Assigned Male Pelvis
Lab Summary
This lab includes a presentation of the inguinal ligament, inguinal canal and testis. The male pelvis and perineum are presented from external structures to pelvic contents. Additionally, the male pelvis and perineal structures are shown from a midline sagittal perspective.
Lab Objectives
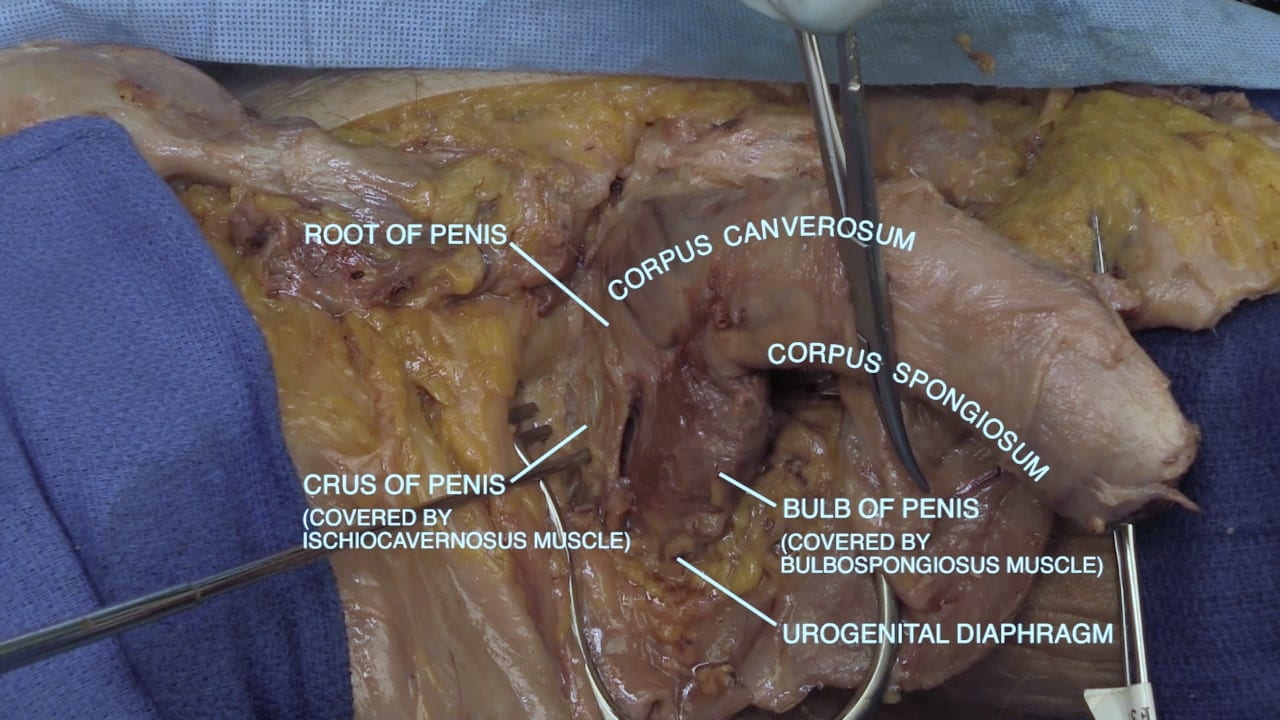
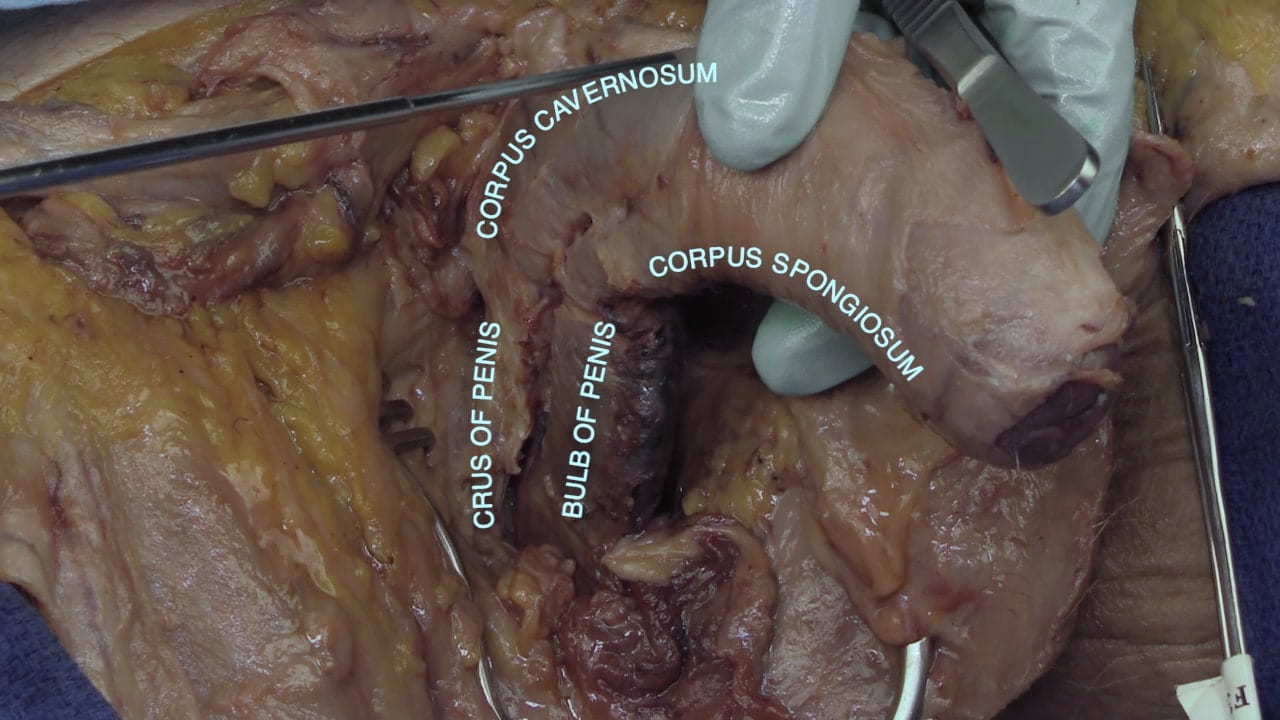
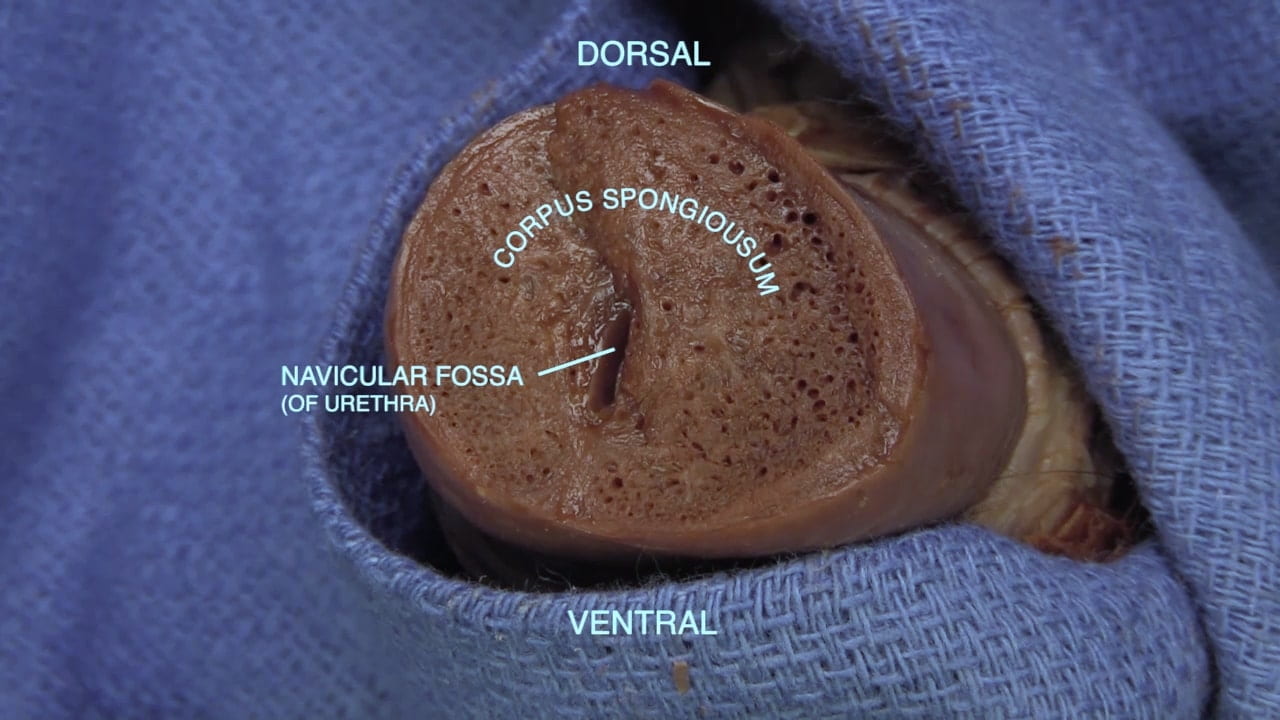
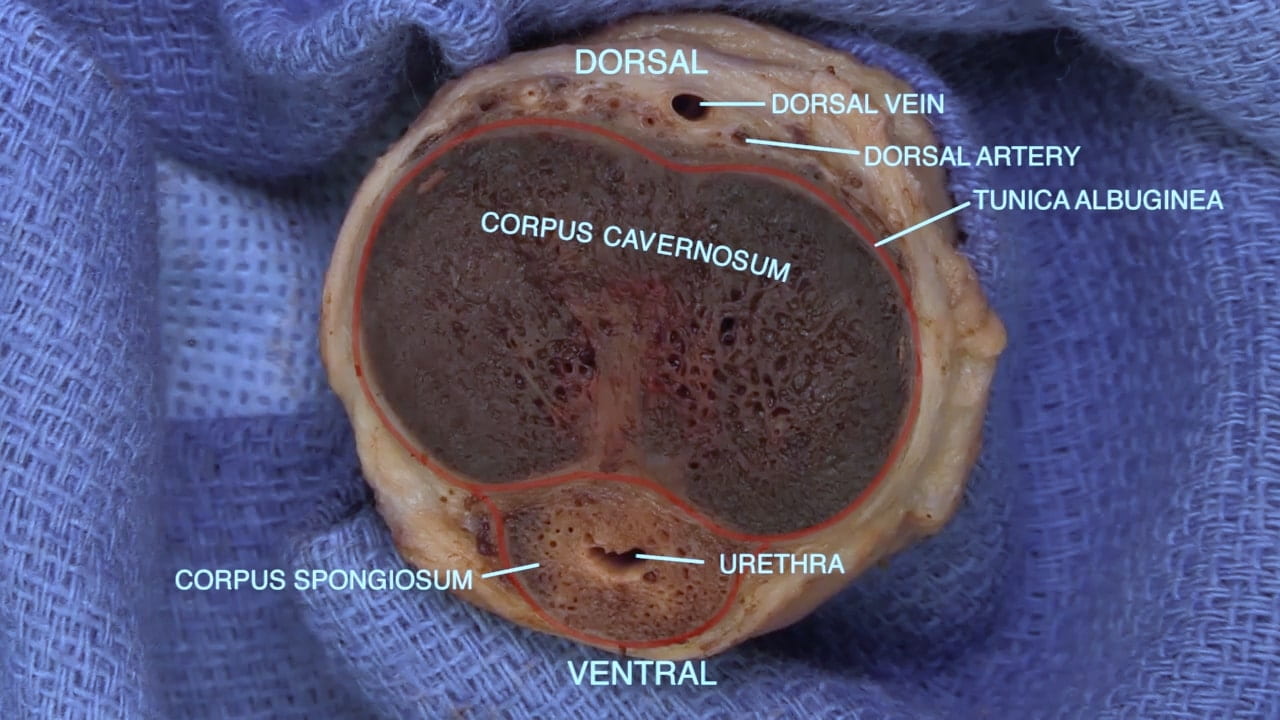
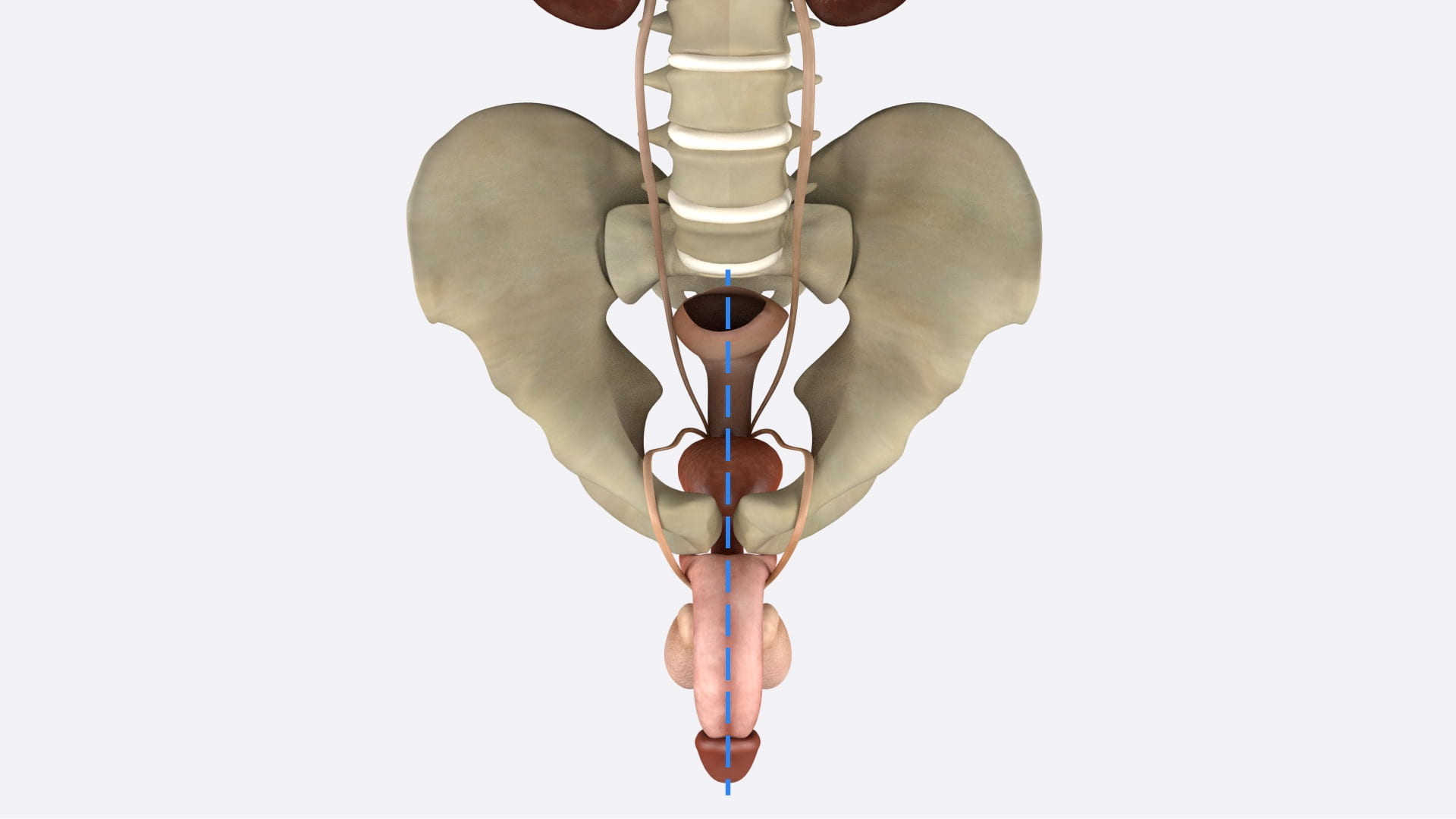
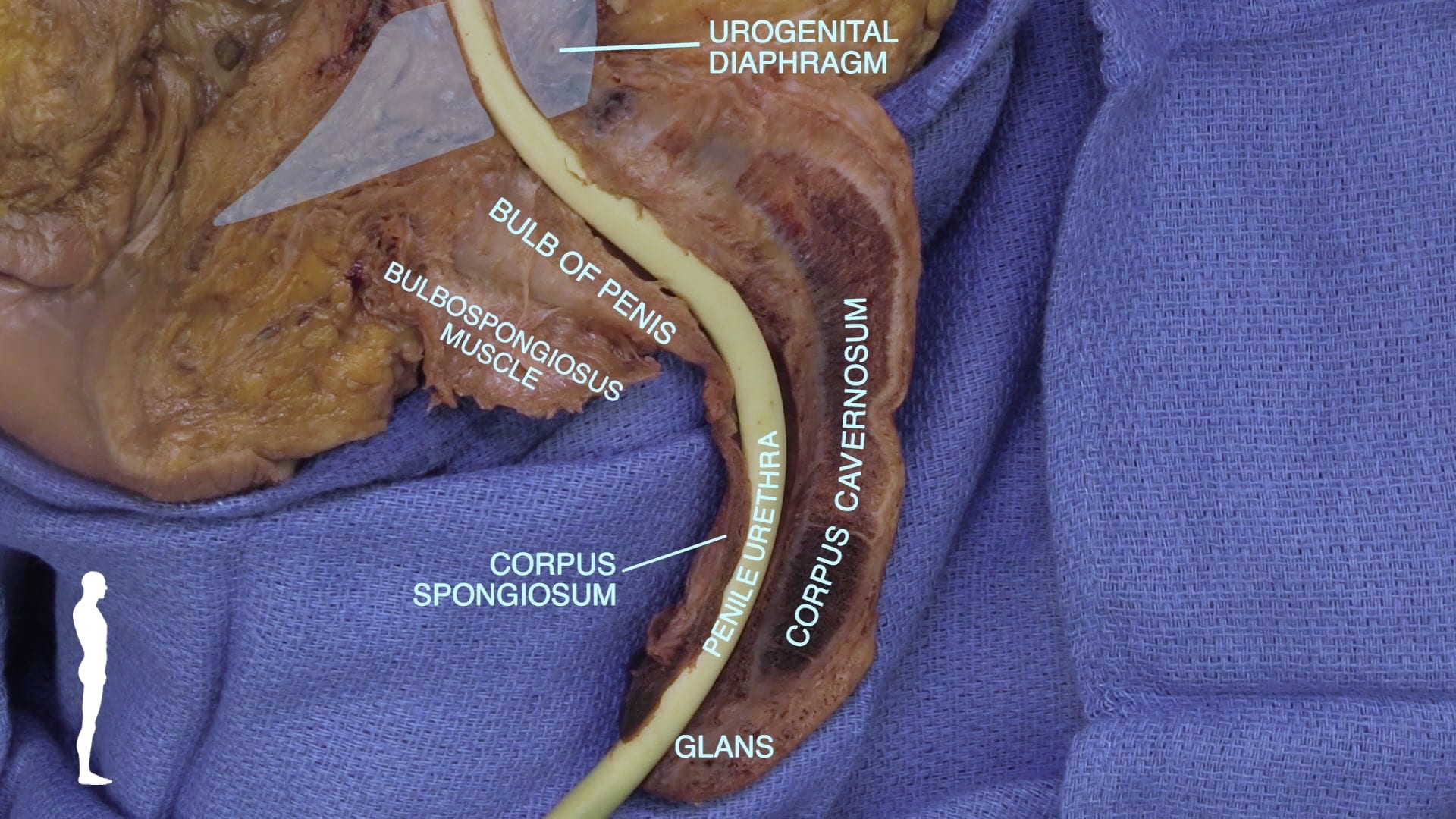
- Describe the erectile tissue of penis including location of penile urethra.
