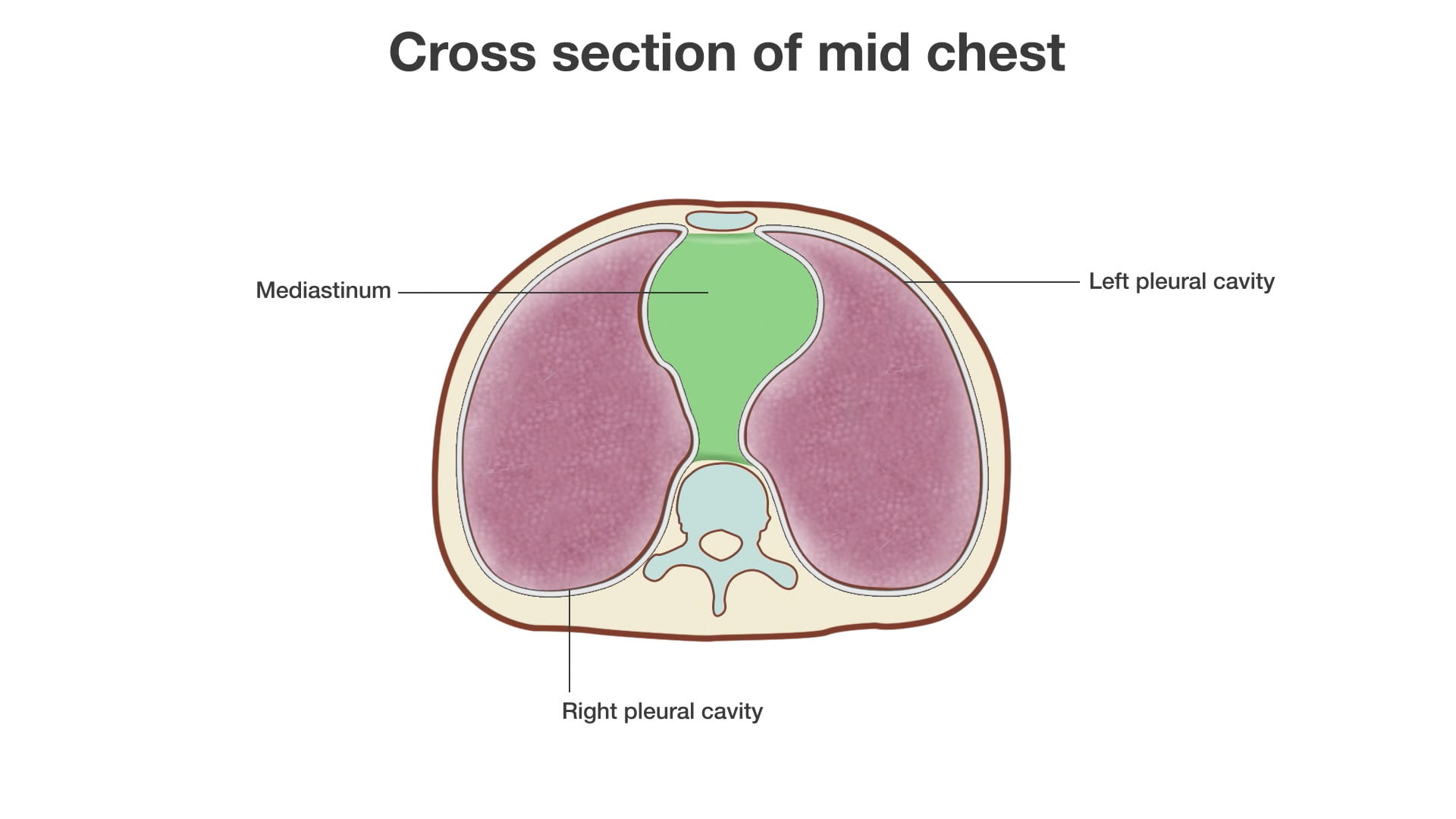
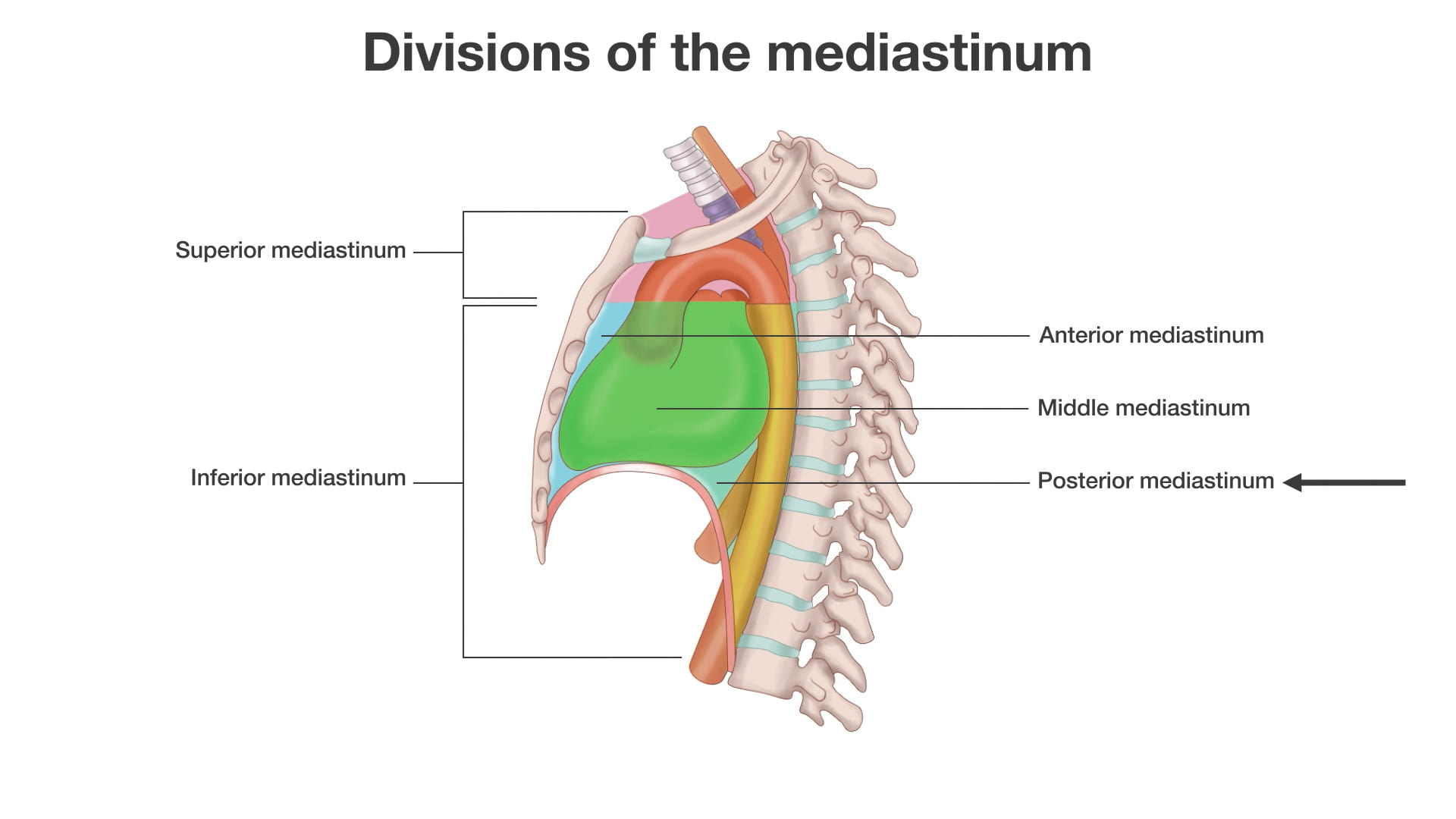
Structures of the mediastinum from cervicothoracic junction to diaphragm are taught. The divisions of the mediastinum along with their components are included in this lab. Great vessels, nerves and their relationships to heart, chest wall and spine will be learned. There is detailed investigation of the apex or cupola of the chest cavity.