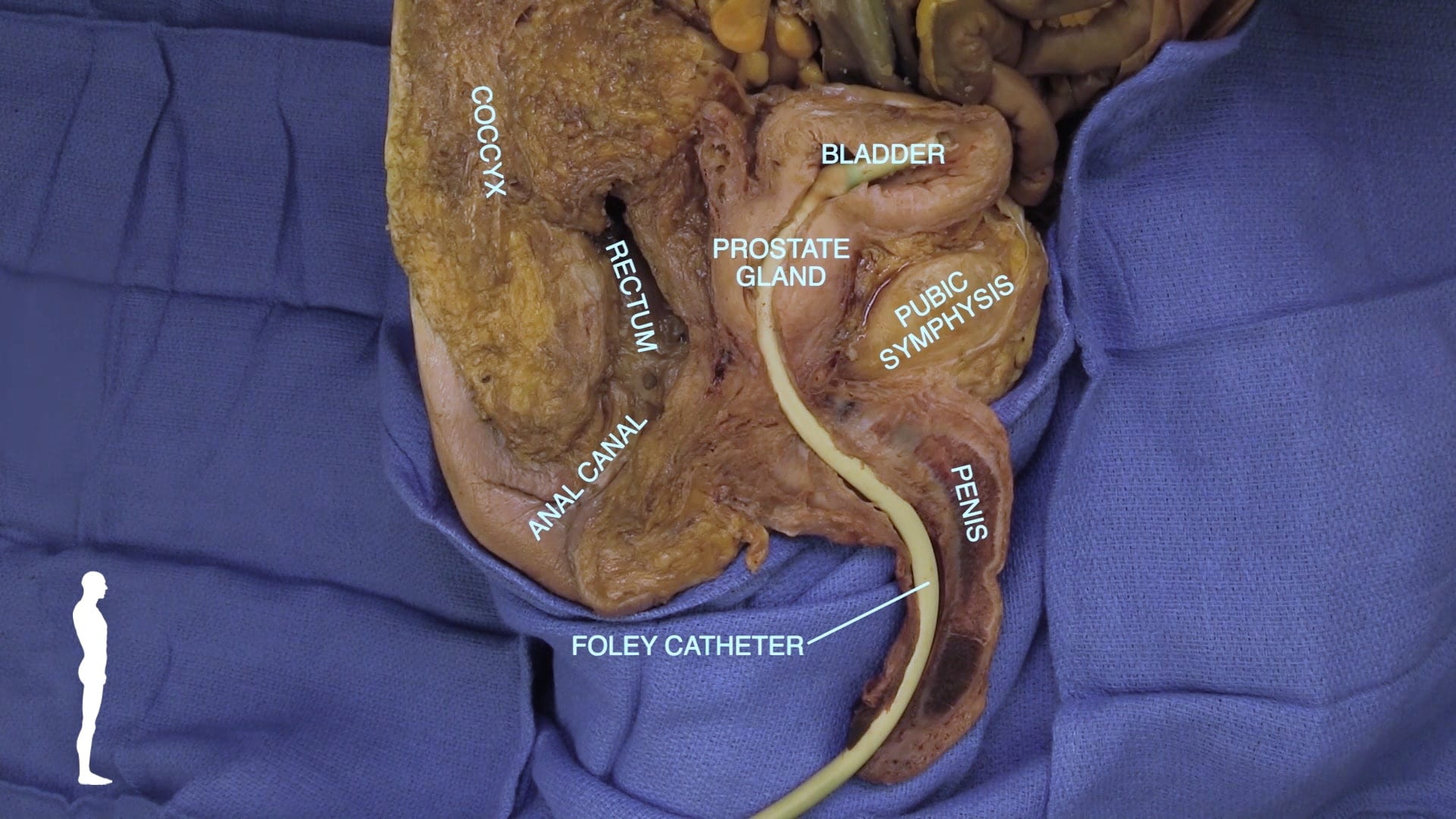
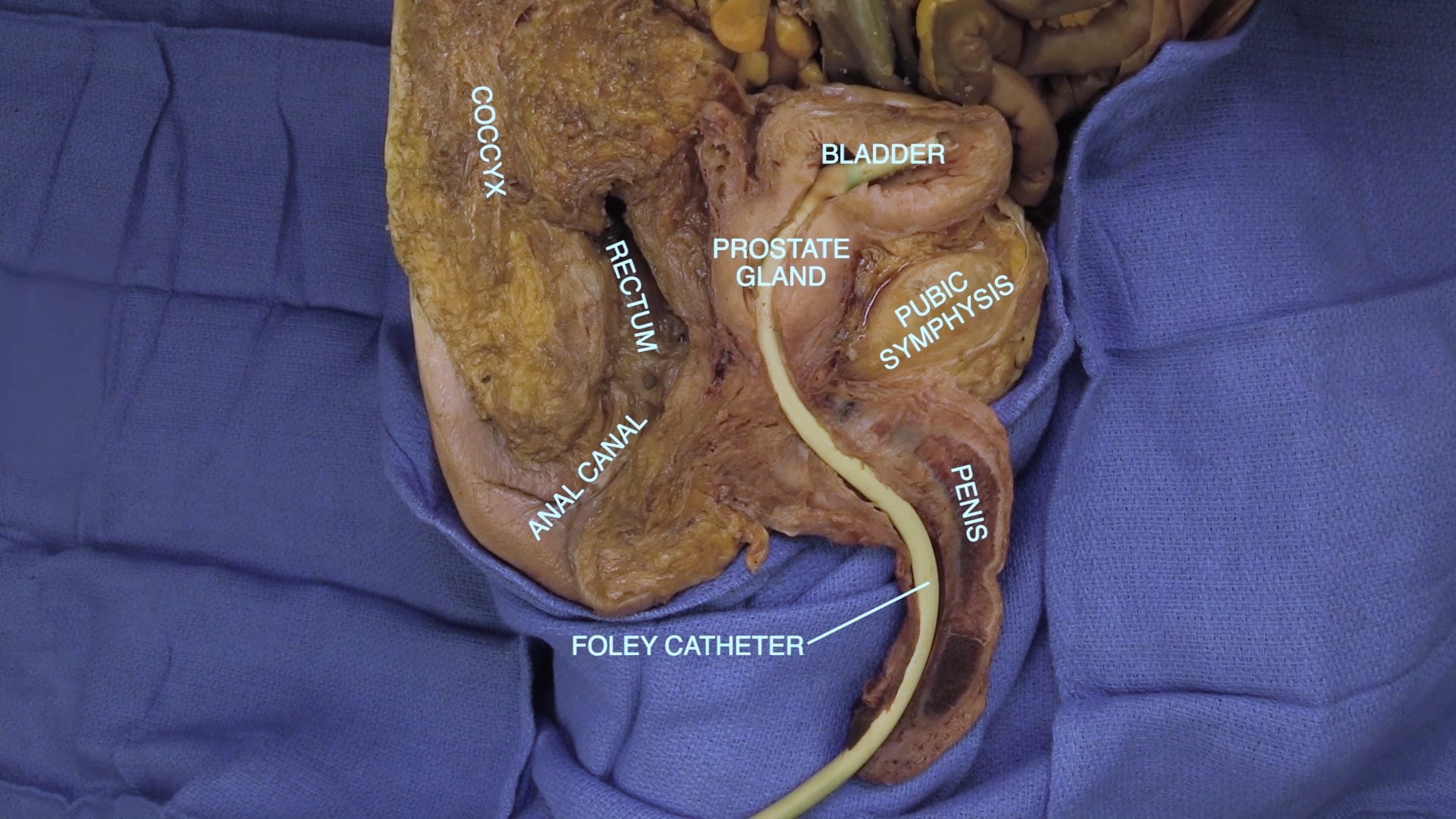
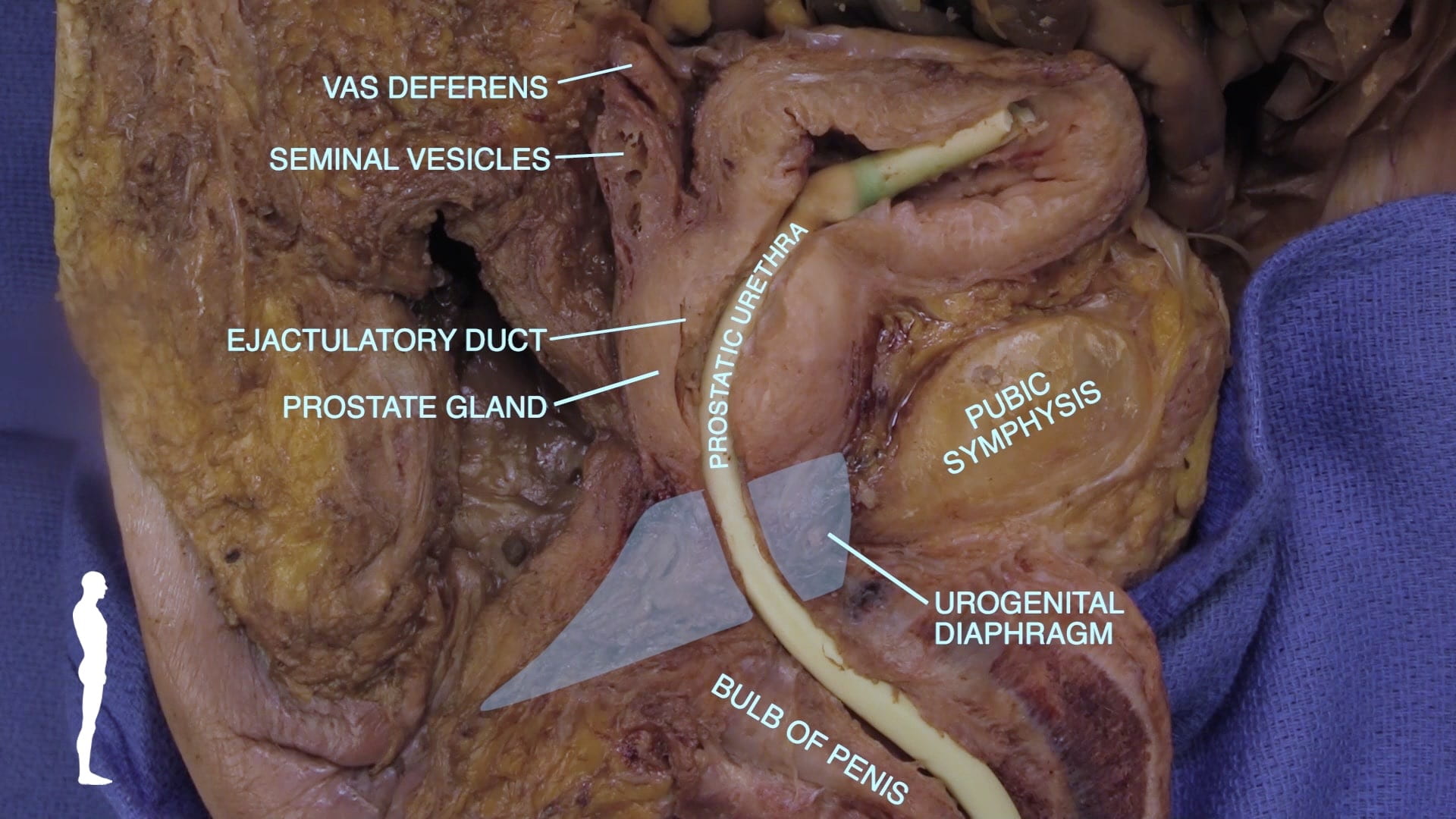
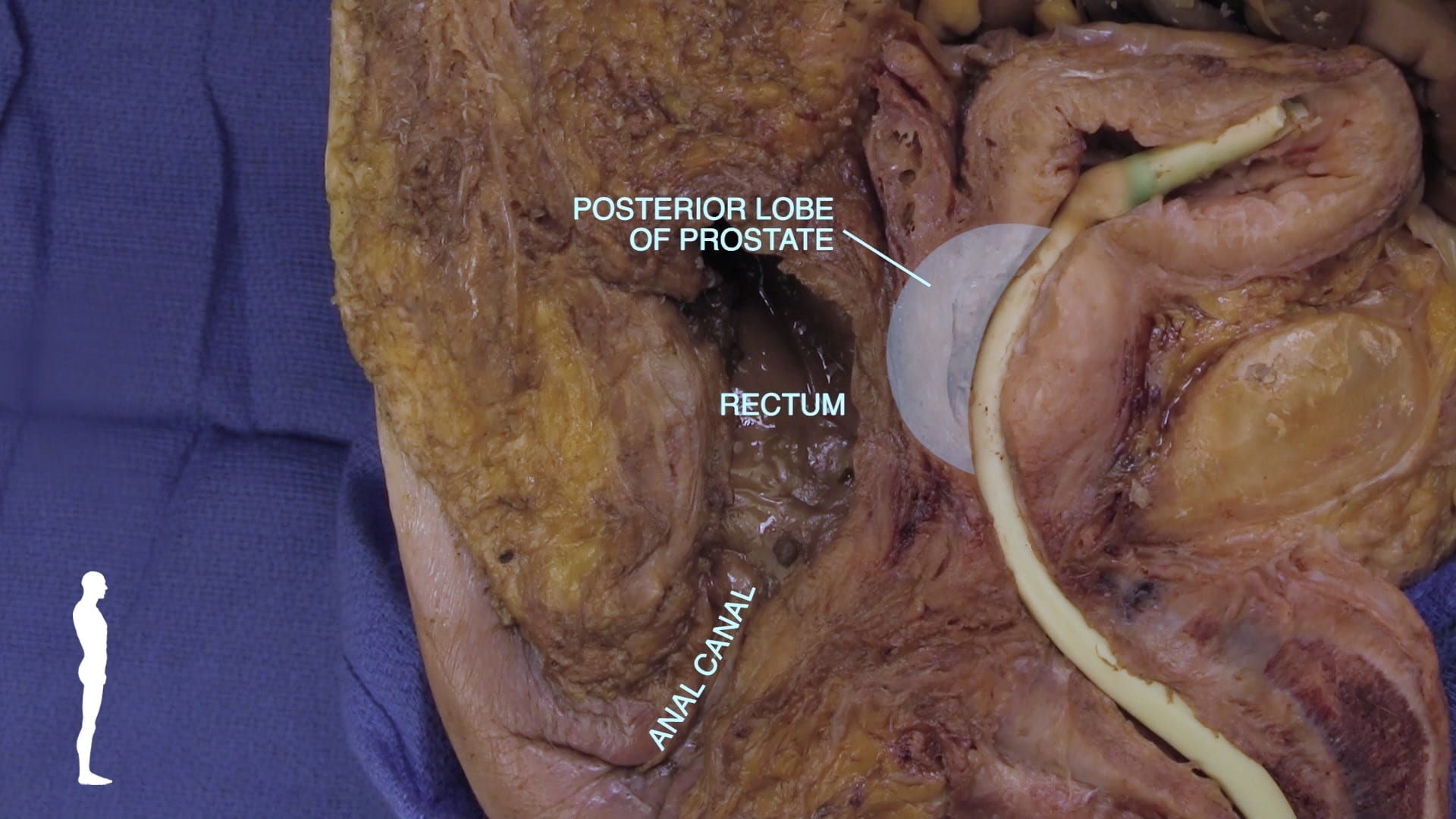
- Describe position of prostate gland and its relation to rectum, bladder and urogenital diaphragm.
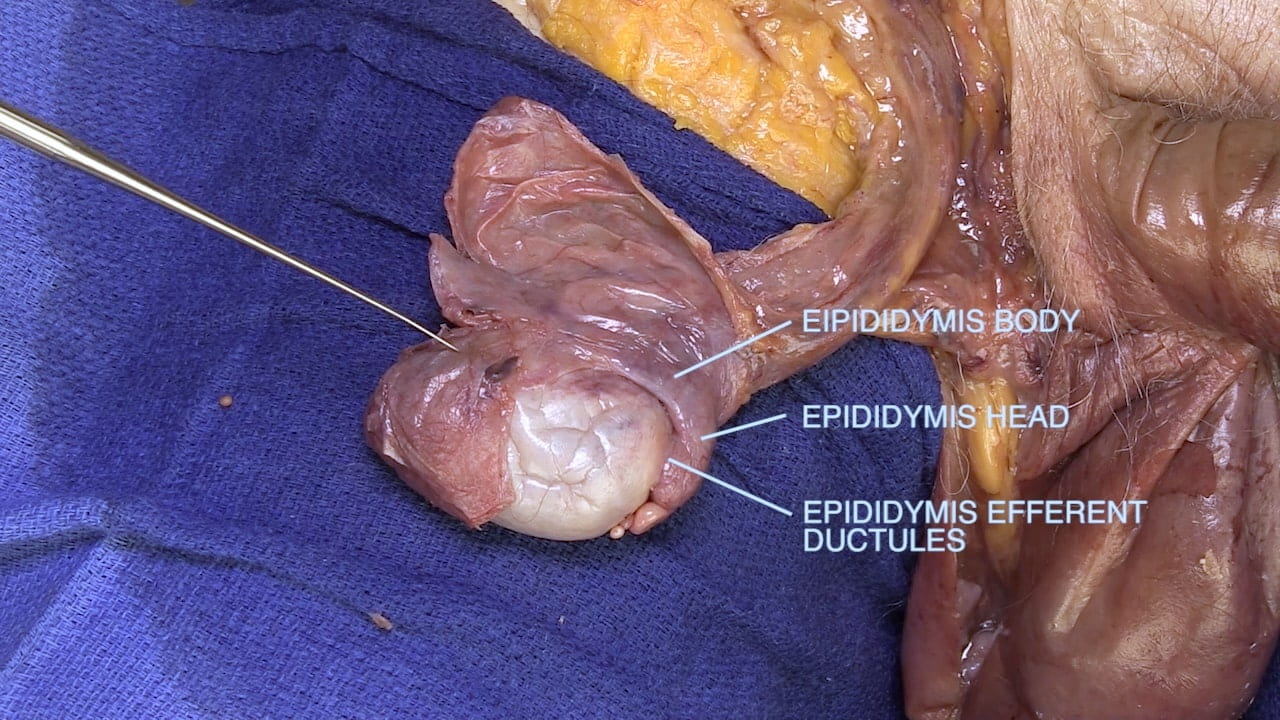
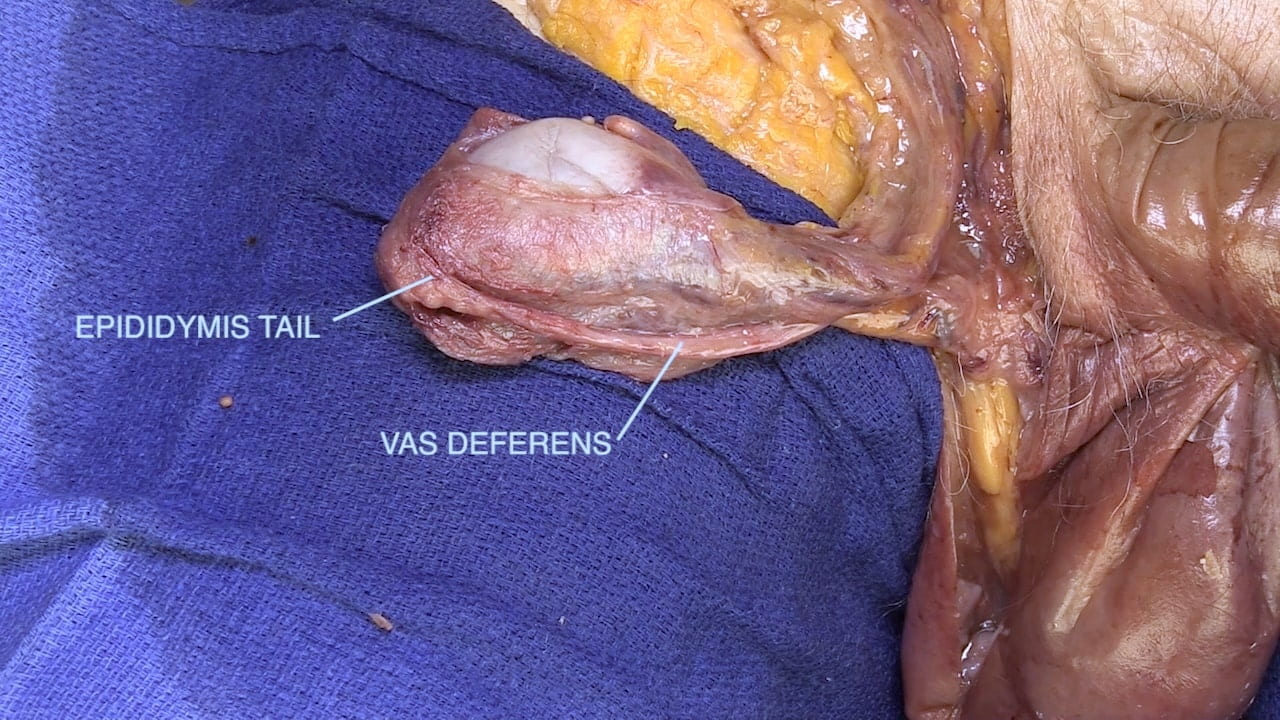
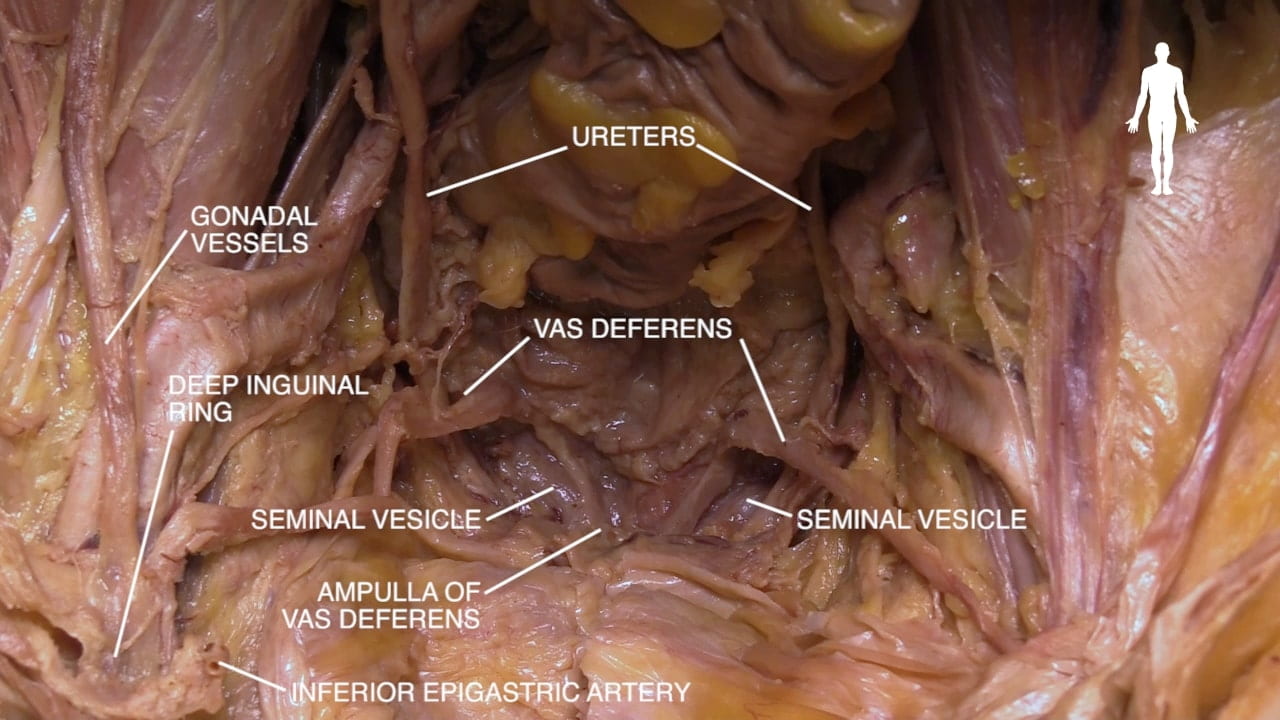
- Describe the pathway of sperm from testis to ejaculatory duct.
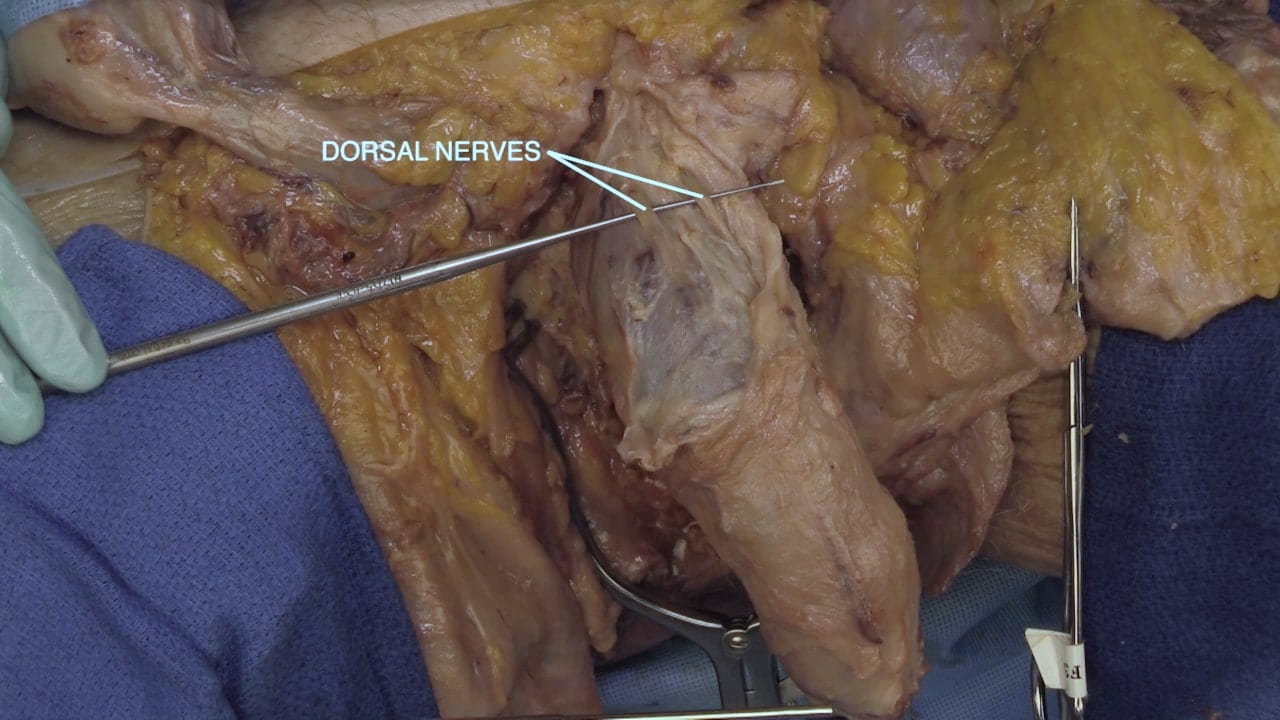
- Describe root of penis.