Lab Objectives
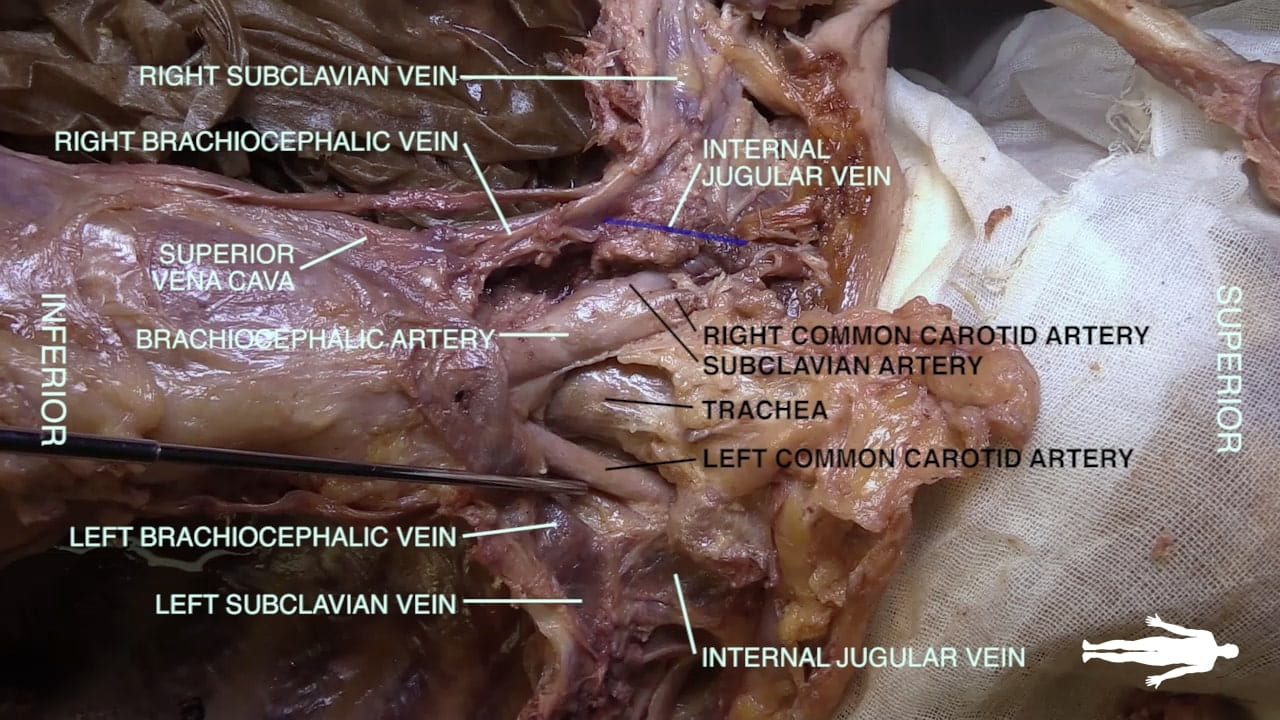
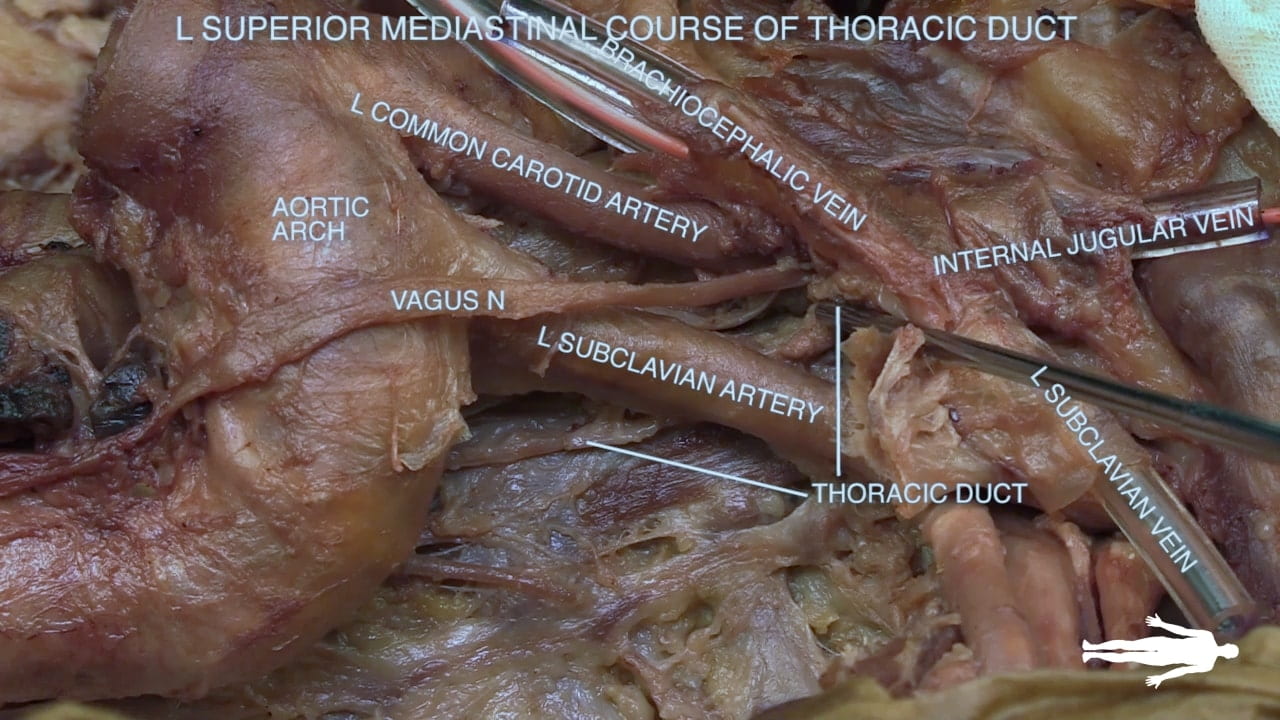
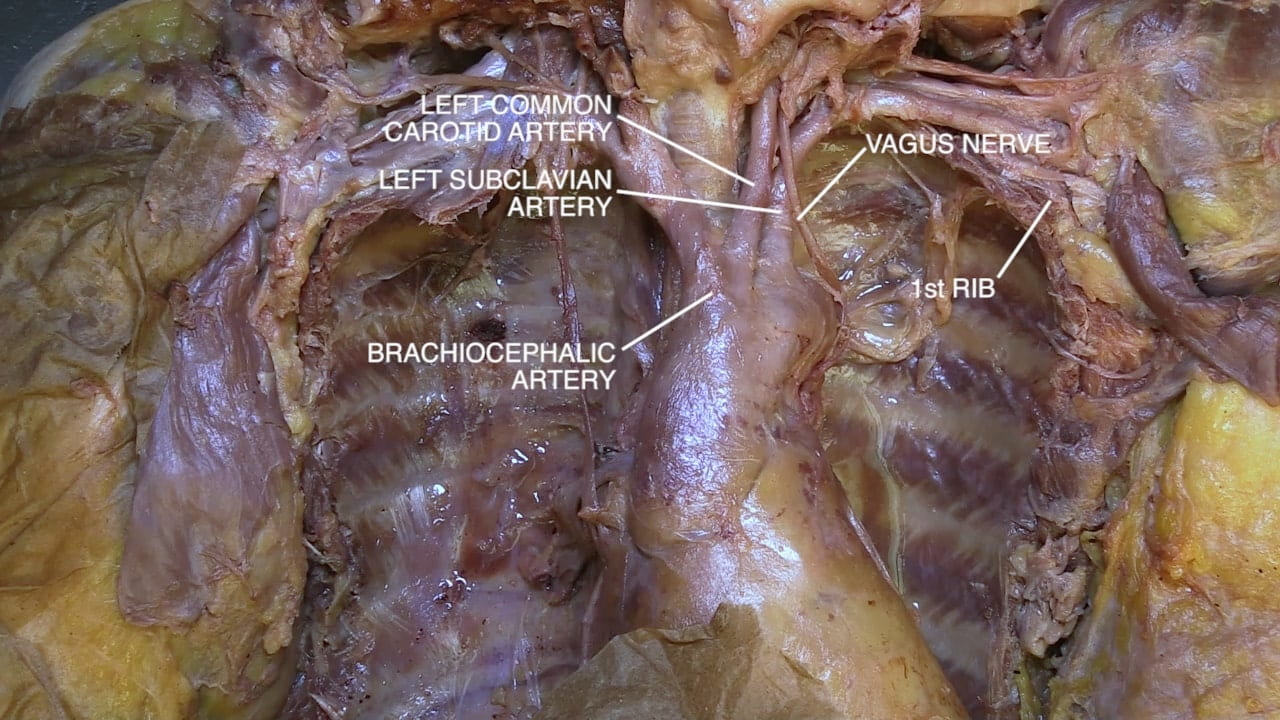
- Name the great vessels and their order of origin from the arch of the aorta.