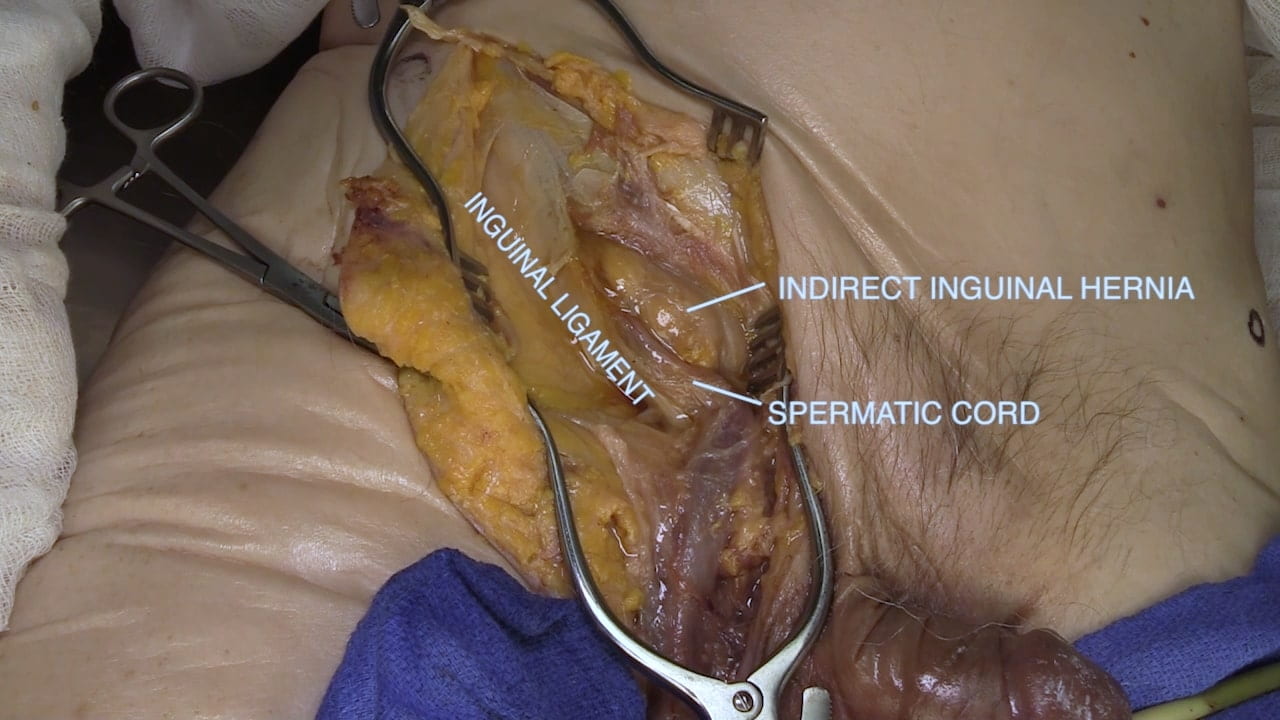
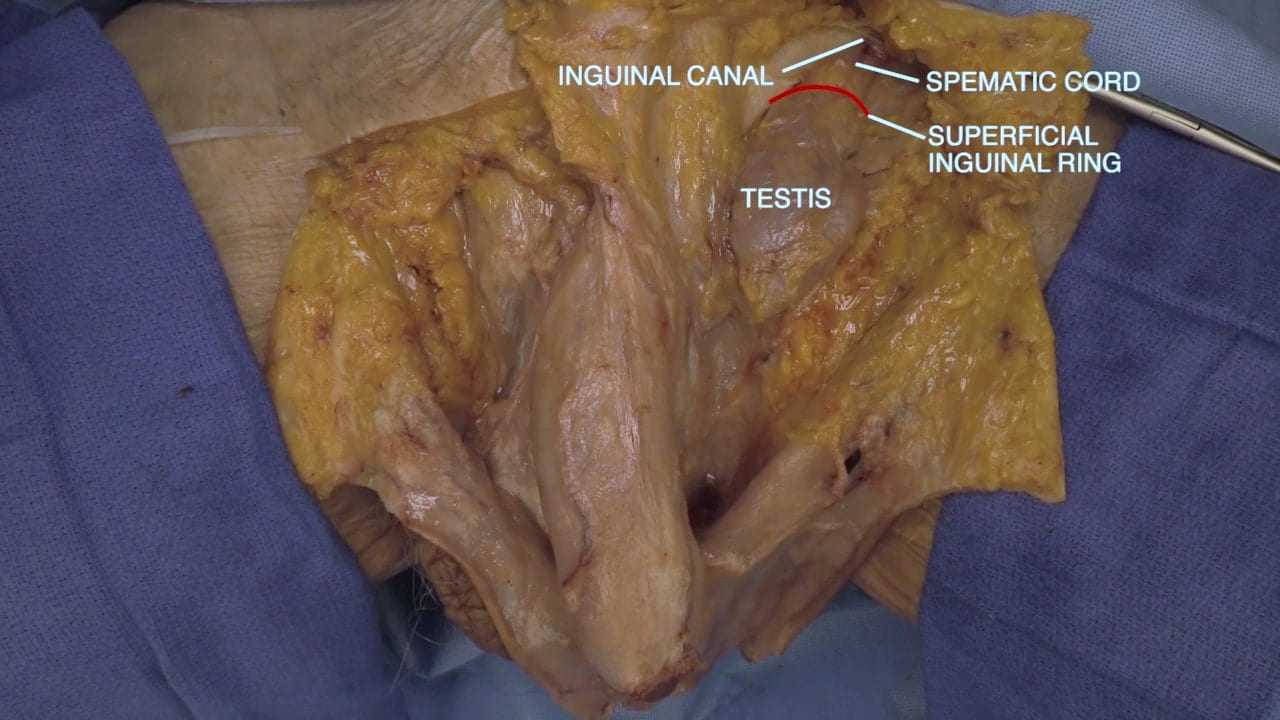
- Describe and differentiate between direct and indirect inguinal hernias.
Lecture List
Inguinal Ligament and Testis, Male Perineum, Male Pelvis, Male Sagittal Pelvis
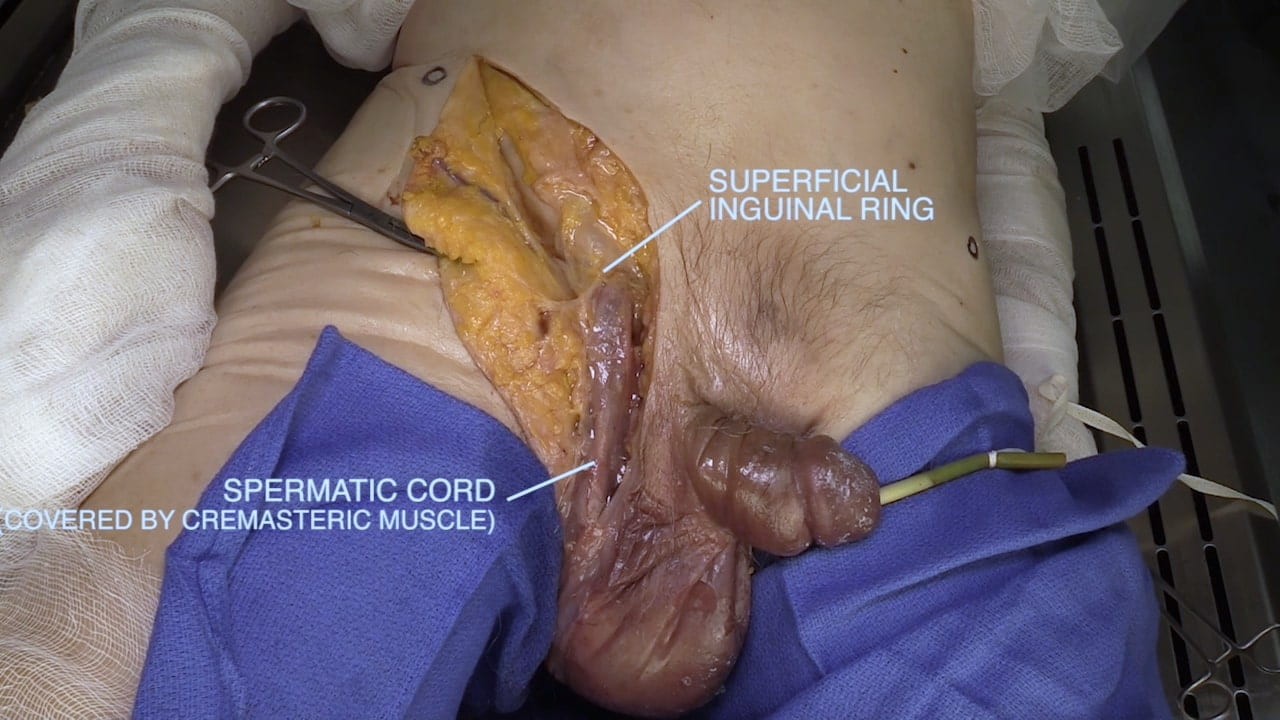
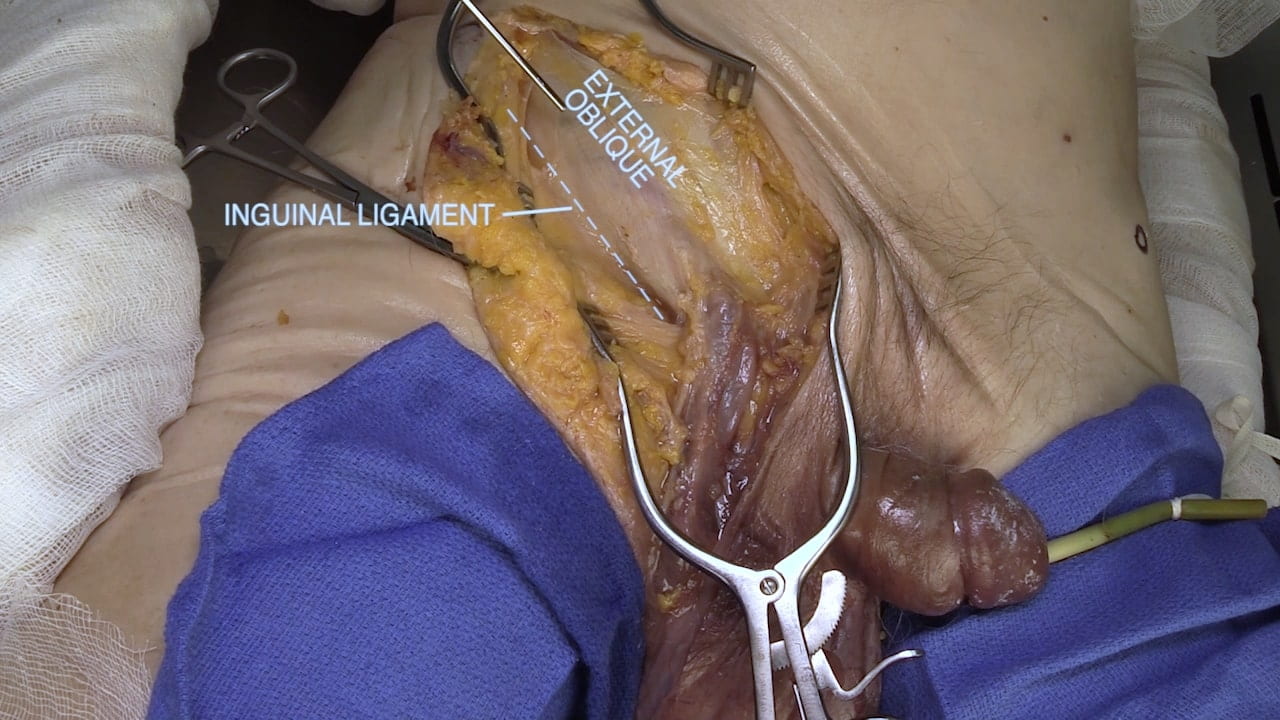
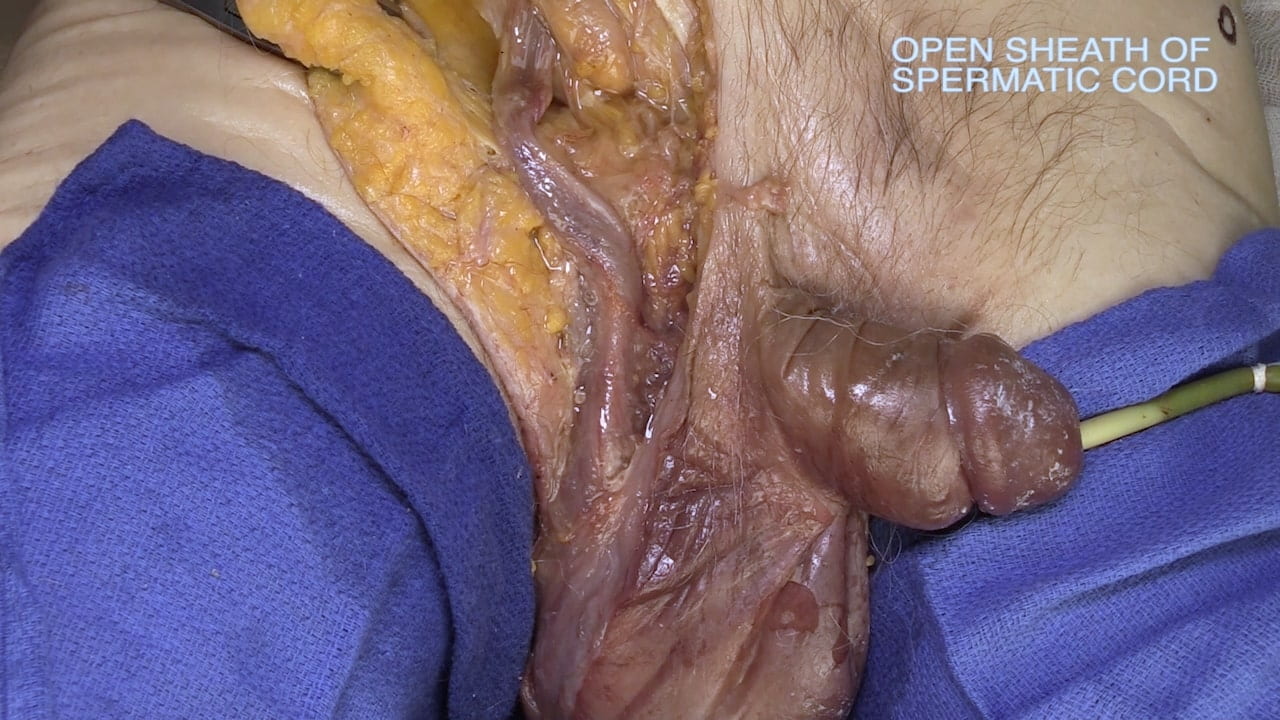