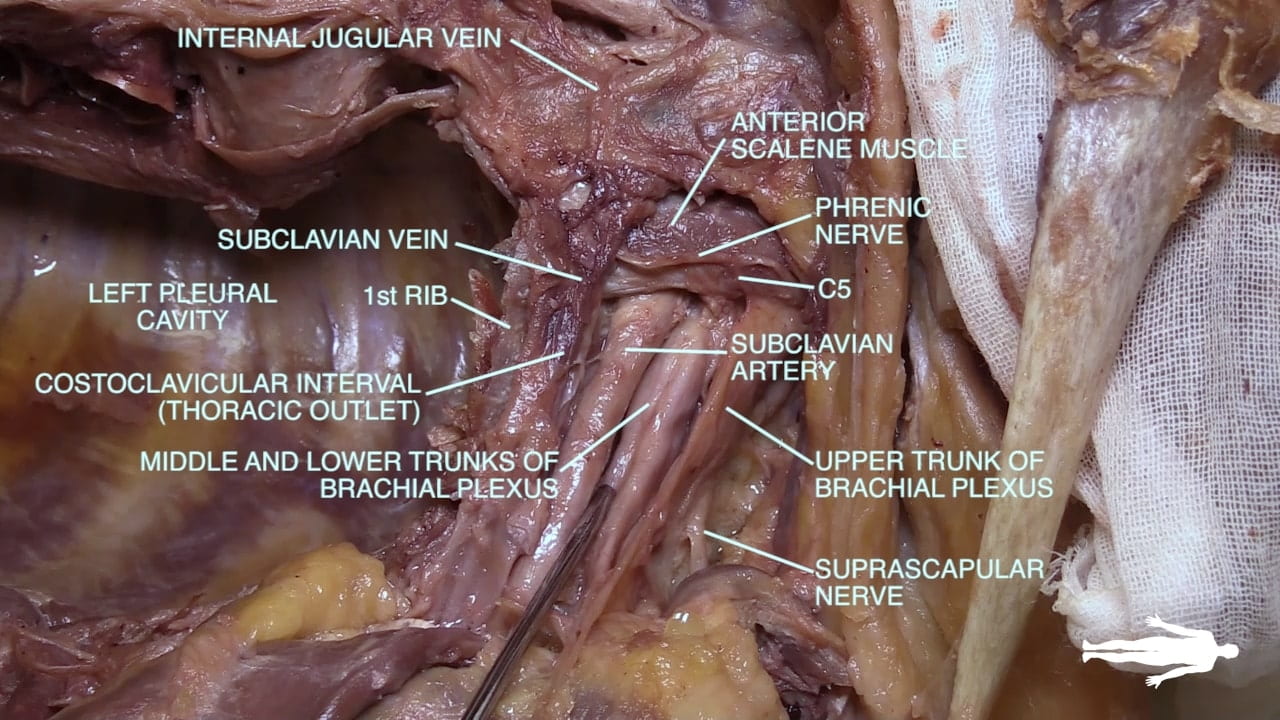
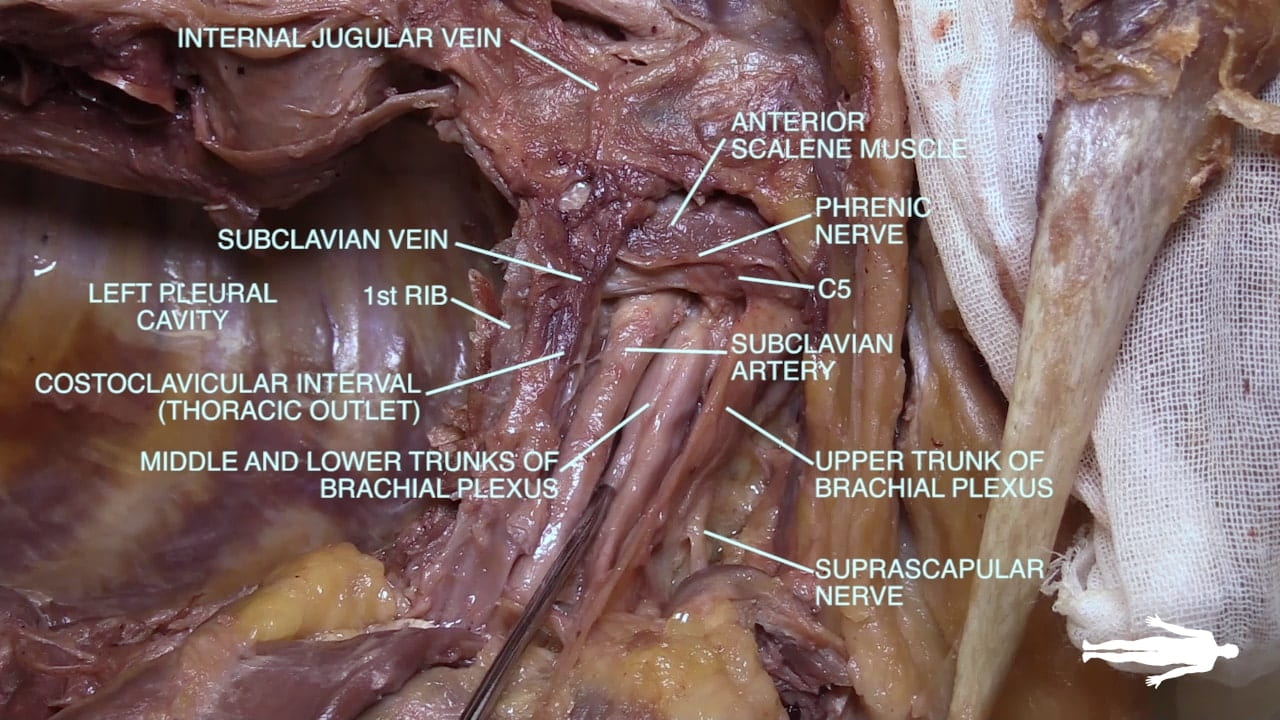
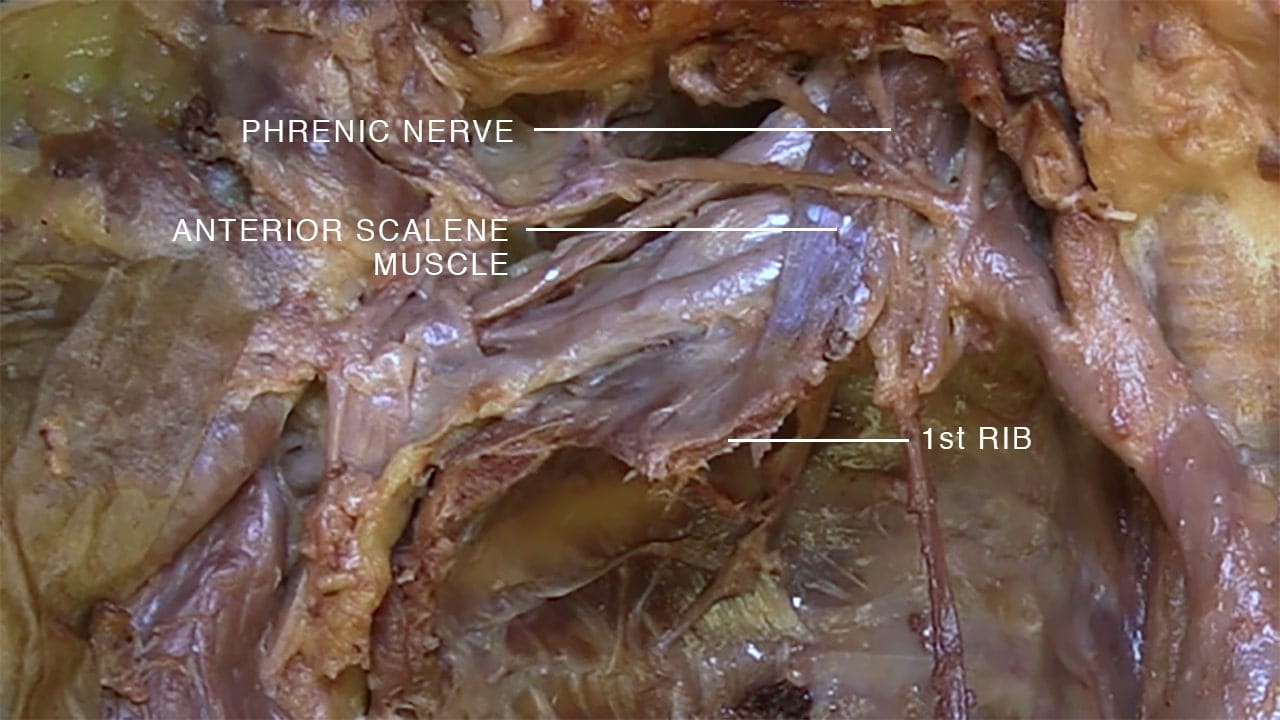
- Describe the relationship of the subclavian vessels to the anterior scalene muscle.
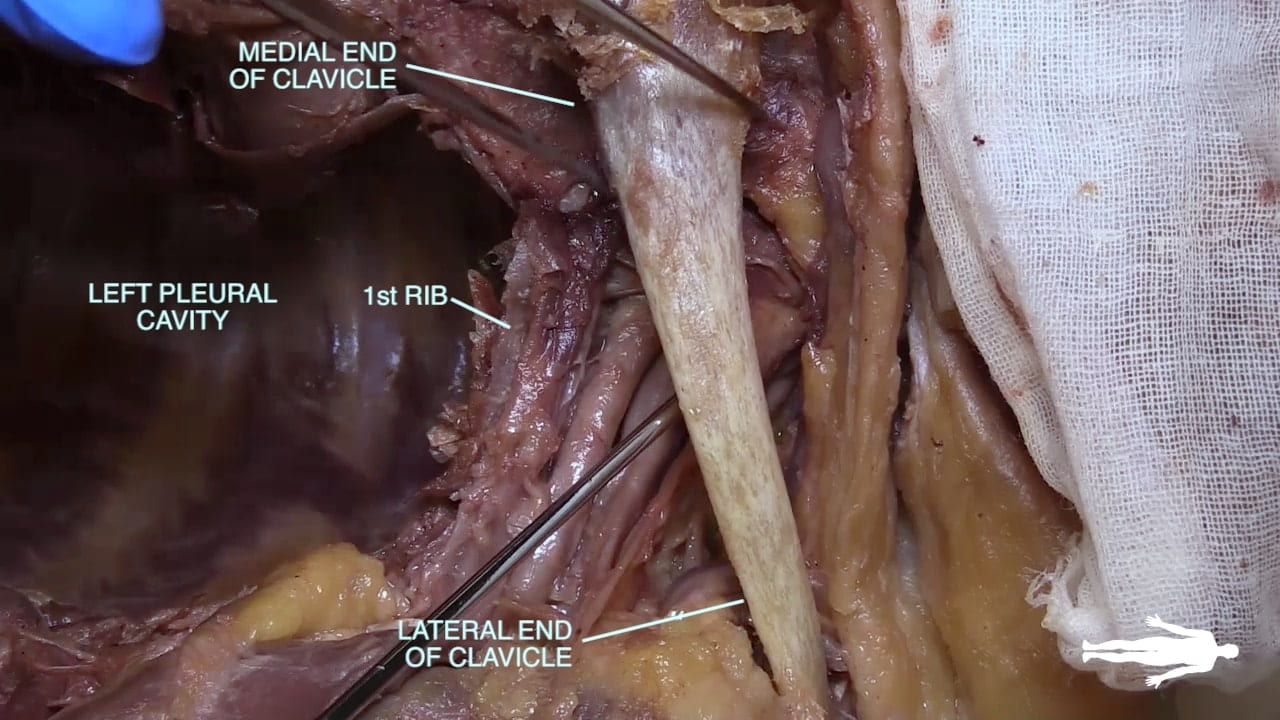
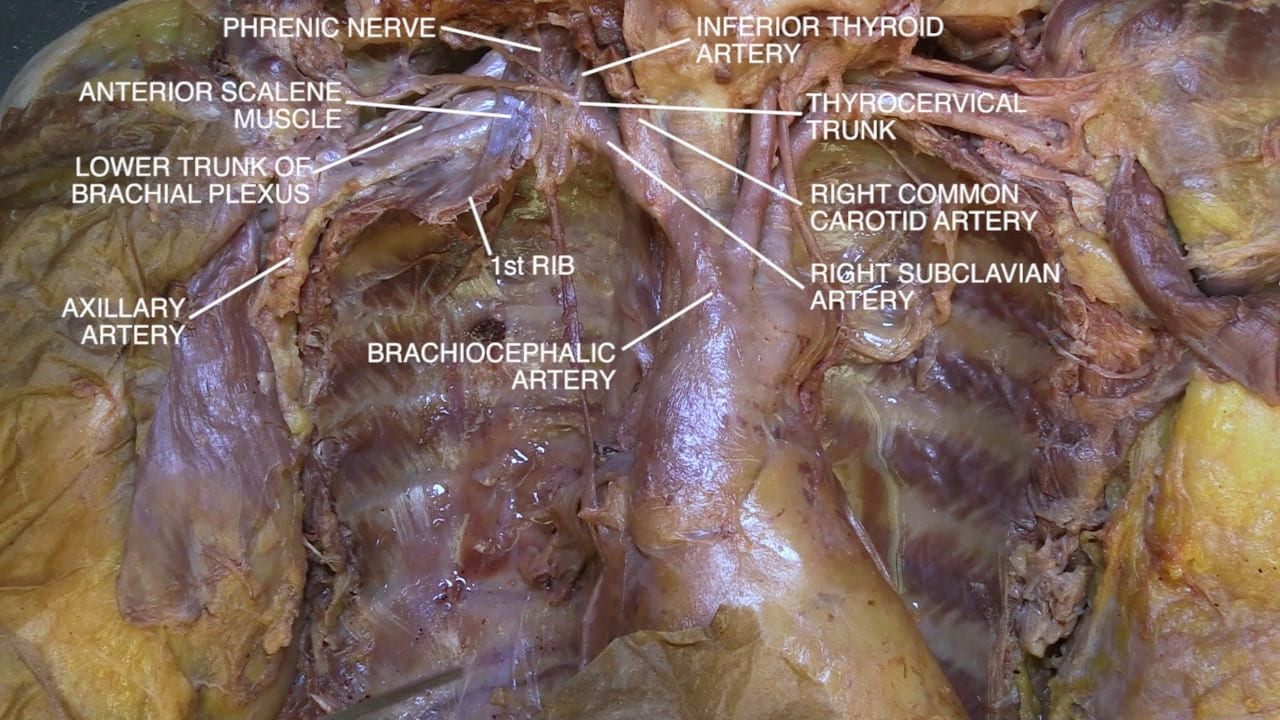
- Name the main structures in the thoracic outlet (costoclavicular interval).
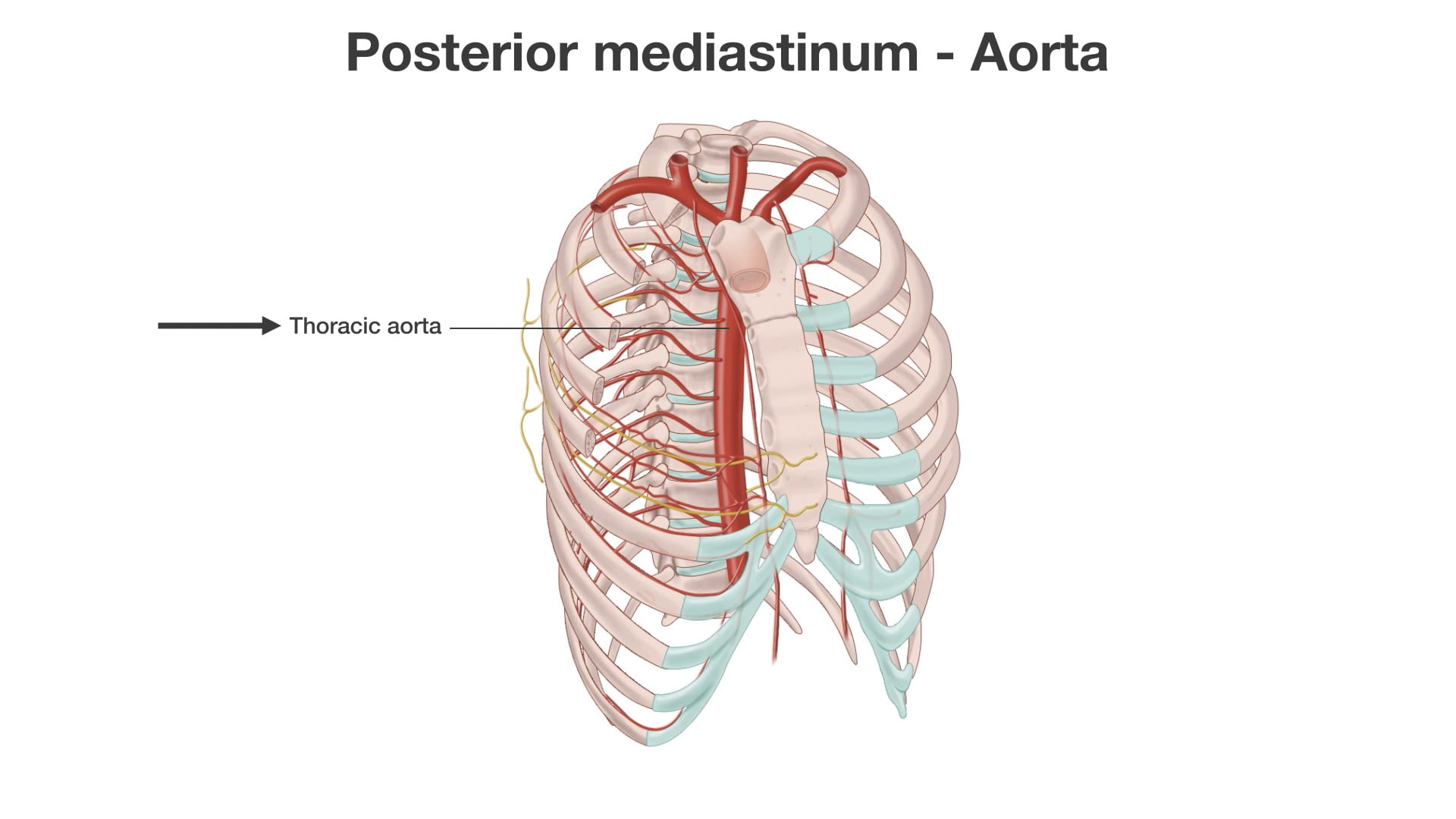
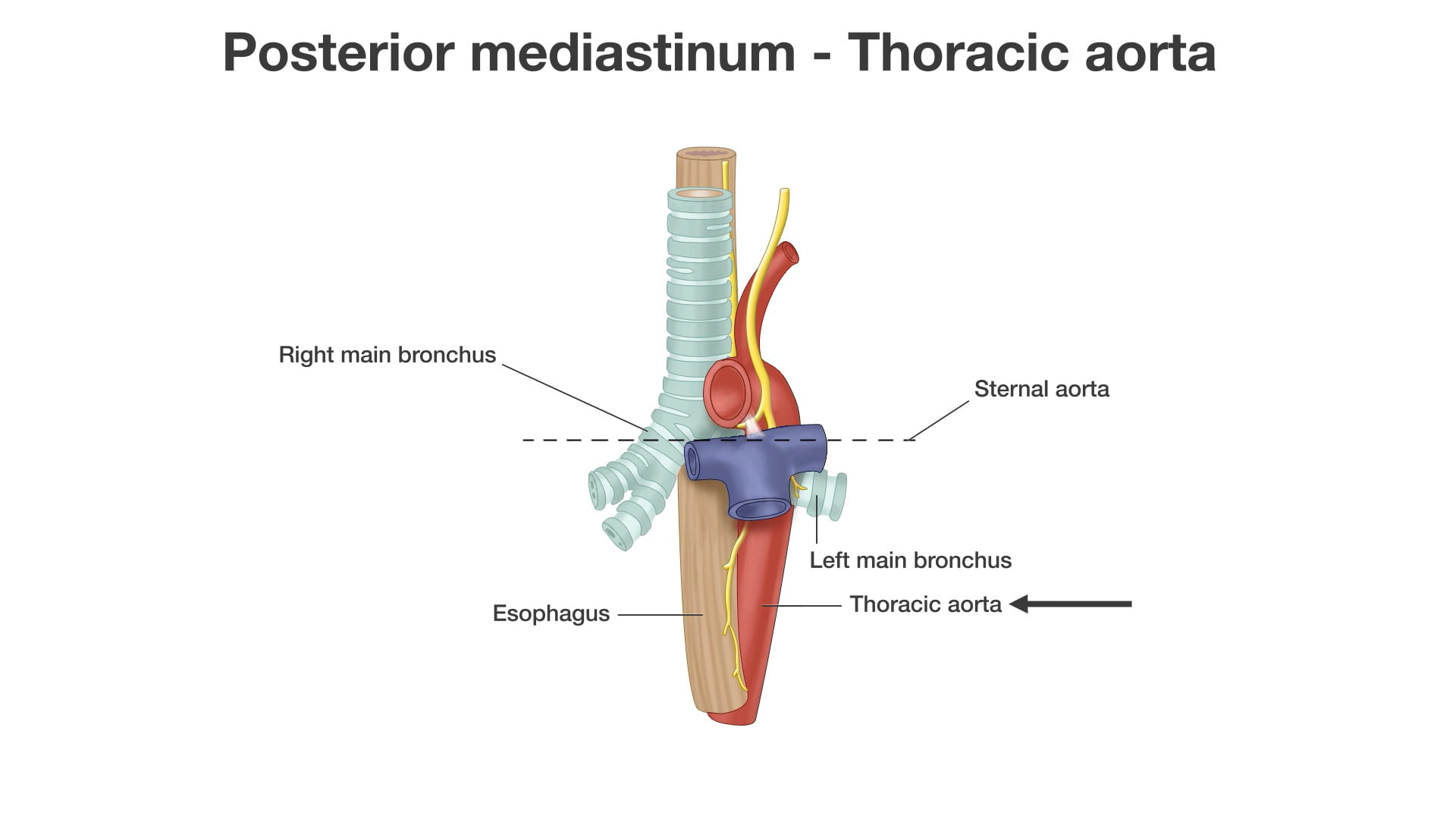
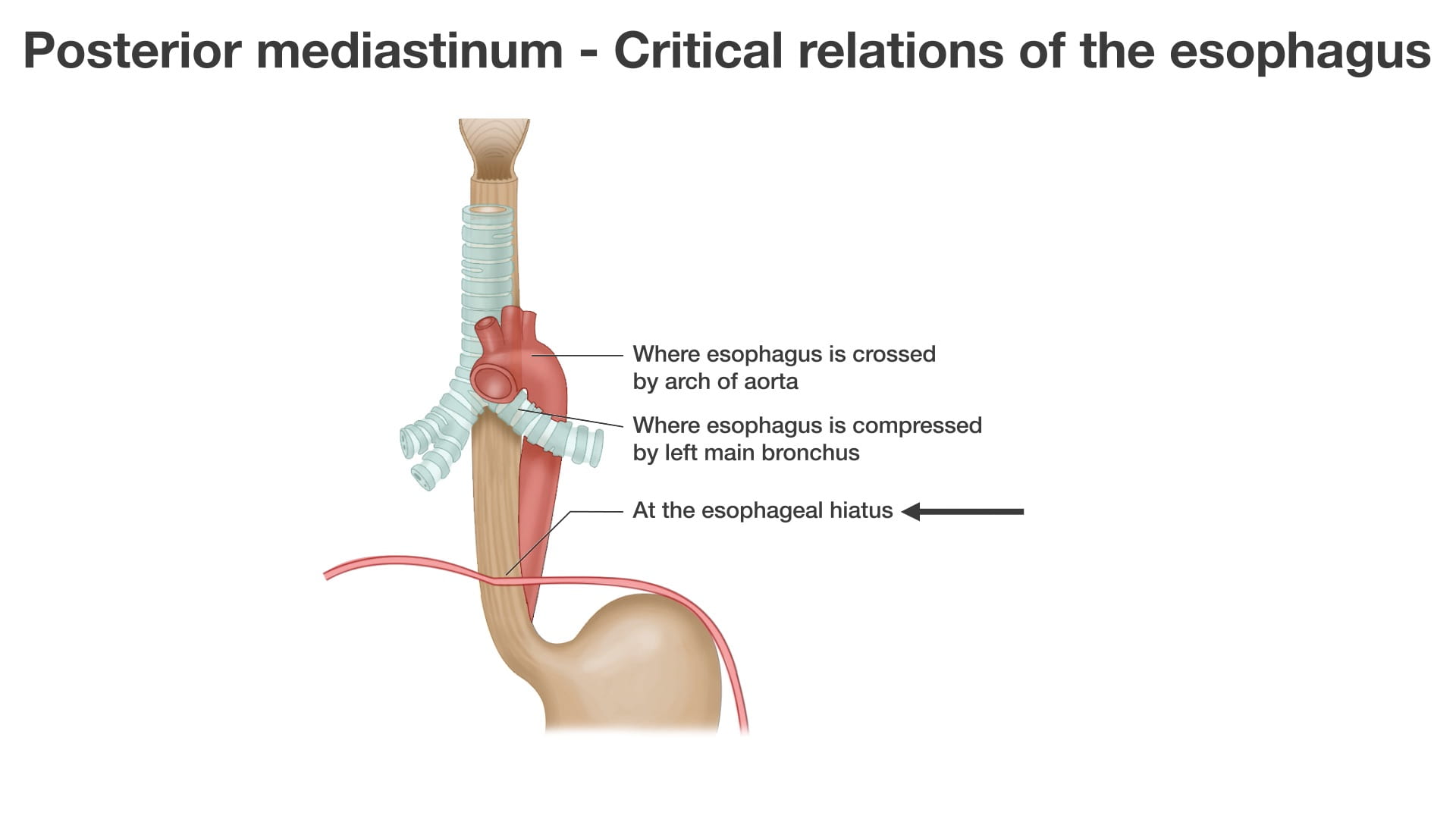
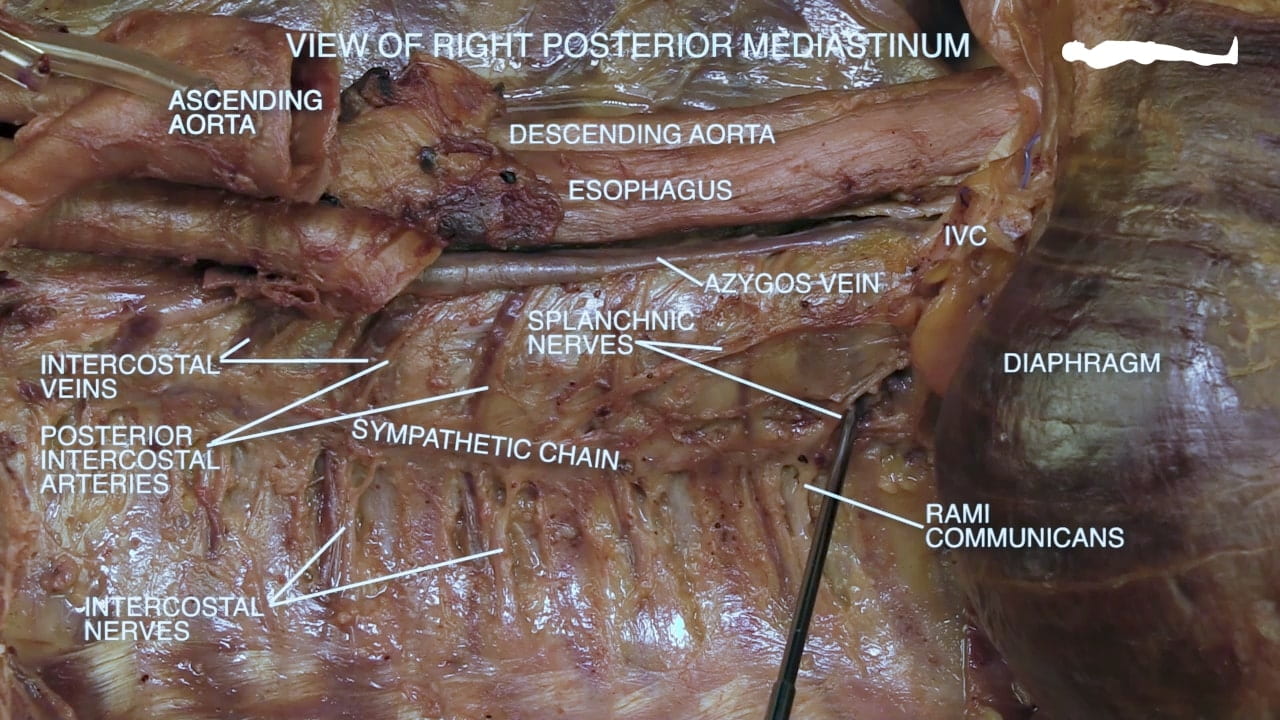