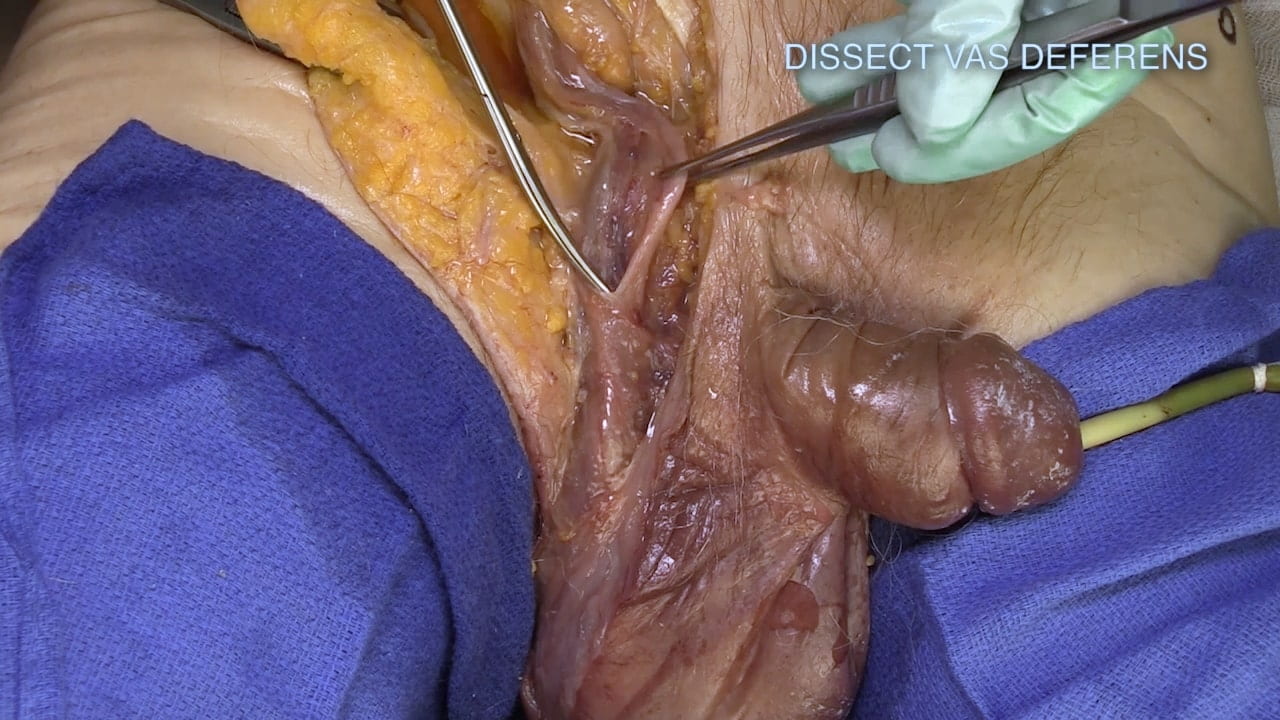
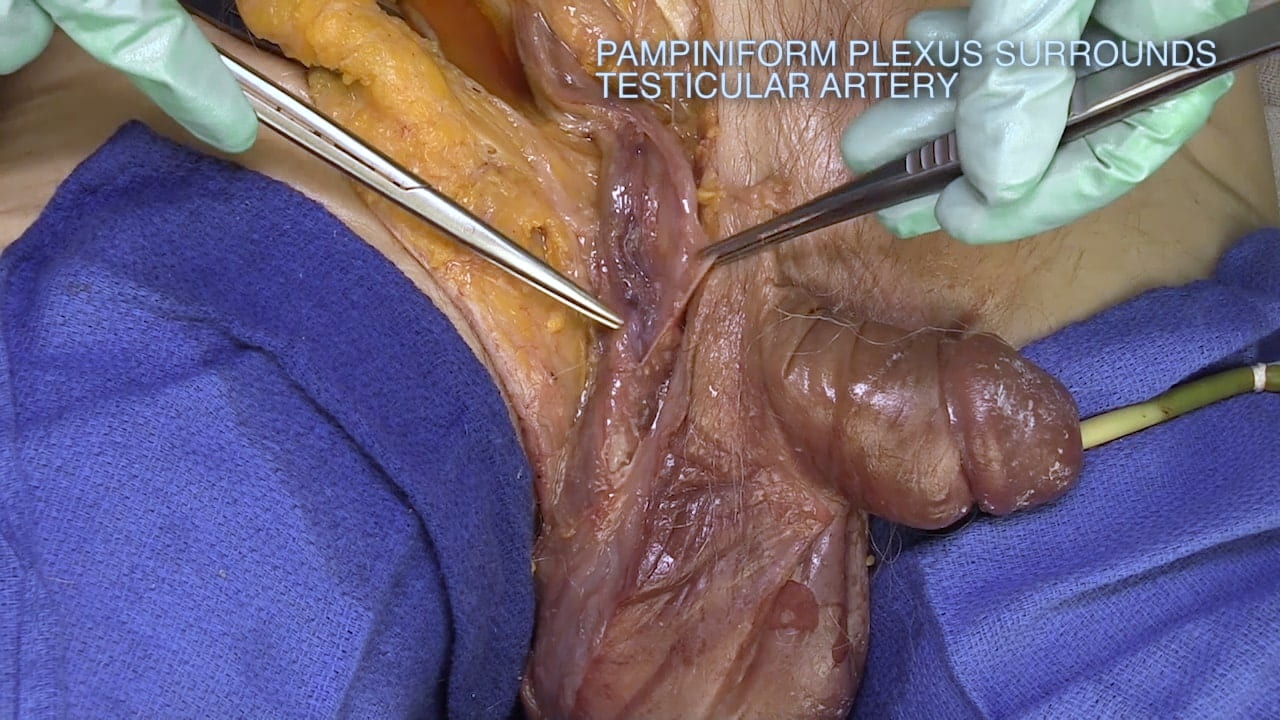
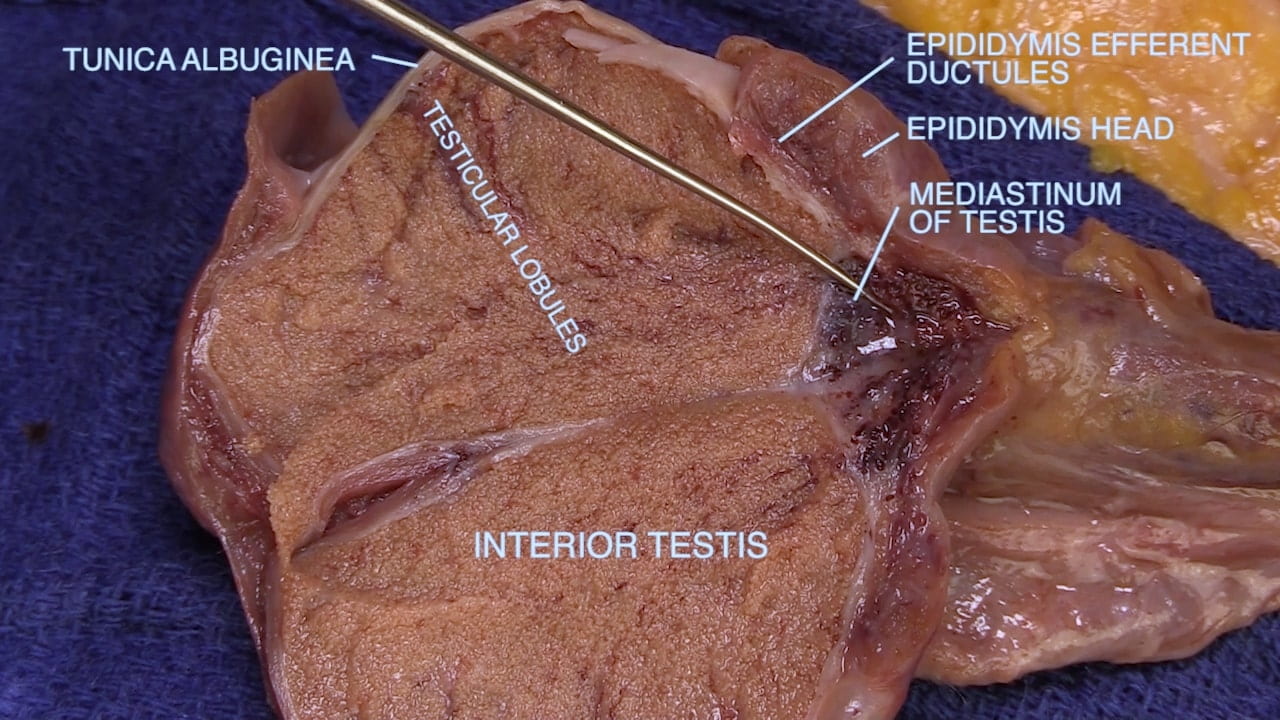
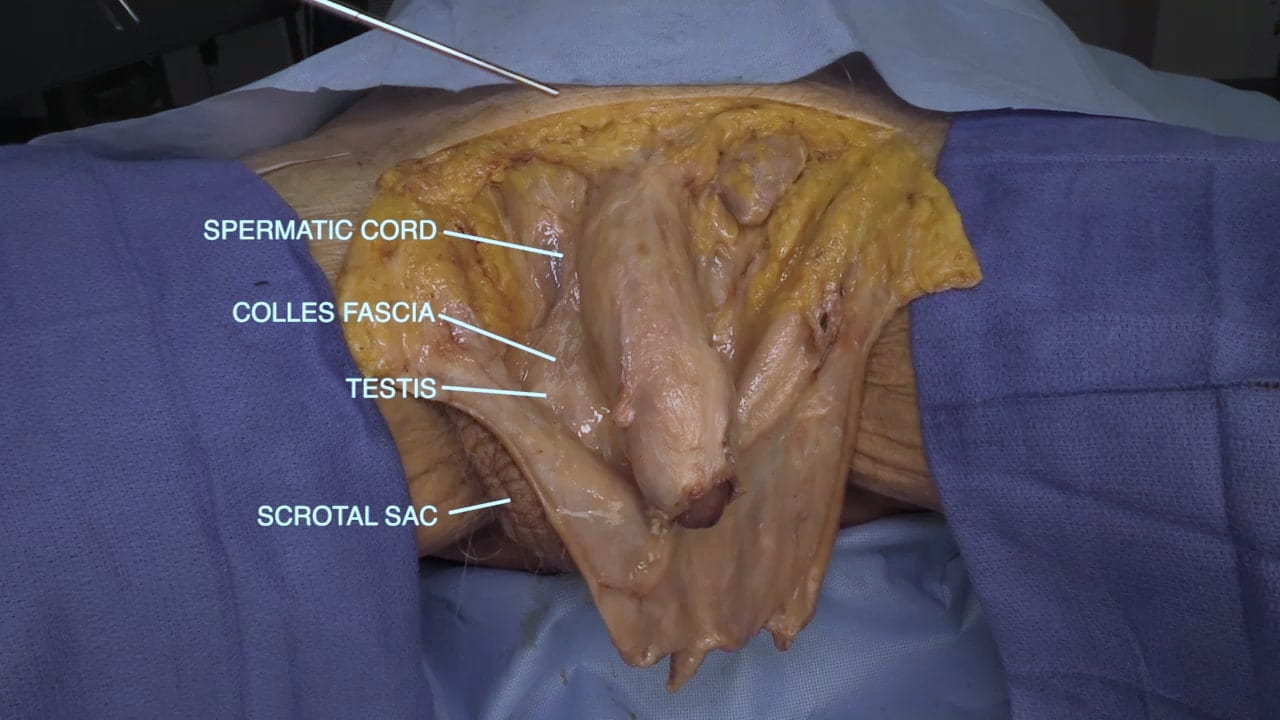
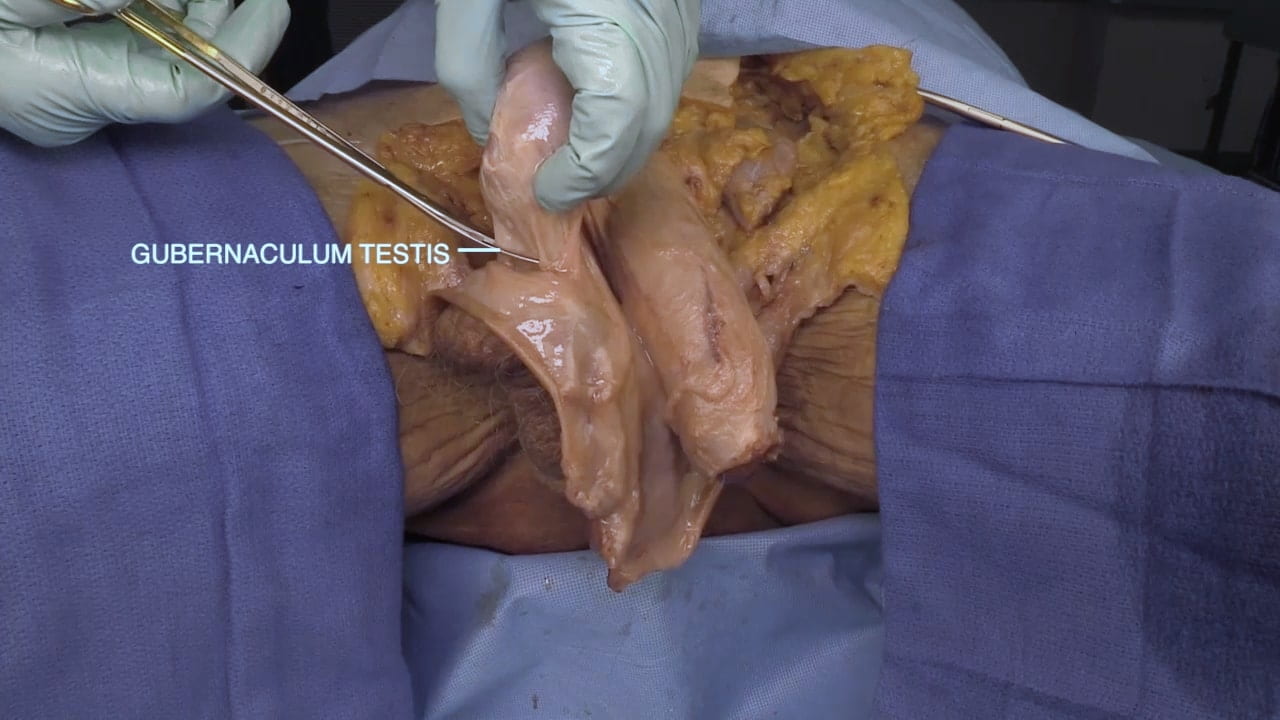
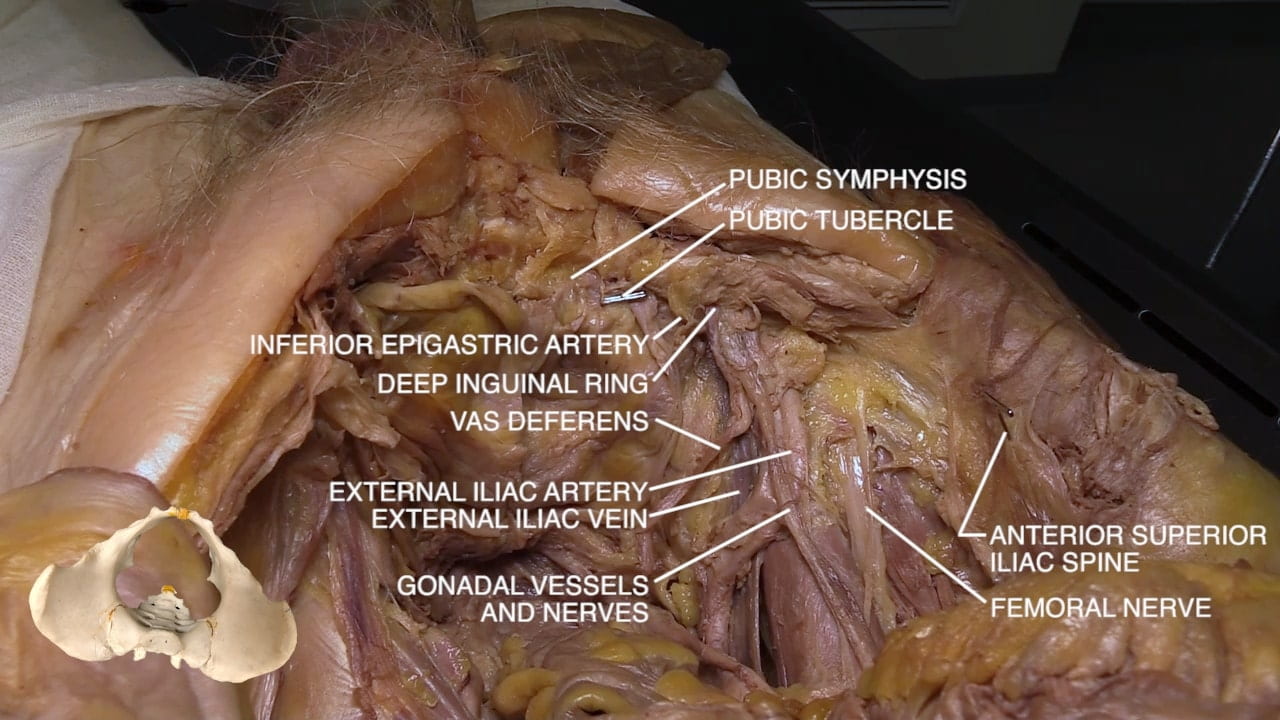
Inguinal Ligament and Testis
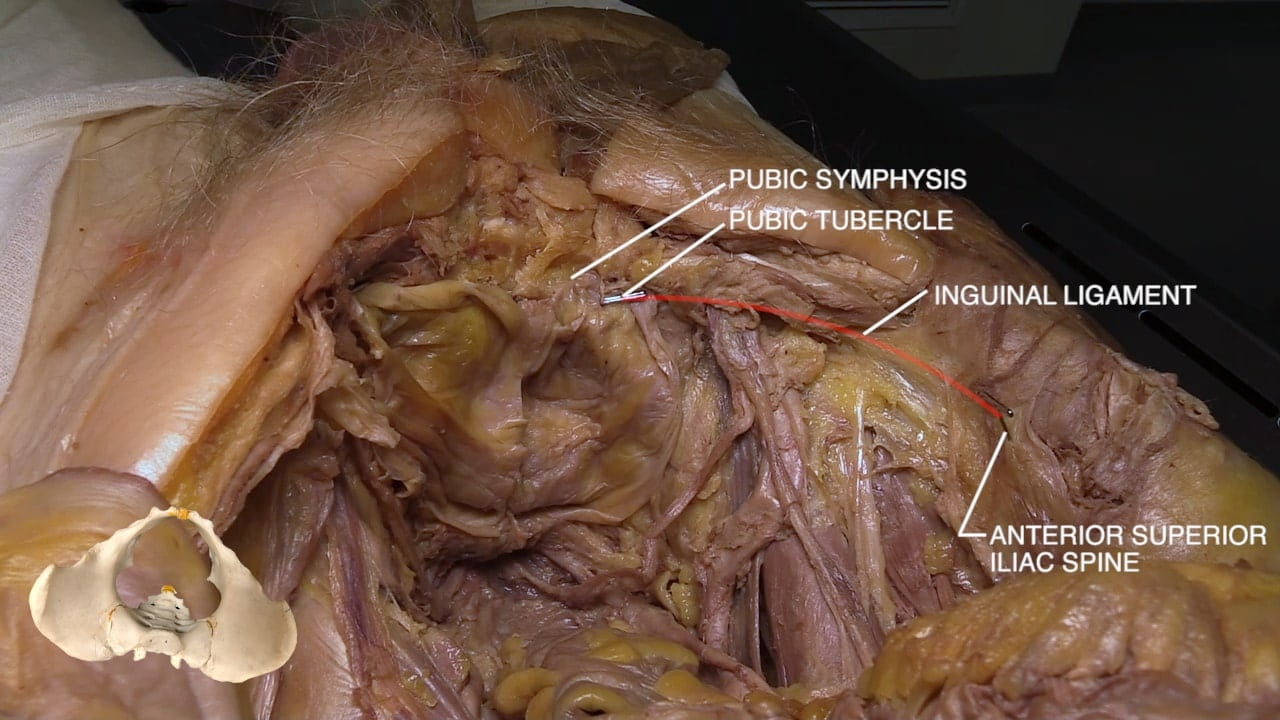
Inguinal Ligament
Spermatic Cord
Epididymis
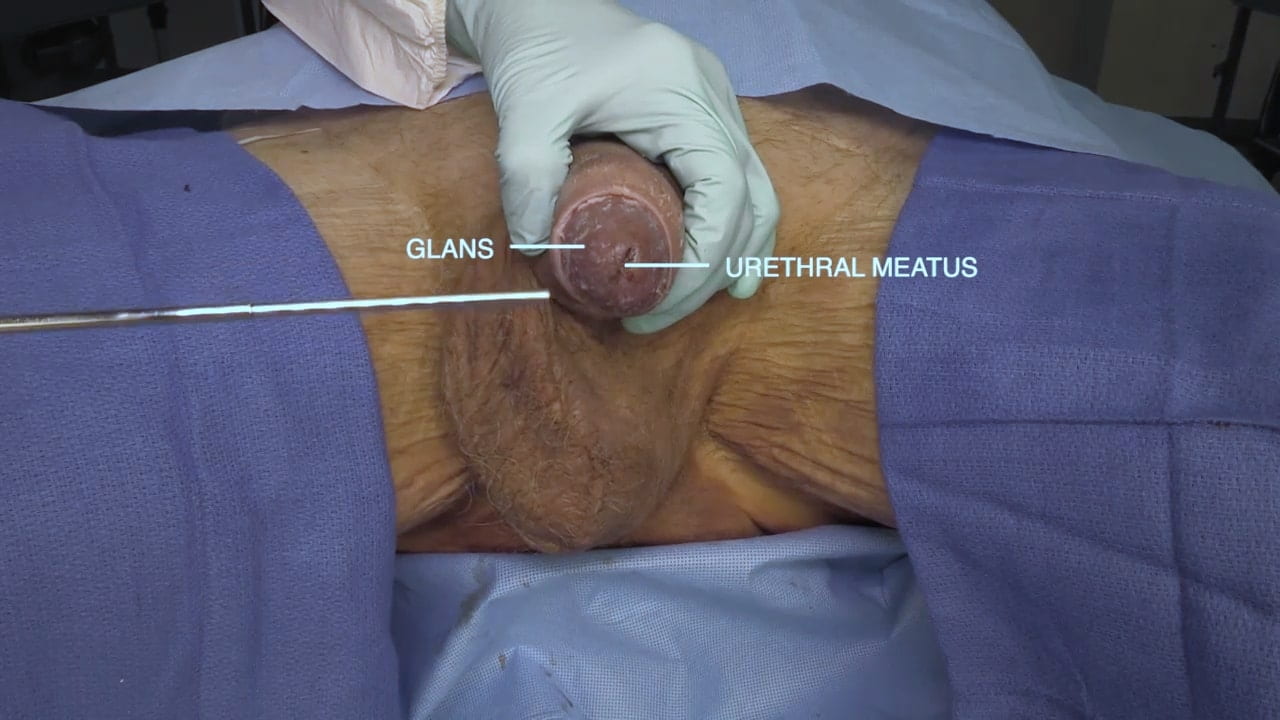
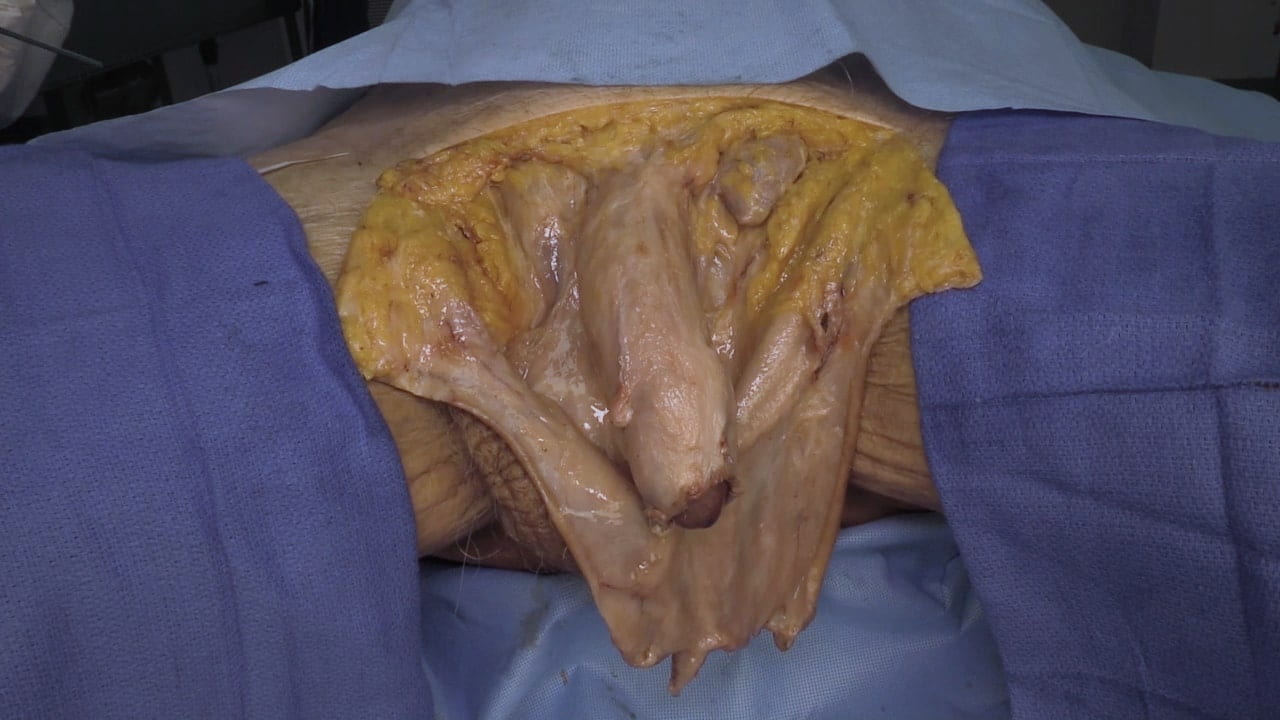
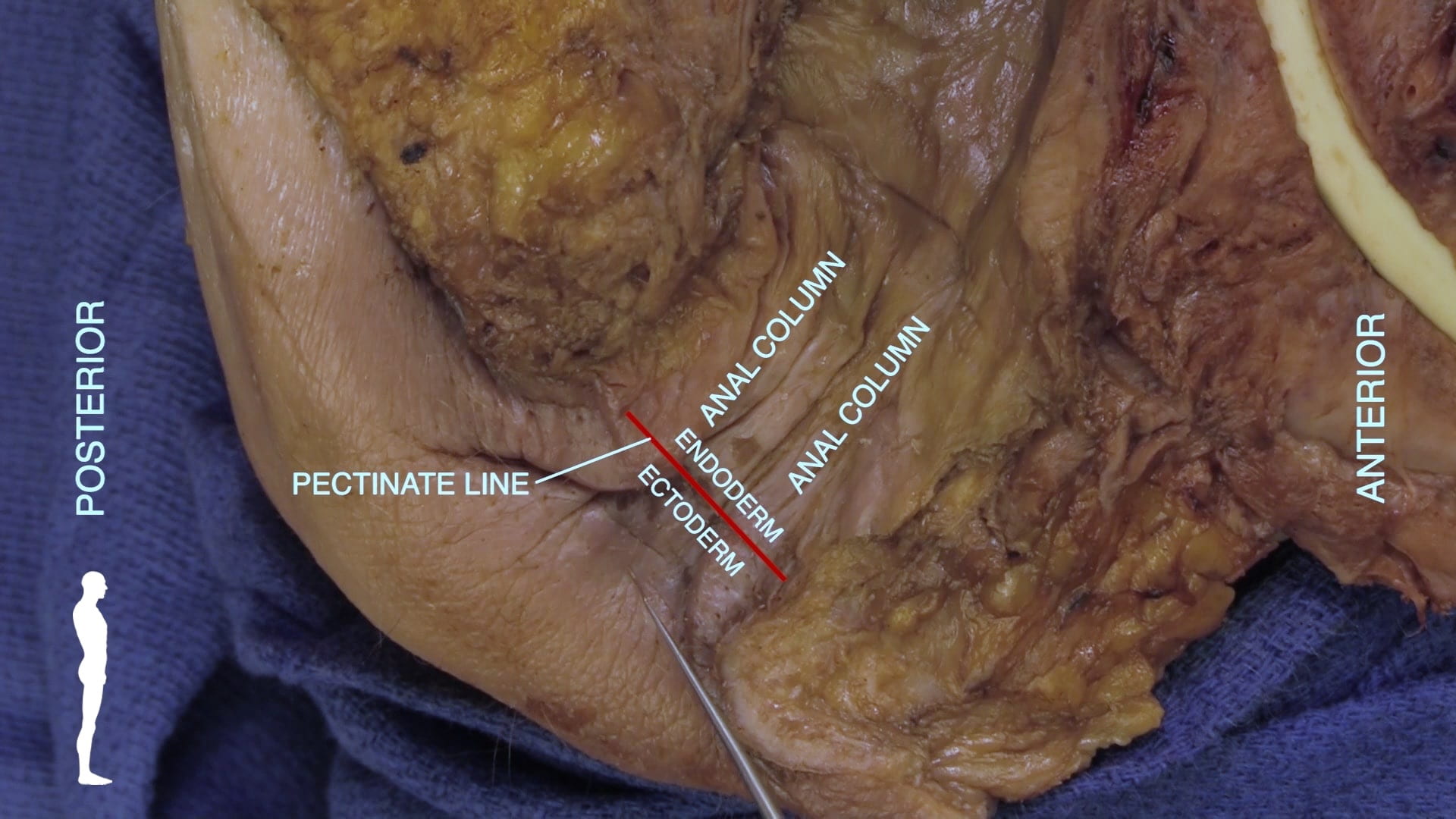
Male Perineum
External Genitalia
Penis and Scrotal Contents
Erectile Tissue
Dorsal Nerve of Penis
Cross Sections of Penis
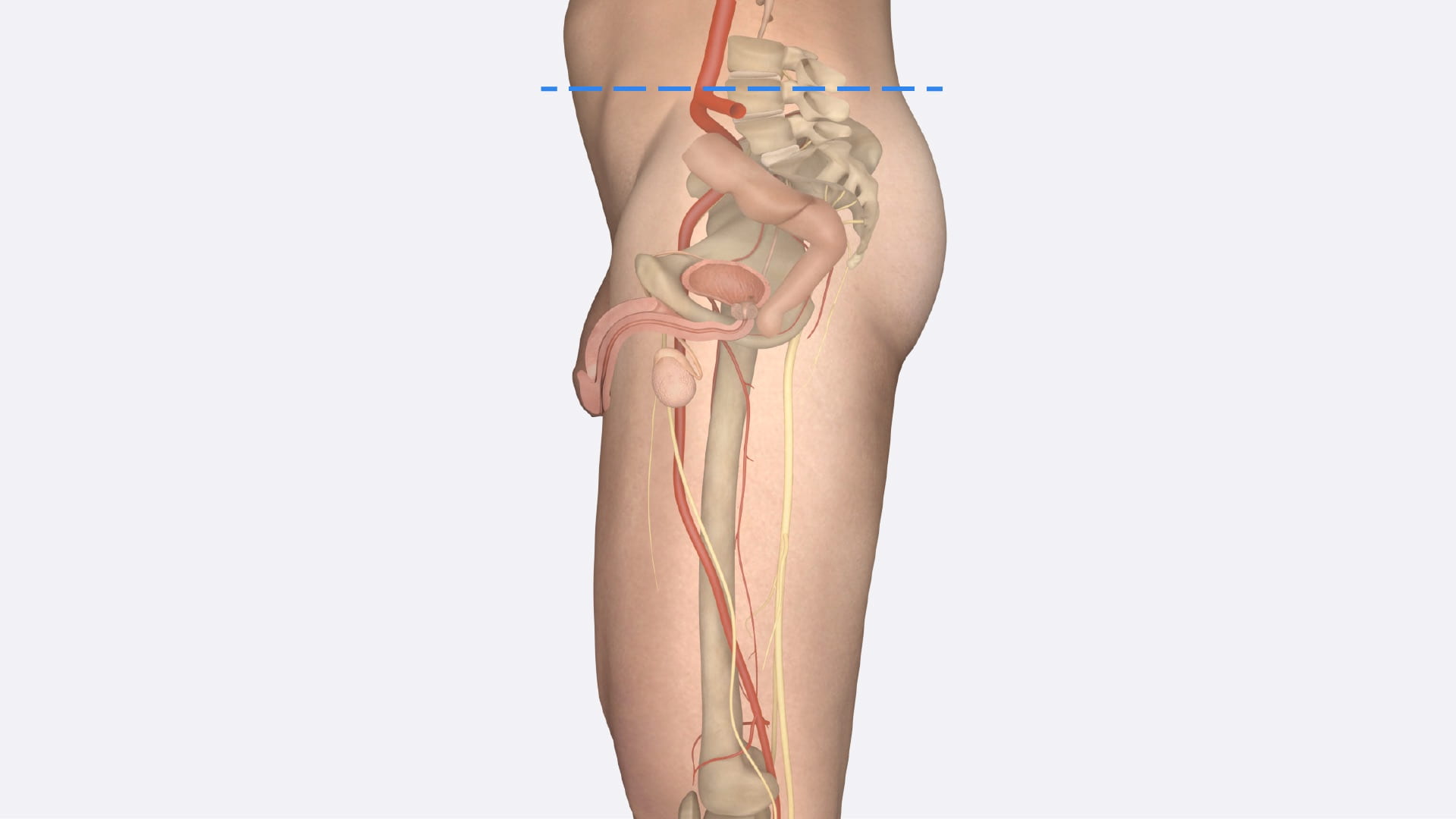
Male Pelvis
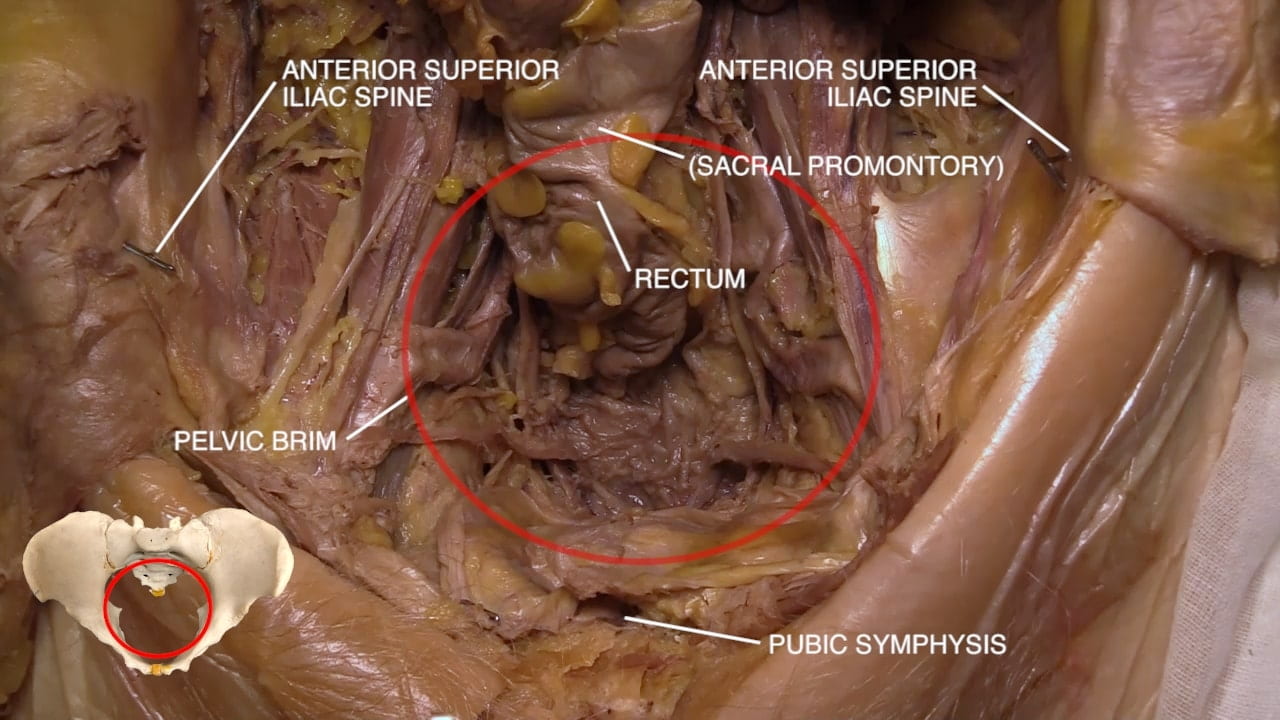
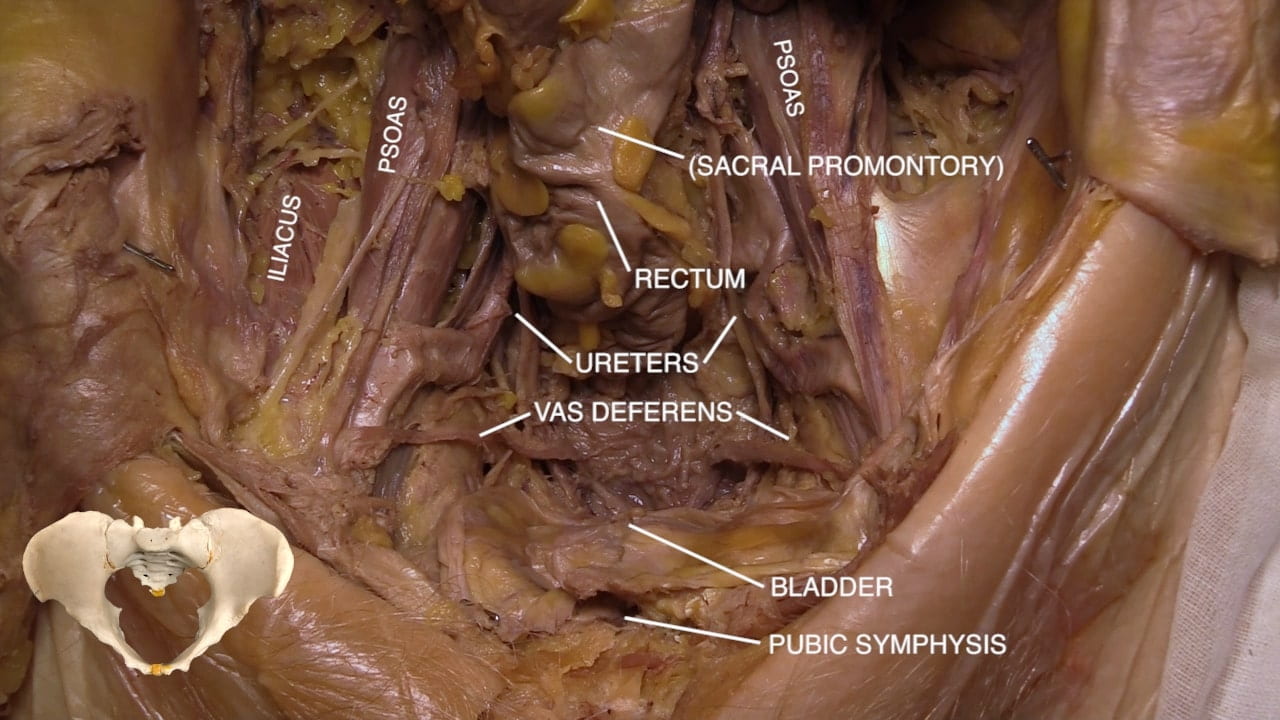