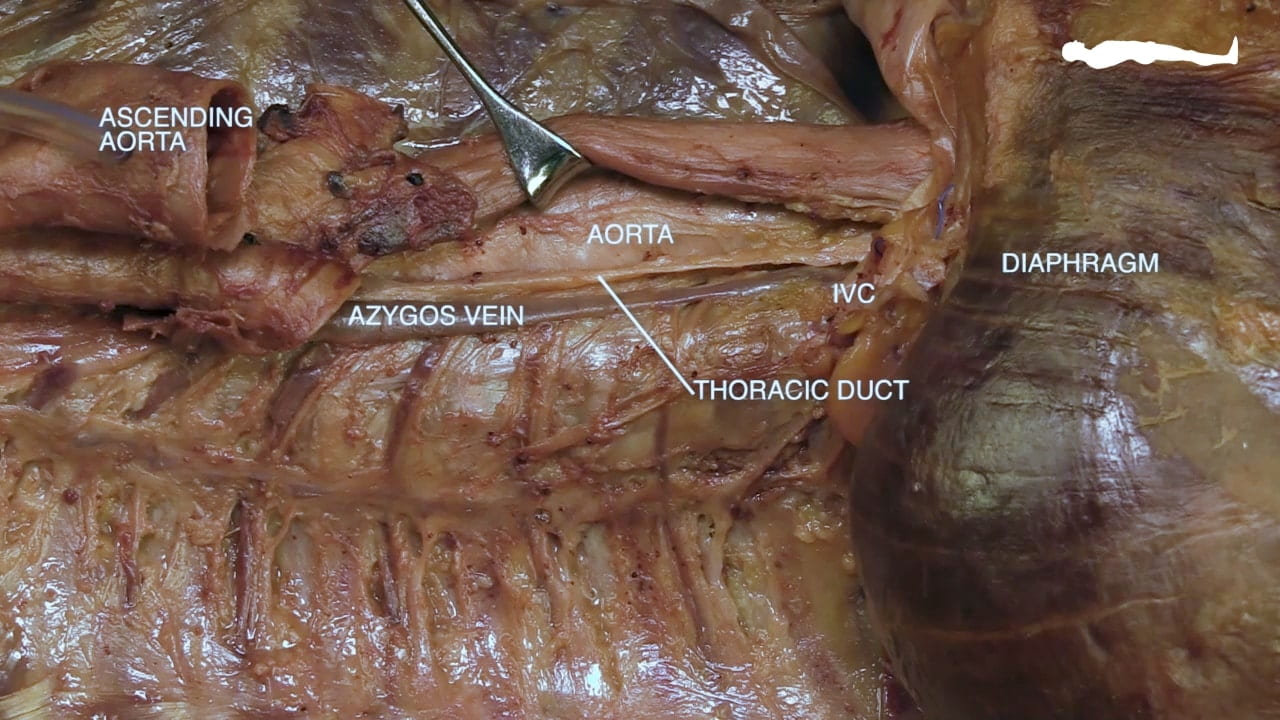
- Describe the spatial relationships of the thoracic aorta, esophagus and thoracic duct in the posterior mediastinum.