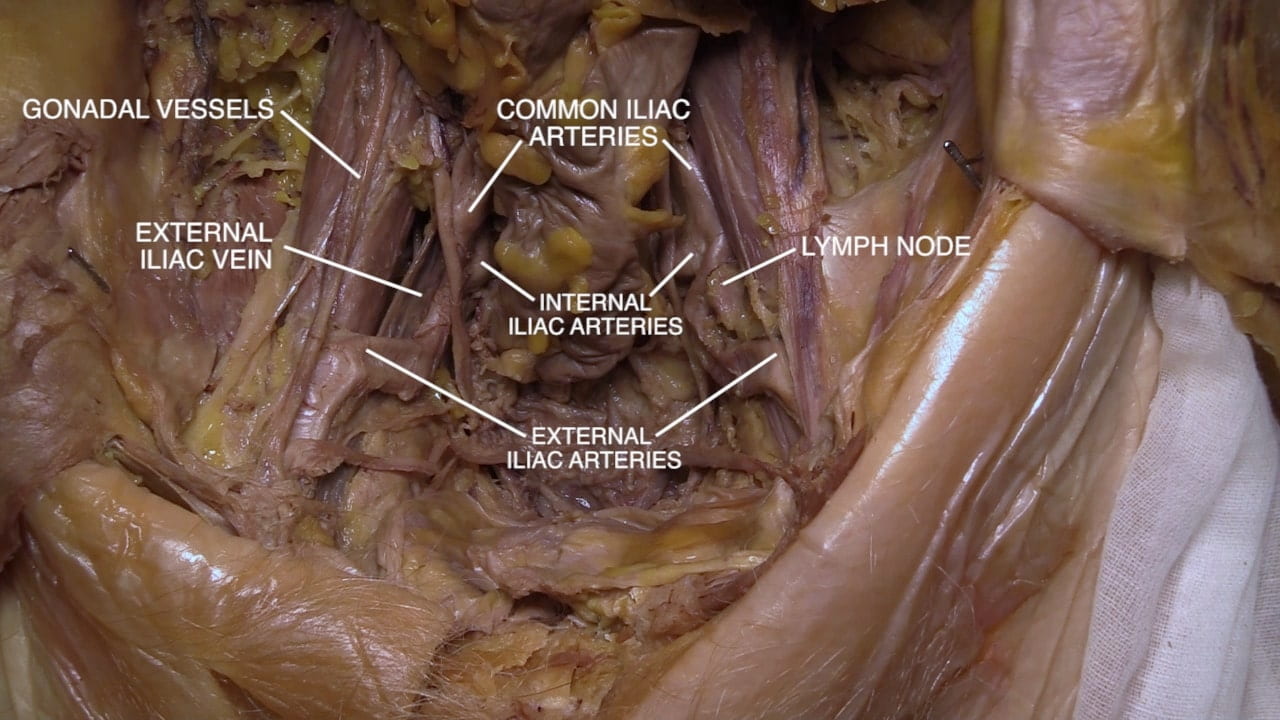
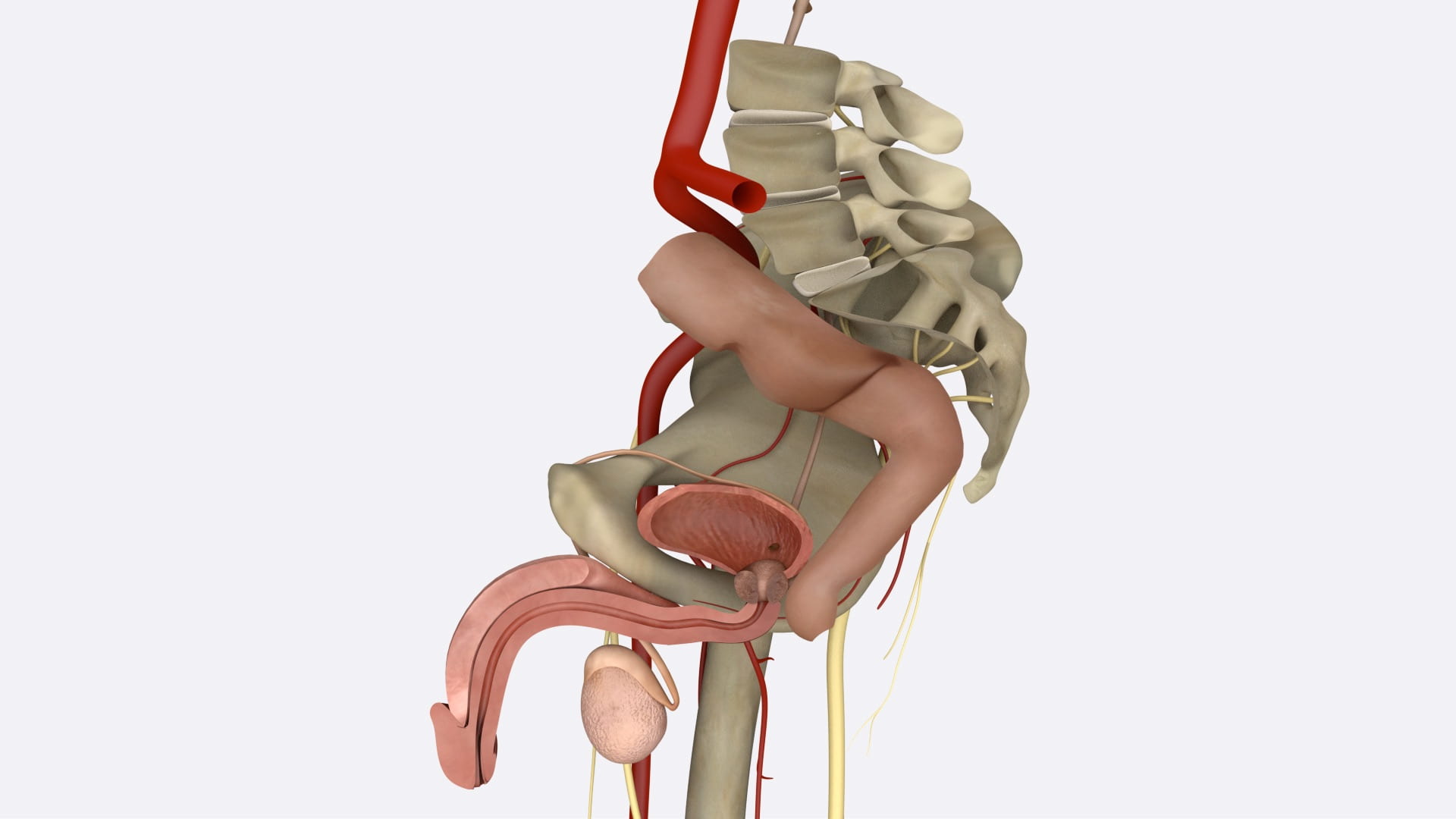
Internal Pelvic Structures
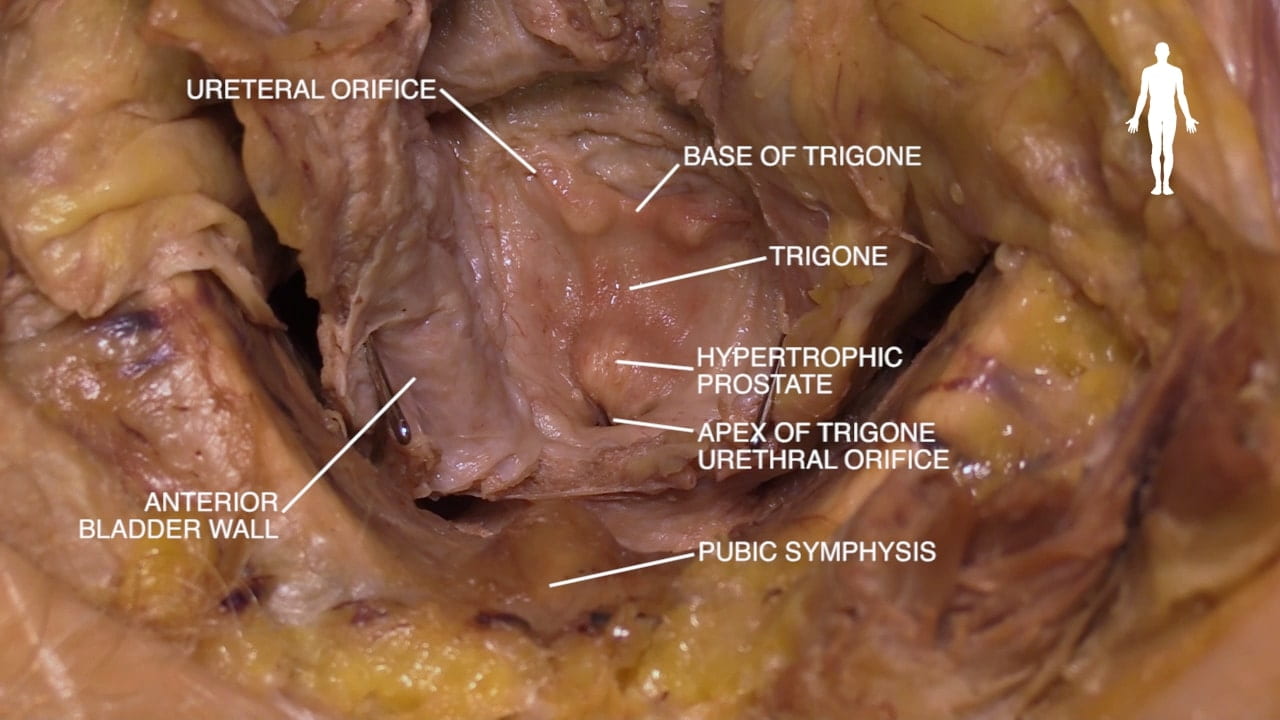
Bladder
Deep Inguinal Ring
Key Sagittal Pelvic Dissection Notes
- Split pelvis
- For AMAB spend time on inguinal canal, testis and try to visualize prostate – laparoscope may be helpful – and maybe even a prostatectomy with Urology.