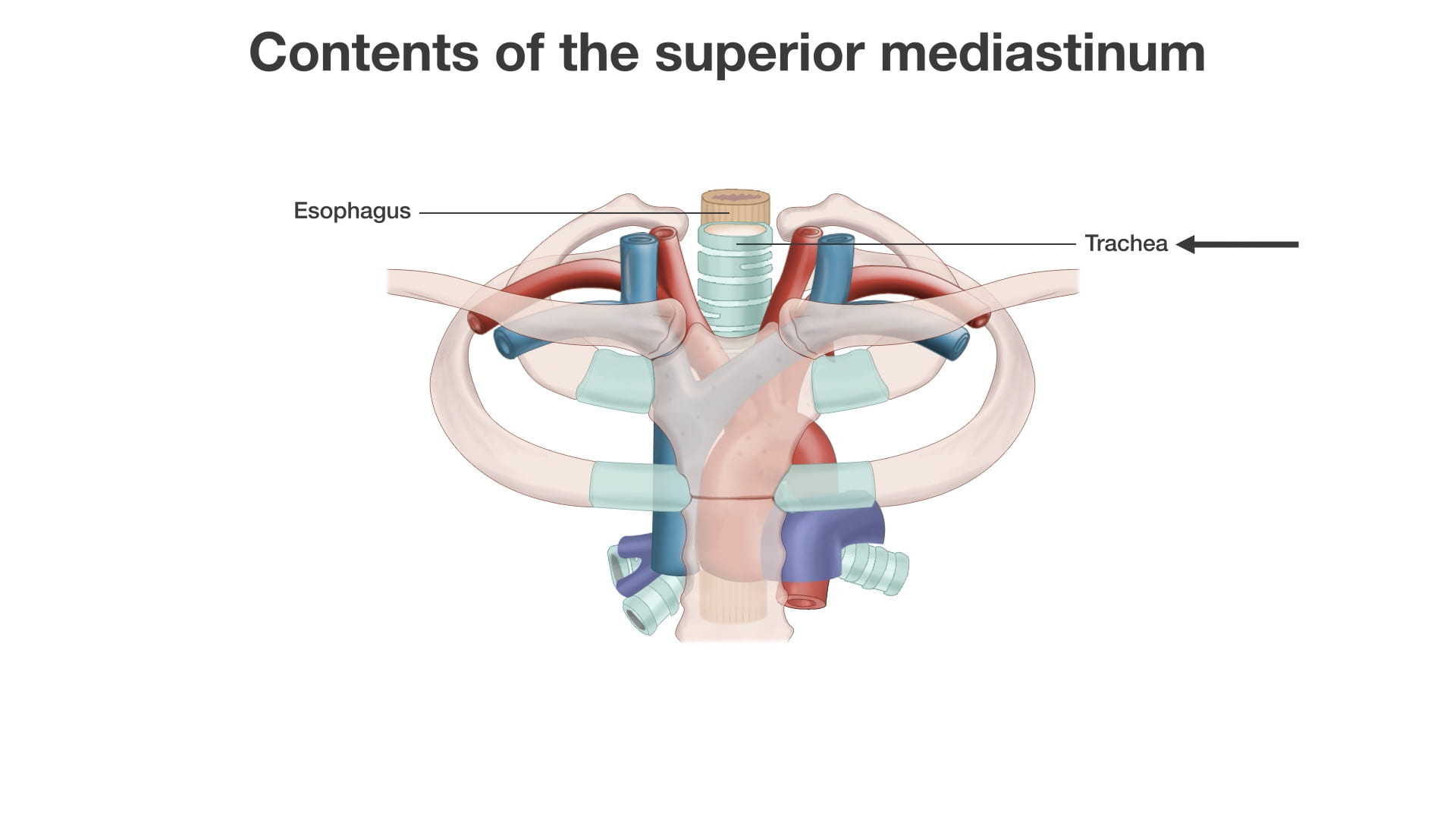
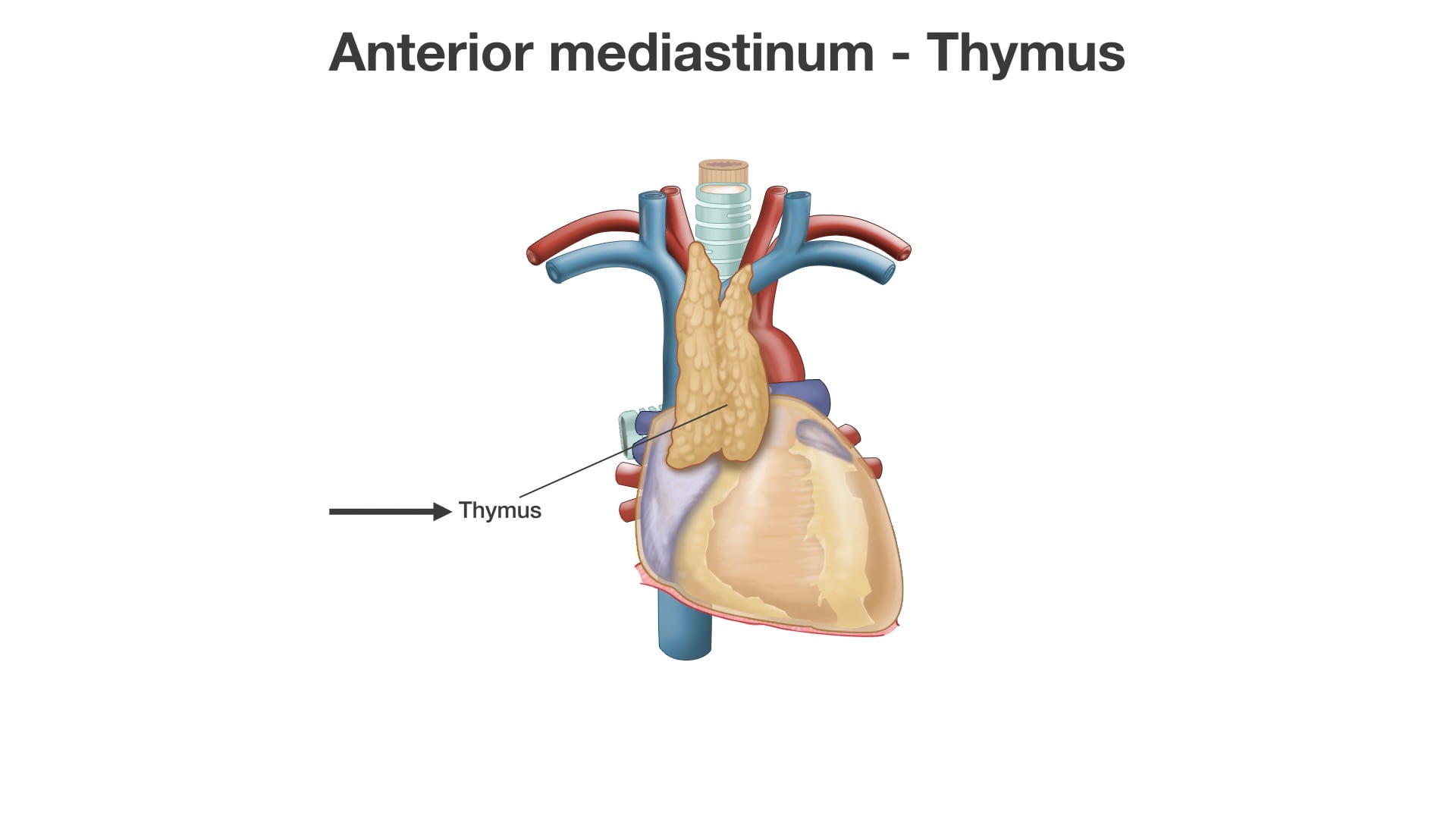
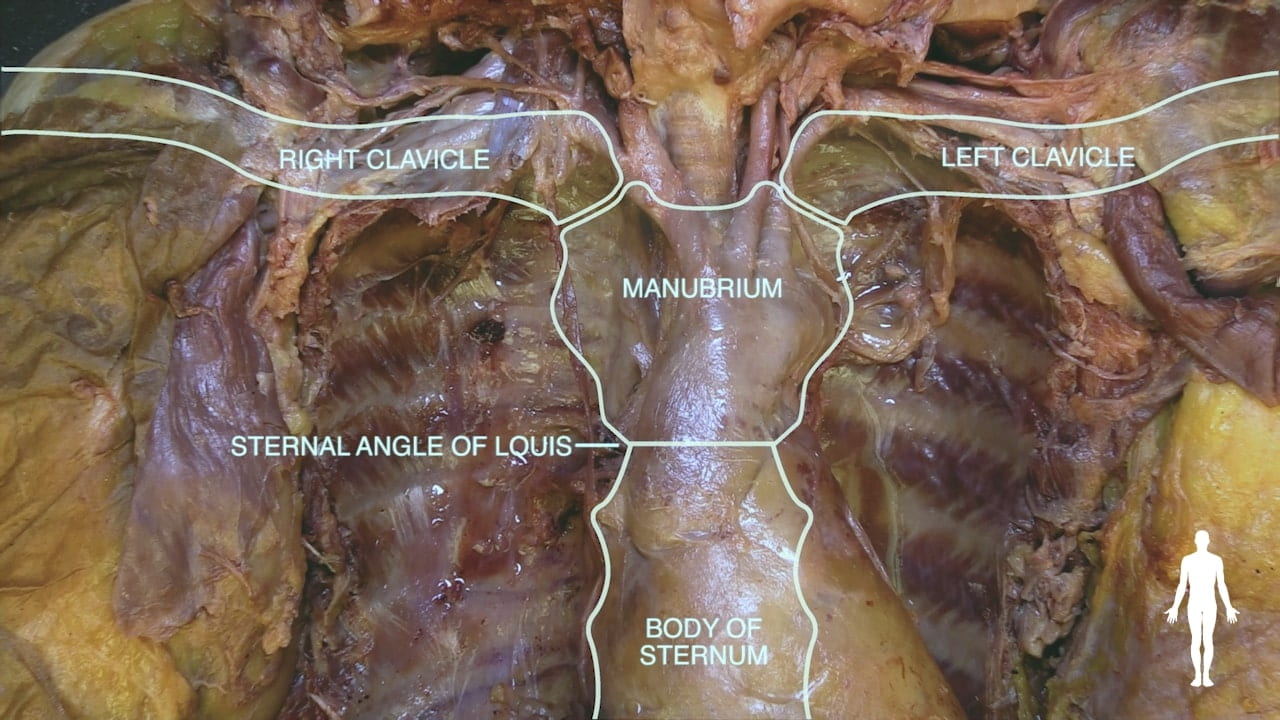
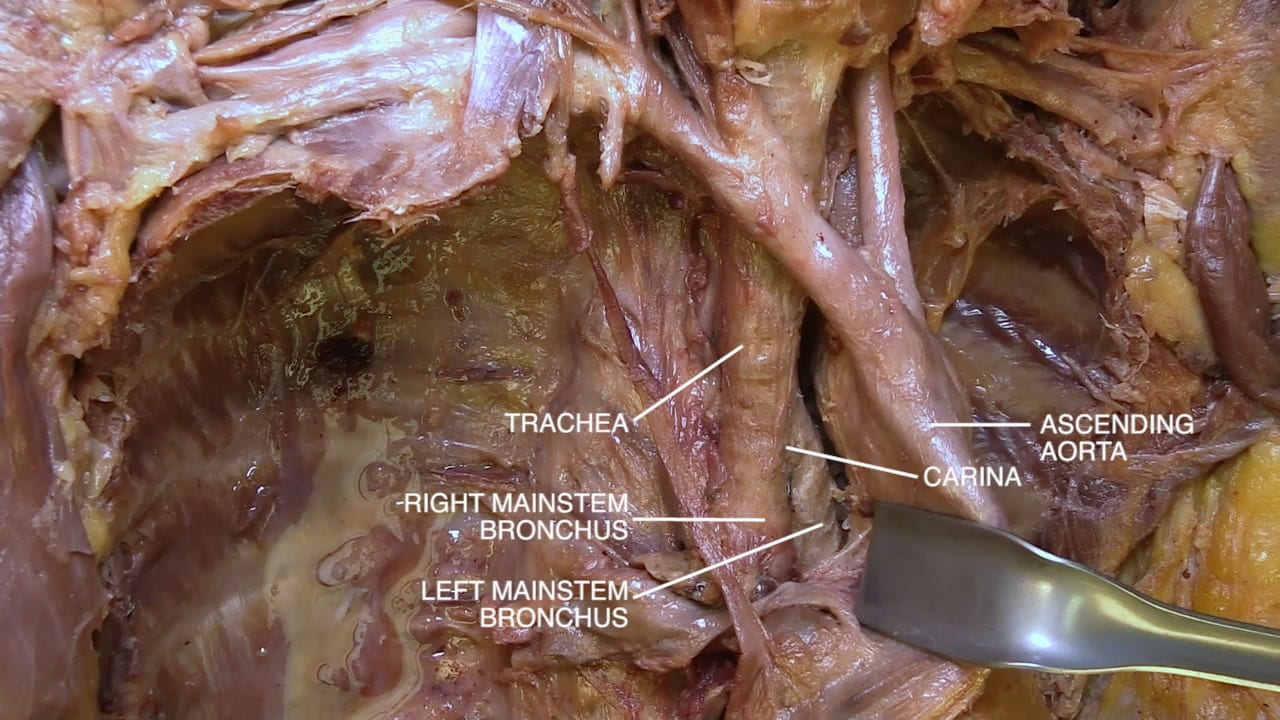
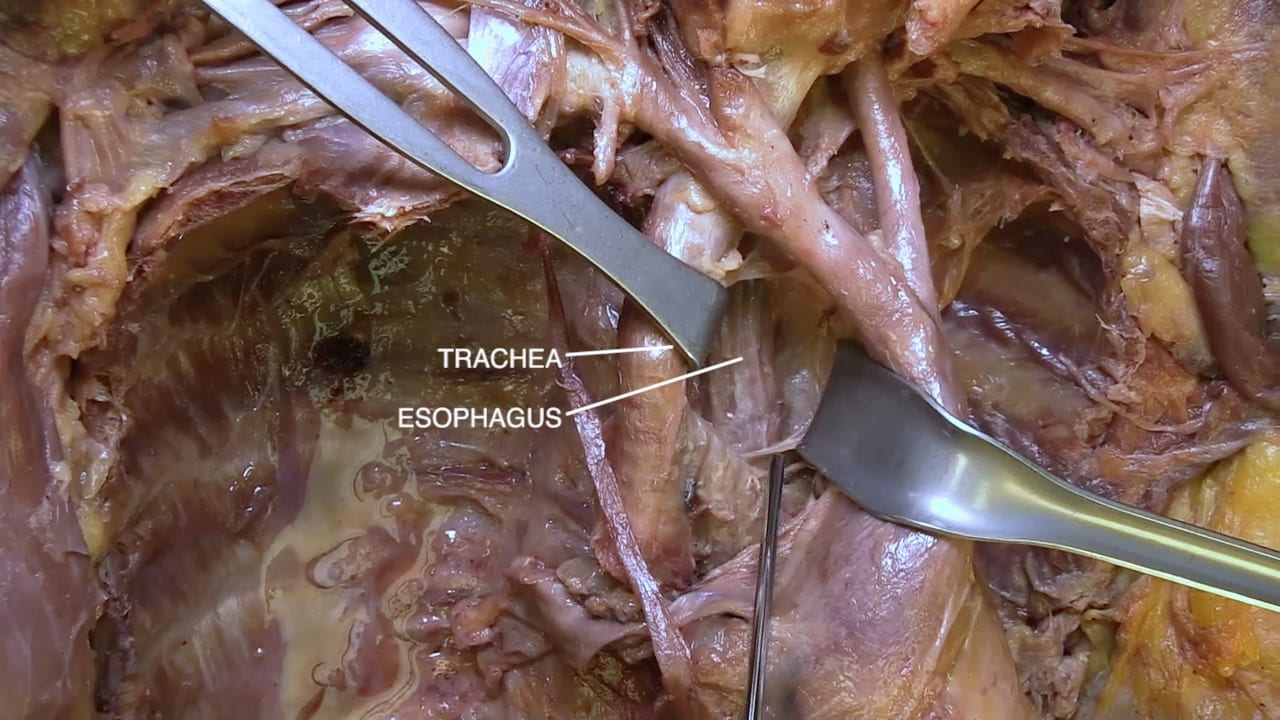
- Name the principal mediastinal structures at the level of the sternal angle.
- Describe the targets of medial branches and lateral branches (rami communicantes) of the sympathetic chain.
- Describe the positions of the aorta, esophagus and inferior vena cava as they pass through the diaphragm, include the vertebral level.
- Describe the position and drainage of the thoracic duct.
Lecture List
Mediastinum and Great Vessels, Superior Mediastinum and Thoracic Outlet, Apex of Pleural Cavity, Great Vessels, Posterior Mediastinum and Diaphragm
Mediastinum and Great Vessels
Mediastinum Gallery
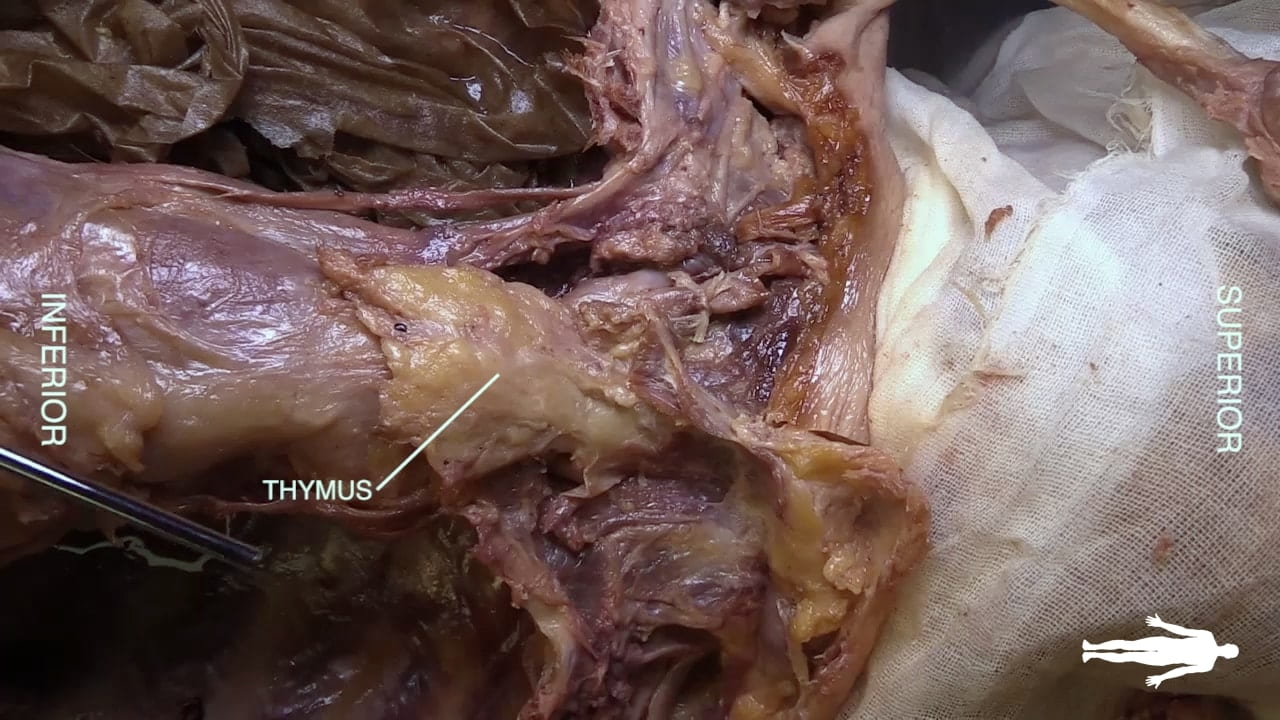
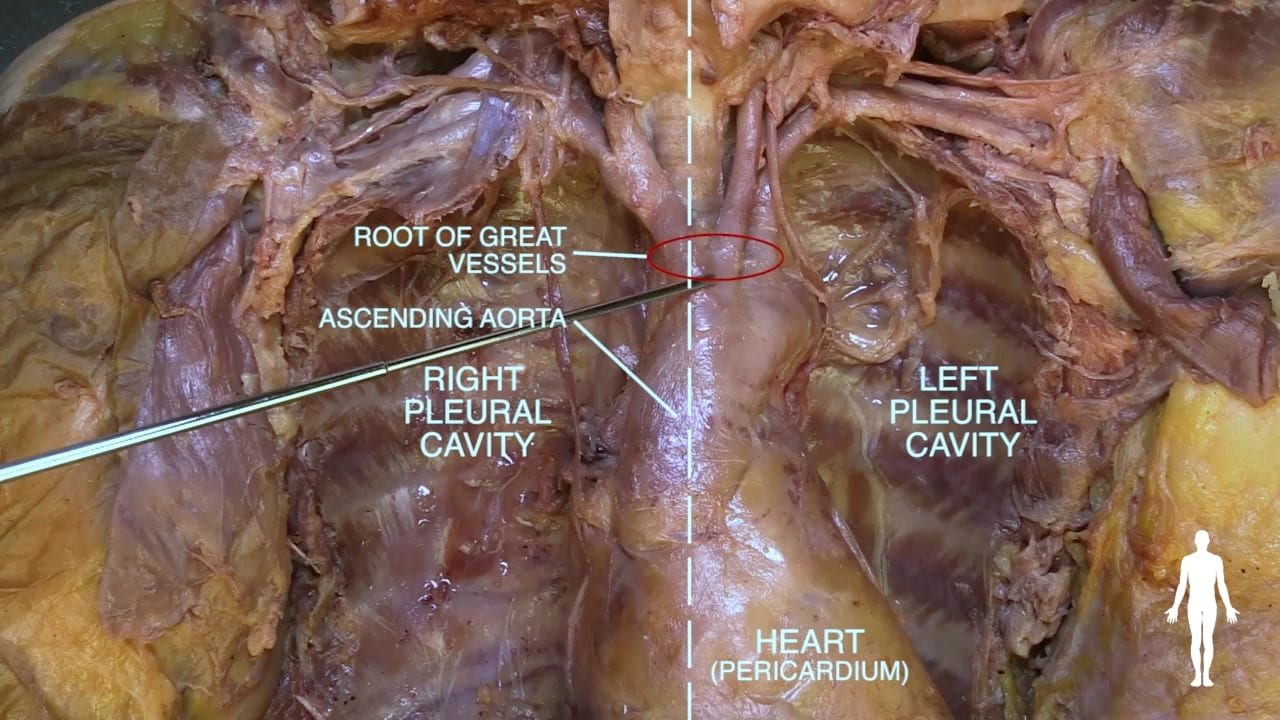
Cervicothoracic Junction
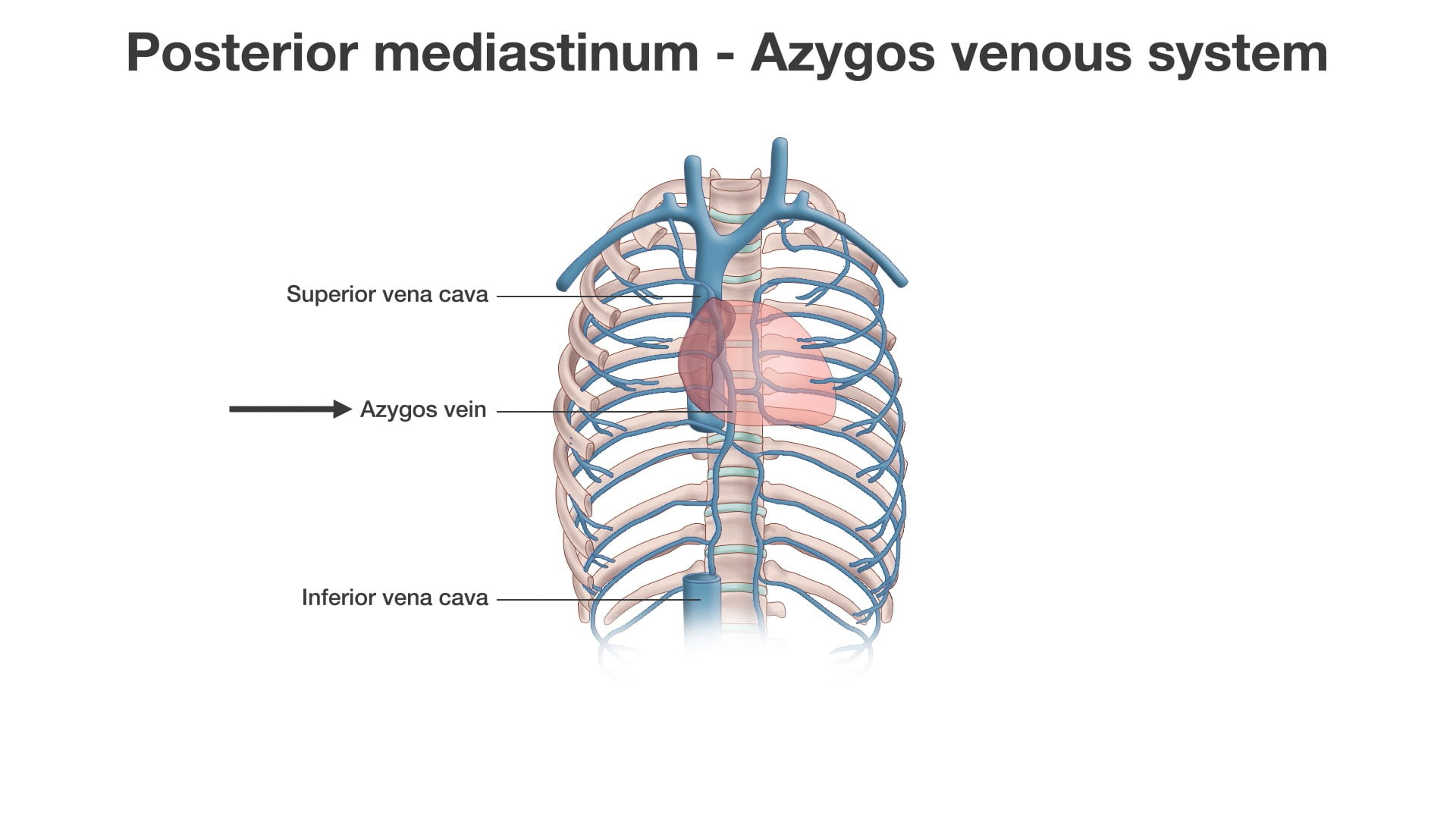
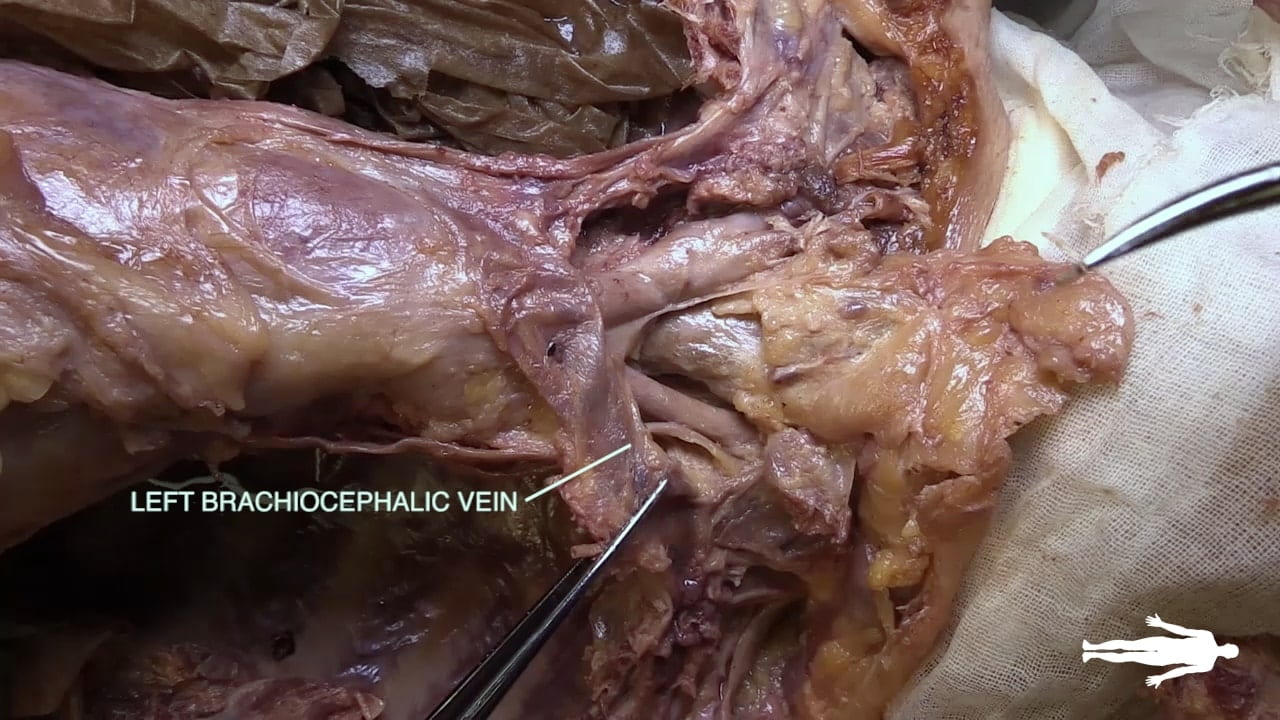
Great Veins
Subclavian Artery and Vein
Thoracic Outlet
Apex of Pleural Cavity
Sympathetic Chain