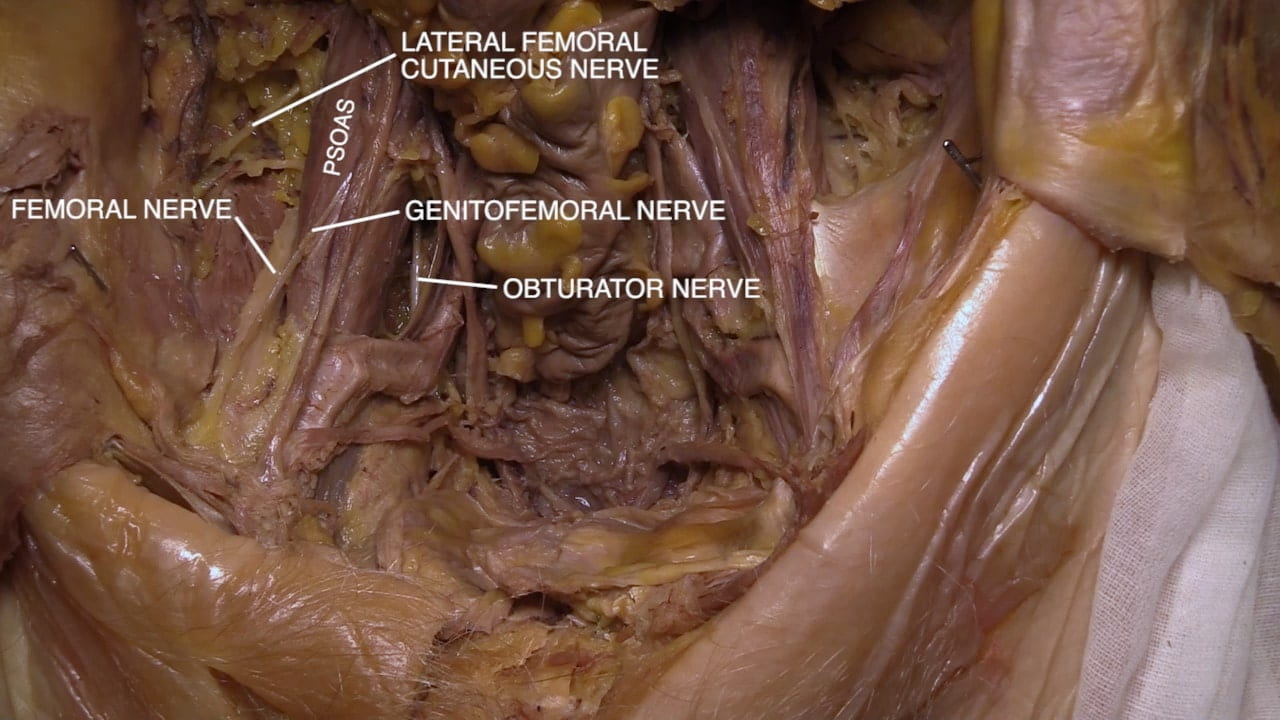
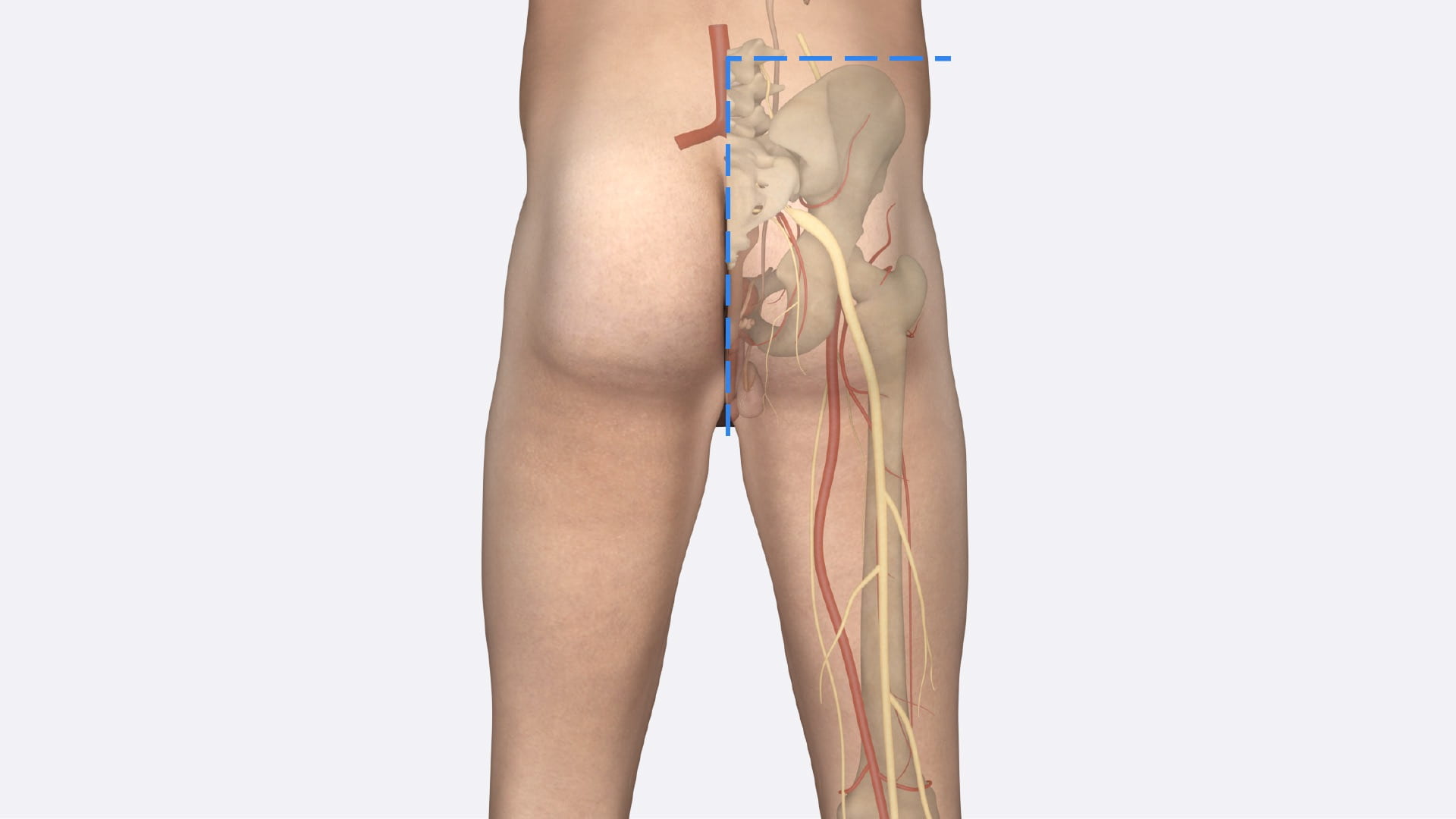
- For all, examine pelvic vasculature, course of ureter and lumbosacral plexus.
As you think through these options and discuss with your partners, please feel free to ask us questions and voice concerns.
Sagittal Dissection Preparation Gallery
Sagittal Dissection Preparation
Male Sagittal Pelvis
Pelvic Hemisection
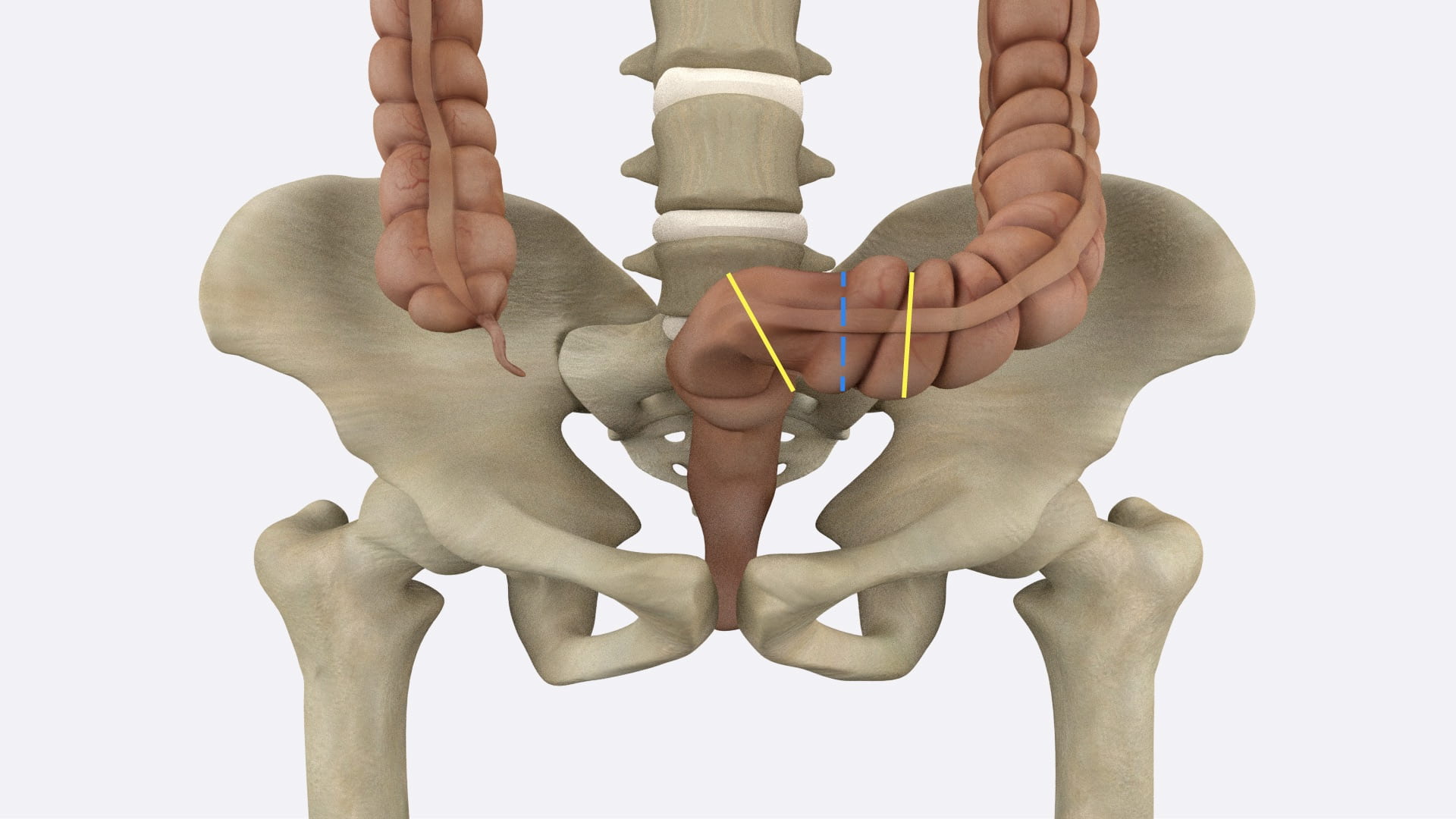
With a long knife, divide the penis in the midline and divide the soft tissues of the perineum and pelvis.
Using a hand saw, divide the pubic symphysis, sacrum, and the lumbar spine as far superiorly as L3. Stay in the midline.
Make a transverse cut across the trunk just superior to the iliac crest to the midline. Remove the attached lower limb and pelvis to view the sagittal pelvis.